The nurse is teaching a pregnant client about fetal kick counts.
Which statement made by the client indicates a need for further instruction?
“I can perform fetal kick counts at home rather than at the clinic.”
“I should call my provider if I feel less than 3 kicks in an hour.”
“I will not feel the baby move as often closer to delivery.”
“I should perform this test daily.”
The Correct Answer is C
Choice C rationale:
It is a misconception that fetal movement decreases as delivery approaches. While the nature of the movements may change— becoming less like kicks and more like rolls or twists due to less space in the uterus—the frequency of movements should remain consistent. In fact, increased fetal movement can be a sign of labor approaching. Therefore, a pregnant client who believes that fetal movements will decrease closer to delivery needs further instruction to ensure they are aware of this important health indicator.
Here's a detailed explanation of why the other choices are correct:
Choice A: This statement is correct. Fetal kick counts can be performed at home, providing a convenient and comfortable way to monitor fetal well-being.
Choice B: This statement is also correct. A decrease in fetal movement, defined as less than 3 kicks in an hour, is a potential concern and warrants contacting a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Choice D: This statement is accurate as well. Daily fetal kick counts are generally recommended to establish a baseline of the baby's usual activity pattern and to detect any significant changes that might indicate a problem.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Fetal position during the first trimester is not definitively determined through ultrasound. While the gestational sac and fetal pole can be visualized, the fetus is still quite small and has ample space to move within the amniotic sac. This makes it challenging to accurately ascertain its position.
Reliable assessment of fetal position typically occurs later in pregnancy, usually between 34 and 36 weeks gestation. At this point, the fetus is larger and less mobile, allowing for a clearer assessment of its position through ultrasound.
The early determination of fetal position in the first trimester is not a primary goal of ultrasound. It is more focused on establishing pregnancy viability, gestational age, and detecting any potential abnormalities.
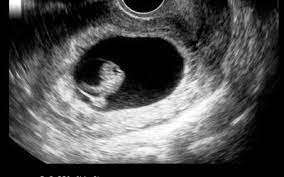
Choice B rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can reliably detect multiple gestations. It can visualize the presence of multiple gestational sacs or fetal poles, clearly indicating whether a woman is carrying twins, triplets, or more.
Early identification of multiple gestations is crucial for optimal pregnancy management. It allows healthcare providers to tailor prenatal care, monitor for potential complications associated with multiple pregnancies, and plan for appropriate delivery. Choice C rationale:
Ultrasound in the first trimester can assist in detecting certain maternal abnormalities that could impact pregnancy. These may include:
Uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or structural defects
Ovarian cysts
Ectopic pregnancies (where the embryo implants outside the uterus)
Gestational trophoblastic disease (abnormal growth of tissue inside the uterus)
Early identification of these maternal abnormalities allows for timely intervention and management, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and fetus.
Choice D rationale:
Confirming pregnancy is a primary reason for ultrasound in the first trimester. It can visualize the gestational sac, which contains the developing embryo and confirms the presence of a pregnancy.
Ultrasound can also detect the fetal heartbeat, which typically becomes visible between 6 and 8 weeks gestation. This provides further confirmation of a viable pregnancy.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Urine output (UO) does not completely stop during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. While it is significantly reduced, some urine production still occurs. Complete cessation of urine output is known as anuria, which is a more severe condition and a medical emergency.
Anuria may occur in the most severe cases of acute renal failure, but it is not the defining characteristic of the oliguric phase.
It's crucial to distinguish between oliguria and anuria, as their management approaches differ significantly.
Choice B rationale:
During the oliguric phase of acute renal failure, urine output (UO) is less than 400 mL/24 hours. This is the defining characteristic of this phase.
The decrease in urine output is due to damage to the kidneys' filtering units, known as nephrons. As a result, the kidneys are unable to filter waste products and excess fluids effectively from the blood, leading to their accumulation in the body.
This reduced urine output can lead to various complications, including fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and a buildup of waste products in the blood (uremia).
Choice C rationale:
Urine output (UO) is always measured during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. It is a vital clinical indicator to monitor the severity of kidney dysfunction and guide treatment decisions.
Accurate measurement of urine output is essential for assessing fluid balance, kidney function, and the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Choice D rationale:
Urine output (UO) is not greater than 500 mL/24 hours during the oliguric phase of acute renal failure. A urine output greater than 500 mL/24 hours would indicate a non-oliguric phase of acute renal failure or a potential recovery phase.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
