Custom SP23 N23 N240 Exam 3 Ch 11 24 32 43 44
ATI Custom SP23 N23 N240 Exam 3 Ch 11 24 32 43 44
Total Questions : 56
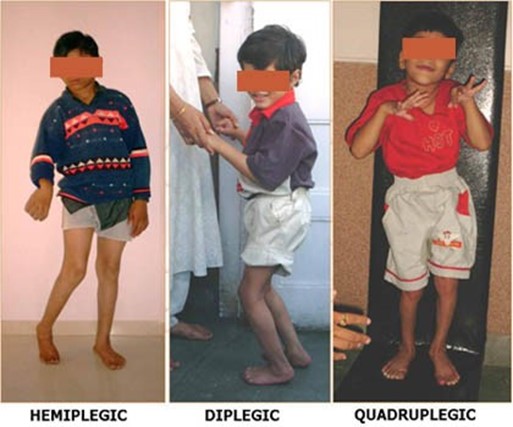
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA home health nurse is developing a plan of care for a child who has hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
Which of the following goals is the priority for the nurse to include in the plan of care?
Explanation
The correct answer is d. Modify the environment.
Rationale for each choice:
Choice a. Improve the client's communication skills.
- Statement:While communication is important,it is not the priority for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Hemiplegic cerebral palsy primarily affects motor skills,not communication abilities.While some children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy may have speech difficulties,it is not the most pressing concern in this case.Addressing environmental barriers to promote mobility and independence takes precedence.
Choice b. Provide respite services for the parents.
- Statement:Respite services can provide valuable support for parents,but they are not the priority in this case.
- Rationale:The focus of the care plan should be on the child's immediate needs and safety.Modifying the environment to enhance the child's functional abilities is crucial for their development and well-being.
Choice c. Foster self-care activities.
- Statement:Encouraging self-care is essential,but it requires a supportive environment.
- Rationale:Before promoting self-care activities,the nurse must ensure the child has the necessary accommodations and modifications in place to facilitate independence.
Choice d. Modify the environment.
- Statement:This is the priority goal for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Modifying the home environment can significantly improve the child's mobility,safety,and ability to participate in daily activities.Examples of modifications include:
- Installing grab bars in the bathroom
- Widening doorways
- Removing tripping hazards
- Providing adaptive equipment such as special chairs or utensils
- Ensuring adequatelighting
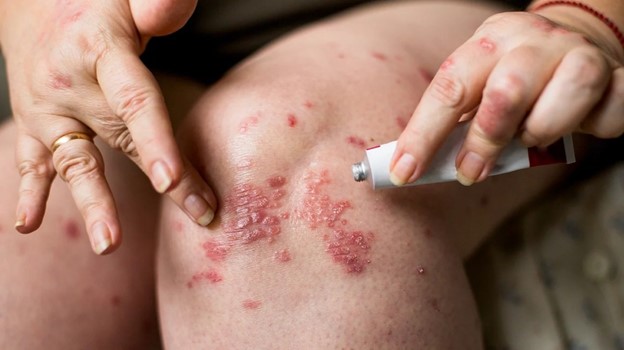
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a preschooler who has eczema.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Treatment of eczema may start with regular moisturizing and other self-care habits.
If these don’t help, a healthcare provider might suggest medicated creams that control itching and help repair skin.
Choice A is not correct because woolen clothes can irritate the skin and worsen
eczema.
Choice B is not correct because fabric softeners can irritate the skin and worsen
eczema.
Choice C is not correct because bubble baths can dry out the skin and worsen eczema.
A nurse is caring for a child who has Legg-Calve-Perthes disease and is in Buck extension traction.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice a. Reposition the child every 2 hr.
Choice A rationale:
Repositioning the child every 2 hours is essential to prevent complications such as pressure ulcers and to promote comfort and circulation.
Choice B rationale:
Removing the traction boot during baths is not recommended as it can disrupt the traction setup and potentially worsen the condition.
Choice C rationale:
Reducing fluid intake is not necessary for managing Legg-Calve-Perthes disease and could lead to dehydration.
Choice D rationale:
Applying antibiotic ointment to pin sites daily is not applicable in this scenario as Buck extension traction typically does not involve pin sites.
A nurse is providing teaching about lice to the parents of a school-age child at a well-child visit.
Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Head lice are spread most commonly by direct head-to-head (hair-to-hair) contact.
However, much less frequently they are spread by sharing clothing or belongings onto which lice have crawled or nits attached to shed hairs may have fallen.
Choice B is not correct because lice cannot jump from one child to another. Choice C is not correct because live lice survive less than 1-2 days if they fall off a
person and cannot feed.
Choice D is not correct because washing your child’s hair daily will not prevent lice.
A school nurse is assessing a school-age child and notices white flakes that don't brush off the hair and a rash on the back of the child's neck.
The nurse should suspect which of the following disorders?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D: Pediculosis capitis.
Choice D rationale: Pediculosis capitis is an infestation of head lice, which causes symptoms such as white flakes that do not brush off the hair easily and a rash on the back of the neck. These symptoms are due to the lice feeding on the scalp and laying eggs (nits), which can cause itching and irritation.
Choice A rationale: Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, typically caused by bacterial or fungal infections. While it can cause a rash, it is not characterized by white flakes in the hair.
Choice B rationale: Tinea capitis, also known as ringworm of the scalp, is a fungal infection that causes scaly, itchy patches on the scalp. It may lead to hair loss in the affected areas, but it does not typically cause white flakes that do not brush off the hair.
Choice C rationale: Impetigo contagiosa is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that causes blisters or sores on the skin. It does not involve white flakes in the hair and primarily affects exposed skin rather than the scalp.
A nurse is assessing an 8-month-old infant for cerebral palsy.
Which of the following findings is a manifestation of the condition?
Explanation
A cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and muscle tone or posture.
It’s caused by damage that occurs to the immature, developing brain, most often before birth.
Signs and symptoms appear during infancy or preschool years.
In general, cerebral palsy causes impaired movement associated with exaggerated reflexes, floppiness or spasticity of the limbs and trunk, unusual posture, involuntary movements, unsteady walking, or some combination of these.
An 8-month-old infant with cerebral palsy may have developmental delays and may require pillow props to sit up.
Choice A, Tracking an object with eyes, is a normal developmental milestone for
an infant.
Choice C, Uses a pincer grasp to pick up a toy, is also a normal developmental
milestone for an infant.
Choice D, Smiles when a parent appears, is also a normal developmental milestone for an infant.
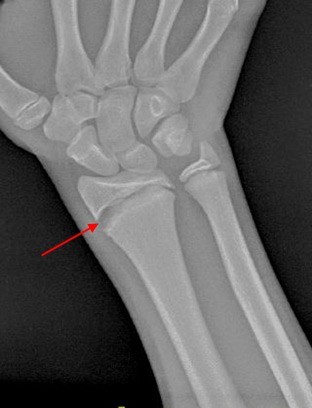
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a child who has a fracture of an epiphyseal plate.
Which of the following statements should the nurse make?
Explanation
An epiphyseal fracture is a fracture that occurs in the epiphyseal plate, which is the layer of cartilage between the end of a long bone and the start of the bone shaft.
This type of fracture is most common in children and adolescents, as their bones are still growing and the epiphyseal plate is not yet fused to the bone shaft.
Because this is where new bone develops, injuries to this area can cause the plate to close prematurely, jeopardizing bone growth.
Choice B, “Bone marrow can be lost through the fracture,” is incorrect because
bone marrow is not lost through an epiphyseal fracture.
Choice C, “The younger the child the longer the healing process will take,” is incorrect because younger children generally heal faster than older children or adults.
Choice D, “The blood supply to the bone is disrupted,” is incorrect because an
epiphyseal fracture does not necessarily disrupt the blood supply to the bone.
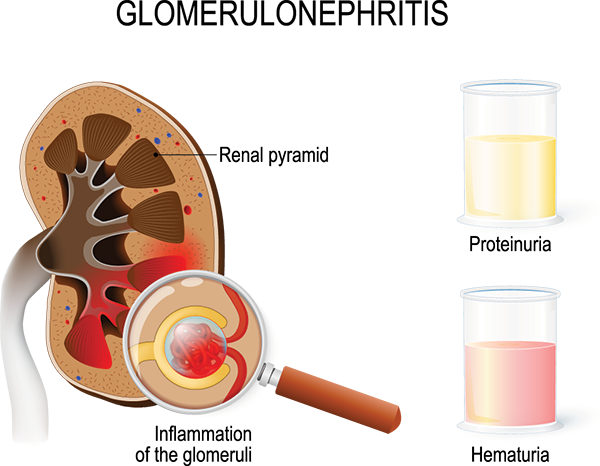
A nurse is caring for a child who has acute glomerulonephritis.
Which of the following actions is the nurse's priority?
Explanation
Nursing care planning goals for a child with acute glomerulonephritis are directed toward the excretion of excess fluid through urination.
Monitoring fluid status is very important and daily weights are an effective way to monitor fluid retention, as weight gain is the earliest sign of fluid retention.
Choice B, Educating the parents about potential complications, is important but not the nurse’s priority.
Choice C, Place the child on a no-salt-added diet, which may be part of the treatment
plan but is not the nurse’s priority.
Choice D, Maintaining a saline lock, may be necessary for administering medications but is not the nurse’s priority.
A nurse is caring for a child who has tinea pedis. The child's parent asks the nurse what this infection is commonly called.
The nurse should respond with which of the following common names?
Explanation
Tinea pedis is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet and is commonly known as an athlete’s foot.
Choice A, Shingles, is incorrect because shingles are a viral infection that causes a
painful rash.
Choice B, Valley fever, is incorrect because valley fever is a fungal infection that affects the lungs.
Choice C, Fever blister, is incorrect because fever blisters are caused by the herpes simplex virus and typically appear on or around the lips.
A nurse is assisting with a routine physical examination of an adolescent. The provider observes a lateral curvature of the spine.
The nurse should expect the provider to document which of the following disorders?
Explanation
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by sideways curvature of the spine or backbone.
A lateral curvature of the spine is called scoliosis.
Choice A, Torticollis, is not the correct answer because it is a condition in which the head becomes persistently turned to one side, often associated with painful muscle spasms.
Choice B, Kyphosis, is not the correct answer because it refers to an excessive outward curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back.
Choice D, Lordosis, is not the correct answer because it refers to an excessive inward curvature of the spine.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 56 questions on the ATI Custom SP23 N23 N240 Exam 3 Ch 11 24 32 43 44 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



