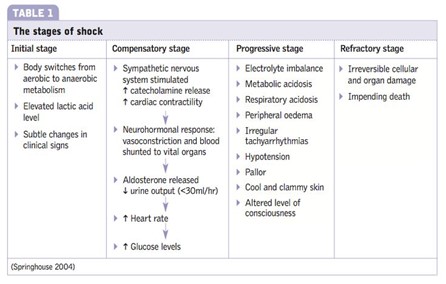
The emergency department nurse provides care for a 50-year-old male patient with septic shock. The nurse recalls that the renin- angiotensin system is activated during which stage of shock?
Initial stage
Progressive stage
Refractory stage
Compensatory stage
The Correct Answer is D
In the compensatory stage of shock, the body initiates various mechanisms to maintain perfusion to vital organs and restore homeostasis. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system is one of the compensatory responses. The decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to the kidneys stimulate the release of renin from the kidneys. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, converting it into angiotensin I, which is further converted to angiotensin II by the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and also stimulates the release of aldosterone, leading to sodium and water retention. These mechanisms aim to increase blood pressure and cardiac output and restore fluid balance.
A. The initial stage of shock in (option A) is incorrect because it is characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion and the activation of various compensatory mechanisms, including the release of stress hormones. However, the renin-angiotensin system is not specifically mentioned as activated in this stage.
B. The progressive stage of shock in (option B) is incorrect because it occurs when compensatory mechanisms fail to maintain adequate perfusion, leading to worsening hypoperfusion and organ dysfunction. The renin-angiotensin system continues to be activated during this stage, but it is primarily associated with the compensatory stage.
C. The refractory stage of shock in (option C) is incorrect because it is the stage of severe and prolonged hypoperfusion, where organ failure becomes irreversible. The renin-angiotensin system may still be activated, but it is not the primary focus of this stage.
Therefore, the activation of the renin-angiotensin system occurs during the compensatory stage of shock.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Hemorrhagic shock is characterized by severe blood loss, leading to inadequate tissue perfusion and hypovolemia. The primary goal in the initial management of hemorrhagic shock is to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion. Administering intravenous fluids, such as normal saline solution, is a critical intervention to address hypovolemia and improve blood pressure.
A. Give Plasmanate 1 unit now in (option A) is incorrect because: Plasmanate is a plasma-derived product used to replace coagulation factors. While it may be necessary to address coagulation abnormalities, administering intravenous fluids to restore volume takes priority over specific blood products.
B. Prepare for endotracheal intubation in (option B) is incorrect because Endotracheal intubation may be required in cases of impending respiratory failure or compromised airway, but it should not be the first action in addressing hypovolemic shock.
D. Type and crossmatch for 4 units of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) in (option D) is incorrect because transferring packed red blood cells is an important intervention to address blood loss and improve oxygen-carrying capacity. However, before administering blood products, it is crucial to stabilize the patient's hemodynamics through fluid resuscitation.
Therefore, in a patient with hemorrhagic shock, the nurse's first priority among the given options is to give normal saline solution of 250 mL/hr to restore intravascular volume and improve tissue perfusion.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Shock is a state of inadequate tissue perfusion, resulting in compromised oxygen and nutrient delivery to cells and impaired cellular metabolism. Regardless of the specific cause or type of shock (e.g., hypovolemic, cardiogenic, distributive), the underlying problem is the failure to supply sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues. This inadequate tissue perfusion can lead to cellular dysfunction, organ failure, and ultimately, life-threatening consequences.
A. Inefficient metabolism resulting from inadequate nutrition in (option A) is incorrect because While inadequate nutrition can contribute to the overall health status and resilience of an individual, it is not the central mechanism underlying all shock states.
C. Vasoconstriction and reflexive vasodilation due to circulating mediators in (option C) is incorrect because Vasoconstriction and vasodilation are physiological responses that can occur in various types of shock, but they are not the fundamental common denominator. Inadequate tissue perfusion remains the core issue.
D. Hypovolemia resulting from blood loss in (option D) is incorrect because Hypovolemia, which refers to decreased blood volume, is one potential cause of shock, specifically hypovolemic shock. However, other types of shock, such as cardiogenic or distributive shock, may not be primarily characterized by hypovolemia.
Therefore, the common denominator of all shock states is inadequate tissue perfusion, resulting in impaired cellular metabolism.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
