The nurse is admitting a client with a thyroid disorder who presents with periorbital edema, cold intolerance, and weight gain. Which intervention should the nurse include in this client's plan of care?
Administer propylthiouracil (PTU).
Provide an electric blanket.
Restrict fluids.
Monitor for hypotension.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: Propylthiouracil (PTU) is an antithyroid medication used to treat hyperthyroidism, which can present with symptoms such as weight loss and heat intolerance. The symptoms listed (periorbital edema, cold intolerance, and weight gain) suggest hypothyroidism, for which PTU is not indicated.
Choice B reason: Providing an electric blanket may offer comfort for cold intolerance but does not address the underlying thyroid disorder.
Choice C reason: Restricting fluids is not a standard intervention for thyroid disorders and could potentially lead to dehydration.
Choice D reason: Monitoring for hypotension is important in thyroid disorders, especially if the client is on antithyroid medications, which can affect blood pressure. However, the symptoms presented suggest hypothyroidism, where hypotension is less of a concern compared to hyperthyroidism.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Assessing for hematuria is important but not the priority action. Hematuria can be a symptom of various conditions and does not directly address the abnormal laboratory results.
Choice B reason: Monitoring temperature is a routine action in sepsis management but does not address the immediate concern of the abnormal laboratory results, specifically the elevated aPTT and low platelet count.
Choice C reason: Evaluating skin turgor is a method to assess dehydration, which is not the immediate concern indicated by the laboratory results.
Choice D reason: The elevated aPTT and low platelet count suggest a potential coagulopathy, which could be a sign of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), a complication of sepsis. Administering heparin may be part of the treatment for DIC to prevent further clotting and is a priority action in this context.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
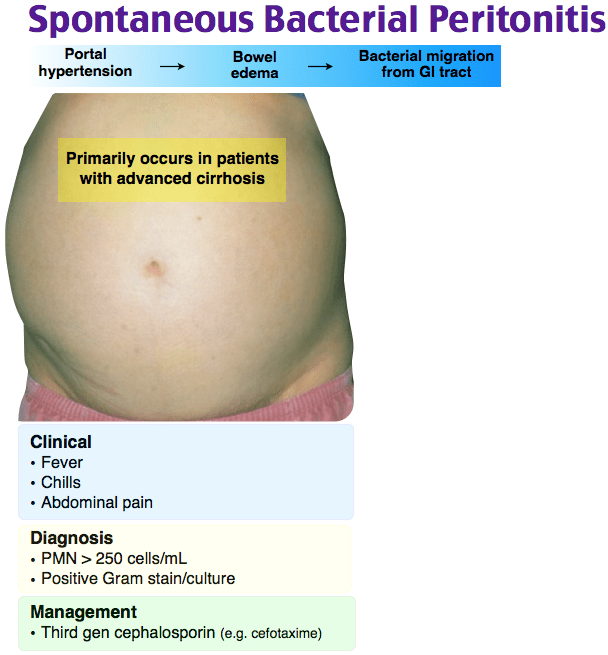
Choice A reason: Petechiae are small red or purple spots caused by bleeding into the skin, typically associated with platelet disorders, and are not a direct indicator of SBP.
Choice B reason: Increased abdominal pain is a common symptom of SBP, as the condition causes inflammation and irritation of the peritoneum, which can lead to significant discomfort.
Choice C reason: Jaundice is a sign of liver dysfunction but is not specific to SBP. It results from high levels of bilirubin in the blood and can occur in various liver diseases.
Choice D reason: Blood in emesis (vomiting) may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding, which can be a complication of cirrhosis but is not specific to SBP.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
