Which of the following factors directly affects stroke volume?
Blood pressure
Preload
Afterload
Heart rate
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason:
Blood pressure itself does not directly affect stroke volume. However, it can influence afterload, which in turn affects stroke volume. Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, and while it is related to cardiac function, it is not a direct determinant of stroke volume.
Choice B Reason:
Preload directly affects stroke volume. Preload refers to the degree of stretch of the cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole, just before contraction. It is influenced by the volume of blood returning to the heart (venous return). According to the Frank-Starling law, an increase in preload leads to an increase in stroke volume due to the enhanced force of contraction.
Choice C Reason:
Afterload also directly affects stroke volume. Afterload is the resistance the ventricles must overcome to eject blood during systole. It is influenced by factors such as arterial blood pressure and vascular resistance. An increase in afterload can decrease stroke volume because the heart has to work harder to pump blood against the higher resistance.
Choice D Reason:
Heart rate does not directly affect stroke volume. Instead, heart rate and stroke volume together determine cardiac output (CO = HR × SV). While heart rate can influence the overall amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute, it does not directly change the volume of blood ejected with each beat.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Difficulty swallowing is a critical finding in a client with burns to the face, ears, and eyelids. This symptom can indicate airway edema or obstruction, which is a life-threatening condition. Burns in these areas can cause significant swelling, leading to compromised airways. Immediate intervention is required to secure the airway and prevent respiratory failure.
Choice B Reason:
Pain of 6 on a scale of 0 to 10 is important to manage for patient comfort and to prevent complications related to pain, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure. However, it is not the immediate priority over potential airway compromise. Pain management can be addressed once the airway is secured.
Choice C Reason:
A heart rate of 122/min indicates tachycardia, which can be a response to pain, stress, or hypovolemia. While it is important to monitor and manage, it is not as immediately life-threatening as airway obstruction. Tachycardia can be addressed after ensuring the airway is clear.
Choice D Reason:
Urinary output of 25 mL/hr is below the normal range (typically 30-50 mL/hr) and can indicate dehydration or renal impairment. While this is a concerning finding, it is not the immediate priority compared to securing the airway. Fluid resuscitation and renal function can be managed once the airway is stabilized.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Improved blood flow to surrounding tissues is generally a desired outcome of treating an aneurysm, not a complication. When an aneurysm is successfully treated, the goal is to restore normal blood flow and prevent the aneurysm from rupturing. Improved blood flow indicates that the treatment was effective and that the risk of complications has been minimized.
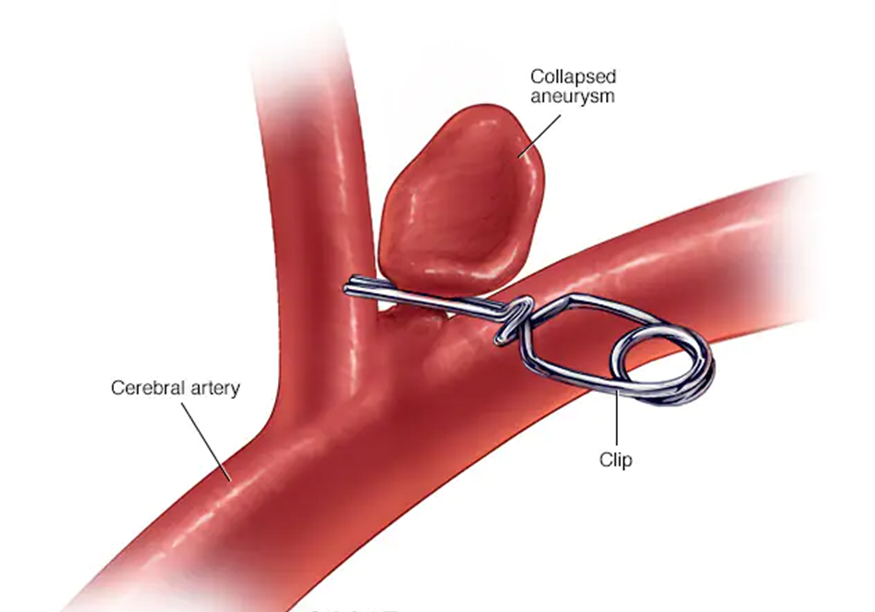
Choice B Reason:
Rupture leading to severe internal bleeding is a significant potential complication of a treated aneurysm. Even after treatment, there is a risk that the aneurysm could rupture, especially if the treatment was not entirely successful or if the aneurysm was particularly large or complex. A rupture can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding and requires immediate medical attention. This is why ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for patients who have had an aneurysm treated.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased risk of blood clot formation is another desired outcome rather than a complication. Treating an aneurysm often involves measures to prevent blood clots, such as using anticoagulant medications. A successful treatment should reduce the risk of clot formation, which can otherwise lead to complications like stroke or embolism.
Choice D Reason:
Reduced risk of infection is also a desired outcome of aneurysm treatment. Infection can be a complication of any surgical procedure, including those used to treat aneurysms. However, with proper surgical techniques and post-operative care, the risk of infection can be minimized. Therefore, a reduced risk of infection is not a complication but rather an indication of successful treatment and good medical practice.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
