The antibody class involved in hypersensitivity reaction Type I is:
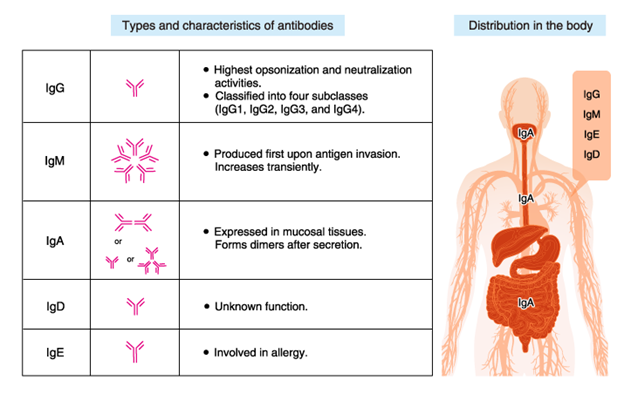
IgE
IgA
IgG
IgM
The Correct Answer is A
A. IgE (Immunoglobulin E): This class of antibodies is primarily involved in hypersensitivity reactions Type I, which are immediate allergic reactions. When a person is exposed to an allergen they are sensitive to, IgE antibodies on the surface of mast cells and basophils bind to the allergen. This triggers the release of inflammatory mediators like histamine, leading to allergic symptoms such as itching, hives, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
B. IgA (Immunoglobulin A): IgA antibodies are primarily found in mucosal areas such as the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. They play a role in immune defense on mucosal surfaces and are important for preventing infections. While IgA is not directly associated with hypersensitivity reactions Type I, deficiencies in IgA can sometimes lead to increased susceptibility to certain infections.
C. IgG (Immunoglobulin G): IgG antibodies are the most common type of antibody in the bloodstream and are involved in various immune responses, including defense against bacterial and viral infections. IgG antibodies are not specific to Type I hypersensitivity reactions; they are part of the immune system's broader defense mechanisms.
D. IgM (Immunoglobulin M): IgM antibodies are the first antibodies to be produced in response to an infection. They are large pentameric molecules and are effective at agglutinating pathogens. IgM antibodies are involved in the primary immune response to infections, but they are not specifically associated with Type I hypersensitivity reactions.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic are used interchangeably.
This statement is incorrect. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic have distinct meanings in pharmacology and microbiology. Bactericidal means the drug kills bacteria, whereas bacteriostatic means the drug inhibits the growth of bacteria without killing them.
B. Bactericidal drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bacteriostatic drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death.
This statement is correct. Bactericidal drugs directly kill bacteria, leading to their death. Bacteriostatic drugs inhibit the growth of bacteria without causing their immediate death. Both types of drugs play different roles in the treatment of bacterial infections.
C. Bacteriostatic drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bactericidal drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death.
This statement is incorrect. It confuses the roles of bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs. Bactericidal drugs directly kill bacteria, while bacteriostatic drugs inhibit bacterial growth without immediate cell death.
D. A bactericidal drug can cause death to the host, whereas a bacteriostatic drug only affects bacteria.
This statement is incorrect. Both bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs primarily affect bacteria, not the host. The difference lies in how they affect bacteria: bactericidal drugs kill bacteria directly, and bacteriostatic drugs inhibit their growth.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type IV hypersensitivity, involves a delayed response by the immune system and is mediated by T cells. It does not necessarily involve a failure of self-tolerance.
B. Antibody-mediated reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type II hypersensitivity, involves antibodies targeting specific antigens on cell surfaces, leading to cell destruction. It doesn't directly indicate a failure of self-tolerance but rather an immune response against specific cells or tissues.
C. Autoimmune reaction: In autoimmune reactions, the immune system fails to recognize certain body tissues or substances as "self," leading to an immune response against the body's own cells or tissues. This results from a breakdown in self-tolerance, where the immune system mistakenly targets its own body.
D. Immediate hypersensitivity reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type I hypersensitivity, involves an immediate response by the immune system to an allergen. It includes conditions like allergies and anaphylaxis, where the immune system reacts strongly to substances that are normally harmless. This response does not necessarily indicate a failure of self-tolerance but rather an exaggerated response to specific antigens.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
