A pediatric nurse is concerned that her patient is exhibiting signs of infective endocarditis. Which of the following symptoms would lead the nurse to suspect that diagnosis?
Proteinuria
ESR-14 mm/hr (Normal: Children<10 mm/hr)
Weight gain of 2 kg since last well visit
Hemoglobin- 13.8 (Normal: children 11.2 to 14.5 g/dl)
Temperature – 102.5°F
The Correct Answer is E
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves. One of the hallmark signs of infective endocarditis is fever, often accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, chills, and joint pain. A persistent fever in a child, especially when associated with other signs or symptoms like new heart murmurs or petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), can be concerning for infective endocarditis.
The other symptoms and findings listed (proteinuria, ESR, weight gain, hemoglobin levels) are not specific to infective endocarditis and may have other potential causes or interpretations. It is important to consider a comprehensive clinical evaluation and laboratory tests when assessing a child with suspected infective endocarditis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
APSGN is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli in the kidneys, which can lead to decreased kidney function and impaired urine output. As the condition begins to improve, one of the first signs is an increase in urine output. This is because the inflammation in the glomeruli starts to resolve, allowing the kidneys to filter blood more effectively and produce a higher volume of urine.
Now, let's discuss why the other options are incorrect:
A. Increased energy levels: While improved energy levels can be a positive sign in a child recovering from an illness, they are not typically the earliest sign of improvement in APSGN. Energy levels may improve as the child's overall condition gets better, but this improvement often follows an increase in urine output.
B. Decreased diarrhea: APSGN primarily affects the kidneys, not the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, diarrhea is not a direct symptom of this condition. Improving kidney function and urine output would not directly impact diarrhea.
D. Increased appetite: Like increased energy levels, an improved appetite can be a positive sign in recovery, but it is not typically the earliest sign of improvement in APSGN. It is generally more related to overall recovery and feeling better after the acute phase of the illness.
In summary, while all of these signs can be positive indicators of a child's recovery, increased urine output is usually the earliest and most specific sign of improvement in acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, as it directly reflects the resolution of kidney dysfunction.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
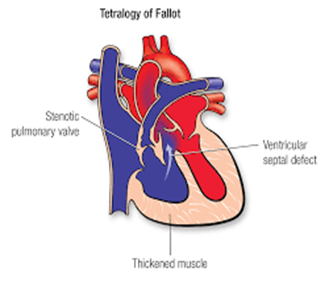
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific abnormalities:
Ventricular septal defect (VSD): This is a hole in the wall (septum) between the two lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart.
Overriding aorta: The aorta is positioned over both the left and right ventricles, which allows oxygen-poor (deoxygenated) blood from the right ventricle to be pumped into the aorta and to the body.
Pulmonic stenosis (PS): This is a narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery that restricts blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Right ventricular hypertrophy: The right ventricle becomes thicker and more muscular as it works harder to pump blood against the narrowed pulmonary valve or artery.
Options A, C, and D describe different congenital heart conditions and defects, but they are not associated with Tetralogy of Fallot:
A. Coarctation of aorta, aortic valve stenosis, mitral valve stenosis, and patent ductus arteriosus are not part of the constellation of defects seen in the Tetralogy of Fallot.
C. Describing the aorta exiting from the right ventricle and pulmonary artery exiting from the left ventricle with two noncommunicating circulations is characteristic of transposition of the great arteries, not Tetralogy of Fallot.
D. Tricuspid valve atresia, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, and hypoplastic right ventricle describe a different congenital heart condition, not Tetralogy of Fallot.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
