Which clinical manifestation should the nurse anticipate for a patient admited to the hospital with diabetes insipidus?
Fluid volume overload
Decreased gas exchange.
Generalized edema.
Polyuria.
The Correct Answer is D
Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive urination (polyuria) and thirst. Therefore, the nurse should anticipate the clinical manifestation of polyuria in a patient admitted to the hospital with diabetes insipidus. The patient may excrete large amounts of dilute urine, which can lead to dehydration if adequate fluid replacement is not provided. The other options listed (fluid volume overload, decreased gas exchange, and generalized edema) are not typically associated with diabetes insipidus, as this condition is characterized by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) rather than an excess of fluid.

Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
The correct answers are a, c, and d. The client will need to take thyroid hormone replacement (levothyroxine) for the rest of her life since she had a total thyroidectomy. The dosage will need to be carefully monitored to ensure that it is correct, and laboratory tests will need to be done frequently to monitor thyroid hormone levels. Taking too much of the drug can cause hyperthyroidism symptoms, so it is important not to take more than prescribed. It is also important to check with a healthcare provider before taking any other medications or herbs, as they can interact with levothyroxine.
Answer b is incorrect because the client will need to take the drug for the rest of her life.
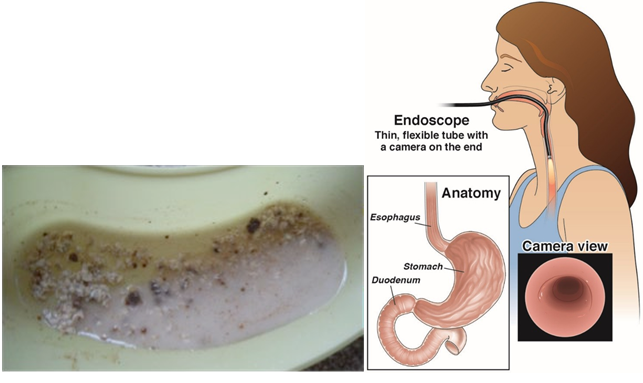
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
"Coffee-ground" emesis is a term used to describe vomit that has the appearance of coffee grounds, which indicates that the vomit contains partially digested blood. This is a serious symptom that could be indicative of an upper gastrointestinal bleed. An endoscopy is a diagnostic test that allows healthcare providers to visually examine the upper gastrointestinal tract and identify the source of bleeding.
Barium studies and angiography are not typically used to diagnose upper gastrointestinal bleeds. Gastric analysis may be useful in other diagnostic situations, but it is not the most appropriate test for a patient with "coffee-ground" emesis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.