The nurse obtains a monitor strip on a patient who has had a myocardial infarction and makes the following analysis: P wave not apparent, ventricular rate 196, R-R interval regular, P-R interval not measurable, QRS complex wide and distorted, QRS duration 0.18 second. The nurse interprets the patient's cardiac rhythm as;
ventricular tachycardia.
atrial fibrillation.
atrial tachycardia.
ventricular fibrillation.
The Correct Answer is A
The characteristics described in the monitor strip analysis suggest ventricular tachycardia. The absence of a visible P wave and the wide and distorted QRS complex indicates that the electrical impulse is originating in the ventricles rather than the atria. The ventricular rate of 196 and regular R-R intervals further support the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia.
B. Atrial fibrillation in (option B) is incorrect because it is characterized by irregularly irregular R-R intervals and the absence of discernible P waves. The QRS complex is typically narrow
C. Atrial tachycardia in (option C) is incorrect because it would have a rapid atrial rate with regular R-R intervals, and P waves may or may not be discernible. The QRS complex is typically narrow.
D. Ventricular fibrillation in (option D) is incorrect because it would present as a chaotic, rapid, and irregular electrical activity with no discernible P waves, QRS complexes, or regular R-R intervals. It is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate defibrillation.
Therefore, based on the provided information, the nurse would interpret the patient's cardiac rhythm as ventricular tachycardia. However, it is important to note that an accurate interpretation should be made by a qualified healthcare professional, and the patient's clinical context should also be considered.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Tachypnoea, which refers to an increased respiratory rate, is an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. It is the body's compensatory response to inadequate tissue perfusion and decreased oxygen delivery. The increased respiratory rate is an attempt to improve oxygenation and maintain vital organ function.
B. Heart blocks in (option B) are incorrect because Heart blocks refer to disruptions in the electrical conduction system of the heart and are not specific to hypovolemic shock.
C. Vomiting in (option C) is incorrect because: Vomiting may occur in various conditions, including shock, but it is not exclusive to hypovolemic shock and can be present in other forms of shock or illnesses.
D. Bradycardia in (option D) is incorrect because Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate, is not typically an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. Instead, tachycardia (rapid heart rate) is more commonly observed as a compensatory response to maintain cardiac output.
E. Hypotension in (option E) is incorrect because Hypotension, or low blood pressure, can occur in hypovolemic shock but is generally considered a later-stage symptom. In the early stages, compensatory mechanisms may help maintain blood pressure, so hypotension may not be present initially.
F. Bradypnea in (option F) is incorrect because: Bradypnea refers to a slow respiratory rate, which is not typically an early symptom of hypovolemic shock. Tachypnoea, as mentioned earlier, is the more common early respiratory symptom.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
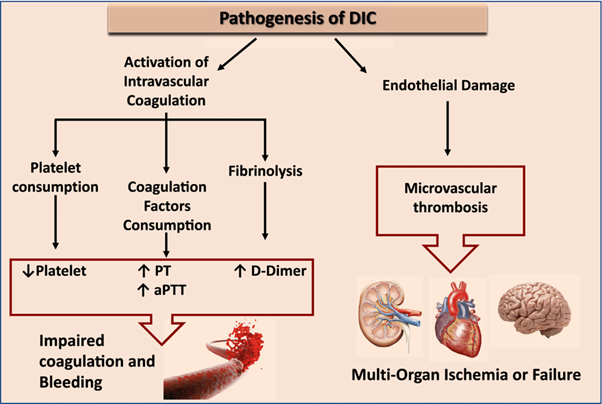
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by both widespread activation of the coagulation system and excessive clotting, leading to the consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This results in a prothrombotic state, which can lead to organ dysfunction and bleeding manifestations.
Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic finding in DIC. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that is elevated when there is excessive fibrin formation and breakdown. Elevated D-dimer indicates ongoing fibrinolysis and activation of the clotting system.
B. Decreased prothrombin time in (option B) is incorrect because: DIC is characterized by consumption of clotting factors, which can result in prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT) as well as other coagulation tests.
C. Decreased partial thromboplastin time in (option C) is incorrect because Similar to the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) can also be prolonged in DIC due to the consumption of clotting factors.
D. Elevated fibrinogen level in (option D) is incorrect because, In DIC, there is consumption of fibrinogen along with other clotting factors. Therefore, elevated fibrinogen levels are not consistent with the pathophysiology of DIC.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
