RN V Adult Medical Surgical S 2019 Proctored Exam
ATI RN VATI Adult Medical Surgical S 2019 Proctored Exam
Total Questions : 89
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse is caring for a client who is hemorrhaging and hypotensive from esophageal variceal bleeding. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Verify that the client has adequate IV access.
Choice A rationale:
Administering vasopressin to the client might be necessary to manage the hemorrhage, but before any medication administration, it is crucial to ensure the client has adequate IV access. Vasopressin is a vasoconstrictor and can help control bleeding from esophageal varices, but its effectiveness relies on IV access to deliver the medication promptly.
Choice B rationale:
Requesting blood from the blood bank is essential for a client experiencing significant bleeding. However, the priority action is to verify IV access to administer any necessary blood products.
Choice C rationale:
This is the correct choice. Before initiating any interventions, ensuring the client has appropriate IV access is a priority. Adequate IV access is necessary to administer fluids, medications, or blood products promptly and effectively stabilize the client's blood pressure.
Choice D rationale:
Inserting an indwelling urinary catheter is not the priority action in this situation. While monitoring urine output is important, it should be secondary to addressing the client's hypotension and hemorrhage.
A nurse is providing teaching about dietary options for a client who has cholelithiasis. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Cauliflower is not a good dietary choice for a client with cholelithiasis. Cholelithiasis refers to the presence of gallstones, and certain foods, including cauliflower, can exacerbate symptoms in some individuals.
Choice B rationale:
Increasing the amount of egg yolks in the diet is not advisable for a client with cholelithiasis. Egg yolks are high in cholesterol and can contribute to gallstone formation.
Choice C rationale:
This is the correct choice. Desserts like angel-food cake are a better dietary option for a client with cholelithiasis. Angel-food cake is typically low in fat and cholesterol, making it a more suitable choice for those with gallbladder issues.
Choice D rationale:
Eating choice or prime cuts of meat is not recommended for clients with cholelithiasis. These types of meat are often higher in fat, which can trigger gallbladder symptoms.
A nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving brachytherapy. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Explanation
Dispose of the client's feces and urine in a special container.
Choice A rationale:
This is the correct choice. Brachytherapy involves the placement of a radiation source in or near the tumor. To minimize radiation exposure to others, the client's bodily fluids (feces and urine) should be considered radioactive and disposed of properly in a designated container.
Choice B rationale:
While limiting the time of visitors can be a good measure to reduce radiation exposure, it is not the priority intervention. The primary concern is proper handling and disposal of radioactive bodily fluids.
Choice C rationale:
Keeping the client's linens in the room until after removal of the radiation source is not the correct choice. Radioactive linens should be handled and laundered separately, following appropriate safety protocols.
Choice D rationale:
Providing one dosimeter badge for staff to share while caring for the client is not adequate. Each staff member involved in direct care should have their dosimeter badge to monitor their individual radiation exposure levels.
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a total left hip arthroplasty. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should not cross the client's legs when sitting in the recliner following a total left hip arthroplasty. Crossing the legs can put strain on the operative hip and may increase the risk of dislocation or other complications.
Choice B rationale:
Providing a heating pad to the operative hip is not recommended. Heat can increase blood flow to the area and may lead to increased swelling and potential complications in the postoperative period.
Choice C rationale:
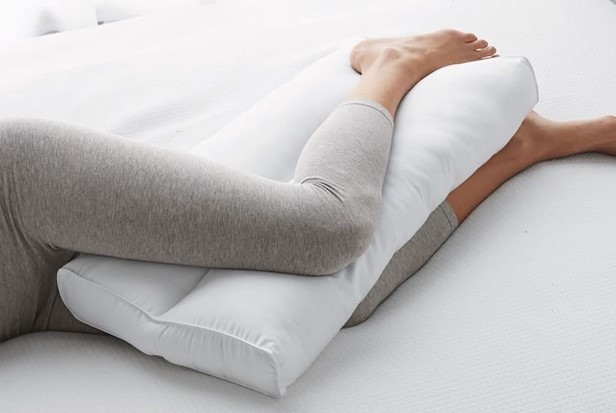

Placing a pillow between the legs when turning the client to their side is the correct action. This technique is known as the "abduction pillow”. or "wedge pillow.”. It helps maintain proper hip alignment and prevents the operated leg from crossing the midline, reducing the risk of dislocation and promoting healing.
Choice D rationale:
Having the client lean forward when assisting them out of the bed is not appropriate after a total left hip arthroplasty. Leaning forward can put strain on the hip joint and increase the risk of injury.
A nurse is caring for a client who had moderate sedation during a procedure. The client's airway is obstructing, and they have an oxygen saturation of 90%. Which of the following interventions is the first action the nurse should take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Preparing an endotracheal tube for intubation is not the first action the nurse should take in this situation. Intubation is an invasive procedure and should be reserved for cases where other, less invasive methods of airway management have failed.
Choice B rationale:
Inserting a plastic oral airway may help maintain the airway in some situations, but it is not the first action to take when the client's airway is obstructing and their oxygen saturation is low.
Choice C rationale:
Providing oxygen using a manual resuscitation bag (bag-valve-mask device) is the correct first action. This allows the nurse to manually assist the client's breathing and deliver oxygen more effectively than just providing supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula or face mask.
Choice D rationale:
Performing a head tilt with a chin-lift is a basic airway maneuver, but it may not be sufficient in this situation, especially if the airway is completely obstructed. Providing oxygen with a manual resuscitation bag takes precedence.
A nurse is providing information about maintaining a special diet with a client who has irritable bowel syndrome. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Increasing the intake of dairy products is not recommended for a client with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) as dairy can exacerbate symptoms in some individuals, particularly if they are lactose intolerant.
Choice B rationale:
Drinking ten glasses of water each day is a helpful recommendation for clients with IBS. Staying hydrated can aid in digestion and help alleviate symptoms like constipation.
Choice C rationale:
Decreasing daily fiber intake to 20 grams is not advisable for IBS management. Adequate fiber intake is essential for maintaining bowel regularity and overall gut health. Instead, it is recommended to focus on soluble fiber and gradually increase fiber intake to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Choice D rationale:
Encouraging the intake of clear carbonated fluids is not ideal for clients with IBS. Carbonated beverages can cause bloating and gas, potentially worsening symptoms in individuals with sensitive digestive systems. It is better to recommend non-carbonated, non-caffeinated fluids for hydration.
A nurse is planning care for a client who has disseminated herpes zoster (shingles). Which of the following interventions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Answer: A
Rationale:
A) Place the client in a room with negative airflow: Disseminated herpes zoster (shingles) requires airborne precautions because the virus can become aerosolized. A room with negative airflow helps prevent the spread of the virus to other areas, protecting healthcare workers and other patients from infection.
B) Remove isolation gown after leaving the client's room: Isolation gowns should be removed before leaving the client's room to prevent the spread of contaminants to other areas. This intervention is important for infection control but is not specific to the requirement for negative airflow in cases of disseminated herpes zoster.
C) Apply ketoconazole to the lesions three times per day: Ketoconazole is an antifungal medication and is not used for treating herpes zoster, which is caused by a viral infection. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, are appropriate for treating herpes zoster lesions.
D) Provide the client with eye protection for ultraviolet B light therapy: Eye protection is necessary during UVB light therapy to protect the eyes, but UVB light therapy is not a standard treatment for disseminated herpes zoster. The priority intervention is to prevent the spread of the infection by using a negative airflow room.
A nurse in the emergency department is preparing to irrigate the eyes of a client who received a chemical splash on their face. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Completely irrigating one eye before irrigating the second eye is the correct action to take when a client receives a chemical splash on their face. This approach helps prevent the potential spread of the chemical from one eye to the other. Irrigation should be done immediately to flush out the chemical and minimize its harmful effects.
Choice B rationale:
Informing the client to blink their eyes rapidly during the irrigation process is not recommended. Blinking may exacerbate the dispersion of the chemical and could lead to further damage to the eyes. Instead, the client should keep their eyes open during irrigation.
Choice C rationale:
Delaying the irrigation process until the type of chemical in the eyes is identified is not appropriate. Time is critical in minimizing the impact of the chemical on the eyes. Immediate irrigation is essential, regardless of the type of chemical, to remove the substance from the eyes.
Choice D rationale:
Asking the client to count the number of fingers held up by the nurse before irrigating their eyes is not relevant in this situation. The priority is to initiate immediate irrigation to remove the chemical from the eyes. Assessing the client's visual acuity can be done later in the evaluation process after the eyes have been irrigated.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a pulmonary embolism and is receiving therapy with unfractionated heparin. Which of the following laboratory results indicates that the therapy is effective?
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
A PT (Prothrombin Time) of 12 seconds is not indicative of the effectiveness of heparin therapy for a pulmonary embolism. PT measures the extrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade, and it is more relevant to monitor in patients on warfarin therapy.
Choice B rationale:
The aPTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time) of 75 seconds is the correct choice as it reflects the effectiveness of unfractionated heparin therapy. Heparin works by inhibiting clotting factors in the intrinsic pathway, and the aPTT is used to monitor heparin's anticoagulant effect. The normal range for aPTT is typically 25-35 seconds.
Choice C rationale:
An INR (International Normalized Ratio) of 1.1 is not the appropriate parameter to assess the effectiveness of heparin therapy. INR is primarily used to monitor the effectiveness of oral anticoagulants like warfarin, not heparin.
Choice D rationale:
The platelet count of 200,000/mm² is not a suitable parameter to evaluate the effectiveness of heparin therapy. Platelet count is important for assessing the risk of bleeding or clotting disorders but does not directly measure the impact of heparin on clotting factors.
A nurse is planning care for a client who has long-term liver cirrhosis and a new diagnosis of abdominal ascites. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care to prevent complications?
Explanation
Answer: A. Administer furosemide.
Rationales
A. Administer furosemide.
Furosemide, a loop diuretic, helps reduce fluid overload by promoting urinary excretion of sodium and water. In a client with cirrhosis and ascites, it decreases abdominal distention, eases breathing by reducing pressure on the diaphragm, and prevents complications related to severe fluid accumulation.
B. Weigh the client weekly.
Weekly weights would not provide sufficient monitoring for a client with ascites, since fluid retention can change rapidly within hours or days. Daily weights are necessary to detect subtle increases in fluid status and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
C. Offer the client a high-sodium diet.
A high-sodium diet would worsen fluid retention and ascites, as sodium promotes water retention. Instead, a low-sodium diet is indicated to limit further fluid buildup in the peritoneal cavity.
D. Administer heparin.
Heparin is not a standard intervention for cirrhosis with ascites. Because the diseased liver produces fewer clotting factors, clients are already at risk for bleeding, and anticoagulant therapy would heighten this risk without addressing the underlying problem of fluid accumulation.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 89 questions on the ATI RN VATI Adult Medical Surgical S 2019 Proctored Exam Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



