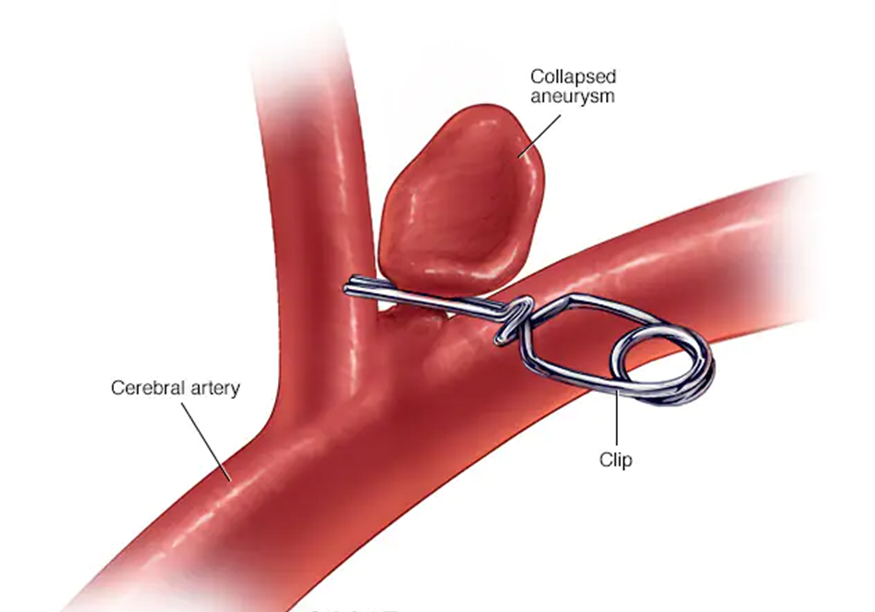
Which of the following is a potential complication of a treated aneurysm?
Improved blood flow to surrounding tissues
Rupture leading to severe internal bleeding
Decreased risk of blood clot formation
Reduced risk of infection
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason:
Improved blood flow to surrounding tissues is generally a desired outcome of treating an aneurysm, not a complication. When an aneurysm is successfully treated, the goal is to restore normal blood flow and prevent the aneurysm from rupturing. Improved blood flow indicates that the treatment was effective and that the risk of complications has been minimized.
Choice B Reason:
Rupture leading to severe internal bleeding is a significant potential complication of a treated aneurysm. Even after treatment, there is a risk that the aneurysm could rupture, especially if the treatment was not entirely successful or if the aneurysm was particularly large or complex. A rupture can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding and requires immediate medical attention. This is why ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for patients who have had an aneurysm treated.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased risk of blood clot formation is another desired outcome rather than a complication. Treating an aneurysm often involves measures to prevent blood clots, such as using anticoagulant medications. A successful treatment should reduce the risk of clot formation, which can otherwise lead to complications like stroke or embolism.
Choice D Reason:
Reduced risk of infection is also a desired outcome of aneurysm treatment. Infection can be a complication of any surgical procedure, including those used to treat aneurysms. However, with proper surgical techniques and post-operative care, the risk of infection can be minimized. Therefore, a reduced risk of infection is not a complication but rather an indication of successful treatment and good medical practice.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Suctioning the nose is not the first action to take. Suctioning can increase intracranial pressure and potentially cause further injury. It is important to first determine the nature of the drainage before taking any invasive actions.
Choice B Reason:
Notifying the physician is important, but it should be done after confirming the nature of the drainage. Testing the fluid for glucose can help determine if it is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which would indicate a serious complication requiring immediate medical attention.
Choice C Reason:
Testing the drainage for glucose is the correct first action. CSF contains glucose, so a positive test would confirm that the clear fluid is CSF. This is a critical step in diagnosing a CSF leak, which can occur with basal skull fractures and requires prompt intervention to prevent infection and other complications.
Choice D Reason:
Asking the client to blow their nose is contraindicated. Blowing the nose can increase intracranial pressure and exacerbate a CSF leak. It is important to avoid any actions that could worsen the condition until the nature of the drainage is confirmed.
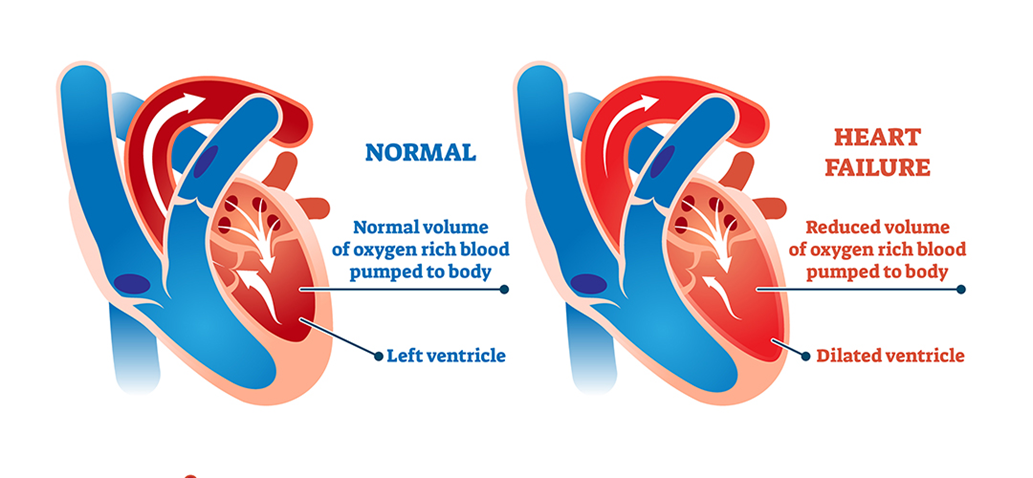
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A: Palpitations
Palpitations, or the sensation of a rapid or irregular heartbeat, can occur in various heart conditions, including left heart failure. However, they are not the most common or specific symptom of left heart failure. Palpitations can be caused by arrhythmias, anxiety, or other cardiac issues. In the context of left heart failure, the heart's inability to pump blood effectively leads to fluid buildup in the lungs, causing shortness of breath, which is a more direct and common manifestation.
Choice B: Peripheral edema
Peripheral edema, or swelling in the legs and ankles, is more commonly associated with right-sided heart failure. In right-sided heart failure, the heart's right ventricle fails to pump blood efficiently, leading to fluid accumulation in the body's extremities. While peripheral edema can occur in left heart failure, it is not as common as shortness of breath. Left heart failure primarily affects the lungs, leading to pulmonary congestion and shortness of breath.
Choice C: Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath, or dyspnea, is the hallmark symptom of left heart failure. When the left side of the heart fails to pump blood effectively, blood backs up into the pulmonary veins, causing fluid to leak into the lungs. This results in pulmonary congestion and difficulty breathing. Patients with left heart failure often experience shortness of breath during physical activity, while lying down (orthopnea), or waking up at night (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea). This symptom is a direct consequence of the heart's reduced ability to manage blood flow and is a key indicator of left heart failure.
Choice D: Chest pain
Chest pain can be a symptom of various cardiac conditions, including coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and angina. While chest pain can occur in heart failure, it is not the most common manifestation of left heart failure. The primary issue in left heart failure is the heart's inability to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and shortness of breath. Chest pain is more typically associated with ischemic heart conditions rather than heart failure itself.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
