Which technique is most appropriate for a nurse to use when cleansing a pressure ulcer?
Cleanse using hydrogen peroxide followed by betadine solution.
Cleanse the wound gently from the outer edges towards the center.
Cleanse using 4x4 gauze to the wound and surrounding skin three times.
Cleanse from the innermost point outwards with a circular movement.
The Correct Answer is D
Cleanse from the innermost point outwards with a circular movement. This technique reduces the risk of contaminating the wound with bacteria from the surrounding skin.
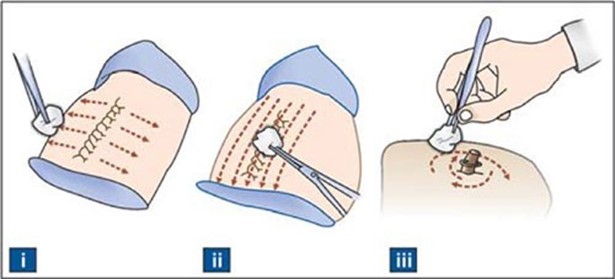
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice A is wrong because hydrogen peroxide and betadine solution can damage healthy tissue and delay wound healing.
Choice B is wrong because cleansing the wound from the outer edges towards the center can introduce bacteria from the skin into the wound.
Choice C is wrong because using 4x4 gauze to the wound and surrounding skin three times can cause trauma and bleeding to the wound.
Normal ranges for pressure ulcer stages are:
- Stage I: A reddened, painful area on the skin that does not turn white when pressed.
- Stage II: The skin blisters or forms an open sore. The area around the sore may be red and irritated.
- Stage III: The skin develops an open, sunken hole called a crater or ulcer. The tissue below the skin is damaged.
- Stage IV: The pressure ulcer has become so deep that there is damage to the muscle and bone, and sometimes to tendons and joints.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
“I can use clean instead of sterile technique to suction my tracheostomy.” This statement demonstrates that the client understands how to care for their tracheostomy at home. According to the American Thoracic Society, clean technique can be used for suctioning at home, as long as the equipment is cleaned and stored properly.
Choice A is wrong because the client should be able to take care of their own tracheostomy as much as possible, with the help of a caregiver if needed. This promotes independence and self-care.
Choice B is wrong because the client should not be the only one who knows how to suction their tracheostomy at home. They should have at least one backup person who can assist them in case of an emergency or if they are unable to do it themselves.
Choice C is wrong because the client should not use saline for longer than 24 hours, even if they boil it.
Saline can become contaminated with bacteria and cause infection. The client should use fresh saline every time they suction their tracheostomy.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Take this medication at least 30 minutes before ingesting any food or medication.
This is because alendronate (Fosamax) is a bisphosphonate that works by inhibiting the breakdown and reabsorption of bone. However, it has a very low bioavailability, which means that only a small amount of the drug is absorbed into the bloodstream when taken orally. Therefore, taking it with food or other medications can interfere with its absorption and reduce its effectiveness.
The other choices are wrong because:
A. Chew the tablet well and report any difficulty swallowing. This is wrong because alendronate tablets should not be chewed or crushed, but swallowed whole with a full glass of plain water. Chewing or crushing the tablets can increase the risk of irritation or damage to the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach). Difficulty swallowing is a possible side effect of alendronate and should be reported to the doctor, but it is not an instruction for taking the medication.
B. Take the medication with six to eight ounces of milk. This is wrong because milk contains calcium, which can bind to alendronate and prevent its absorption. Alendronate should not be taken with any beverages other than plain water.
C. Lie down for 15 to 30 minutes after taking the medication. This is wrong because lying down after taking alendronate can increase the risk of esophageal irritation or
ulceration. Alendronate should be taken in the morning, at least 30 minutes before eating or drinking anything, and the person should remain upright (sitting or standing) for at least 30 minutes after taking it.
Normal ranges for bone density are expressed as T-scores, which compare a person’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same sex. A T-score of -1.0 or above is normal, a T-score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates low bone density (osteopenia), and a T-score of -2.5 or below indicates osteoporosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
