Medical Surgical integ/burns Exam
ATI Medical Surgical integ/burns Exam
Total Questions : 40
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse is teaching a class about expected changes to the skin in older adults. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: the epidermis becomes thinner and more fragile with age hence making the skin of elderly individuals more prone to injury, bruising, and infections.
Choice B rationale: this is incorrect because the skin in old age loses its elasticity and becomes more wrinkled due to the loss of collagen and elastin fibers responsible for maintaining the elasticity of the skin.
Choice C rationale: subcutaneous tissue comprising mainly of fat and connective tissue increases with age especially in regions such as the abdomen.
Choice D rationale: blood vessels within the skin become narrower and less efficient with increasing age thus resulting in decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to the skin.
Choice E rationale: sebum production which is responsible for skin lubrication increases with age thus making this statement incorrect.
A nurse is obtaining an aerobic wound culture for a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
- A: Swabbing the wound bed is an essential step in obtaining a wound culture, but it is not the first action that should be taken. This step is performed after the wound has been cleansed to ensure that the sample is not contaminated with debris or bacteria from the surrounding skin.
- B: Cleansing the area around the wound with sterile saline is the correct first step. This action helps to remove any contaminants or debris from the wound surface, ensuring that the culture obtained is from the wound itself and not from the surrounding skin, which could lead to inaccurate results.
- C: Donning sterile gloves is a crucial step to maintain sterility during the procedure. However, it is not the first action because the nurse must first cleanse the wound area to prevent contamination of the culture specimen.
- D: Placing the collection tube in a specimen bag is done after obtaining the wound culture to transport the specimen to the laboratory. This is one of the final steps in the process, not the first.
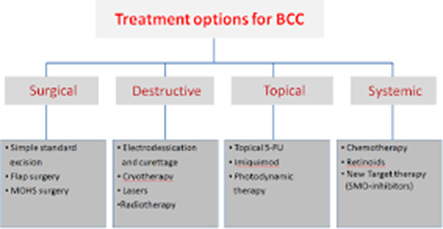
A nurse is caring for a client who has questions concerning the various treatment options for his new diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Which of the following treatments should the nurse include in the discussion? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
Choice A rationale: radiation therapy is one of the possible management options for basal cell carcinoma (BCC) that uses high-energy rays to kill the cancerous cells.
Choice B rationale: this is incorrect since topical corticosteroids are ineffective in BCC management and may worsen the patient’s condition by suppressing their immune system.
Choice C rationale: micrographic surgery can be used in BCC management and it involves the removal of thin layers of skin to a point where no cancer cells can be detected.
Choice D rationale: this is appropriate and involves the use of electric current to burn off the cancer cells.
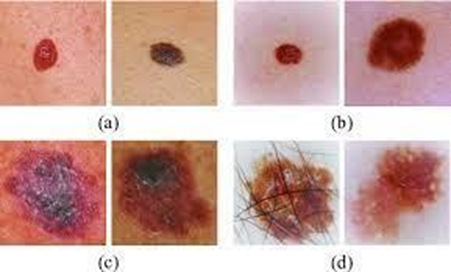
A nurse is caring for a client who has malignant melanoma. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect when assessing?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: pruritus is one of the symptoms of malignant melanoma, as well as changes in the shape, size, color, or texture of a mole or other skin lesion. However, pruritus is not specific to the disease and should always serve as a clue prompting further examination.
Choice B rationale: pain is a very rare symptom in malignant melanoma especially during the early stages of the disease. However, pain may occur in advanced stages of the disease when deeper tissues have been invaded and in cases of metastasis to distant sites.
Choice C rationale: purulent discharge is an indication of an underlying infection rather than malignant melanoma.
Choice D rationale: purplish skin discoloration is common in Kaposi’s sarcoma which manifests as purplish skin nodules rather than malignant melanoma. Furthermore, it may suggest bruising or bleeding under the skin. Malignant melanoma can have various colors, such as black, brown, red, blue, or white, depending on the type and amount of melanin produced by the tumor cells.
A nurse is caring for a male client who has a new diagnosis of genital herpes (HSV 2).
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: white-or flesh-colored papillary growths in the genital region is a common finding in human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, not HSV 2 infection.
Choice B rationale: a patient with HSV 2 usually develop influenza-like symptoms such as headache, muscle aches, fever, and generalized body malaise. However, the above symptoms usually subside within a few days to weeks.
Choice C rationale: anuria refers to the absence of urine output indicating renal failure which is not associated with HSV 2 infection.
Choice D rationale: green penile discharge is associated with gonorrhea infection rather than HSV 2 infection.
A nurse is caring for a client who has burns to his face, ears, and eyelids. The nurse should identify which of the following is the priority report to the provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: tachycardia is an expected finding in burns patients due to the increase in metabolic rate and fluid loss.
Choice B rationale: a urine output of 25 ml/hr is too low for an individual with burns hence the need for adequate fluid resuscitation. However, this is not a priority sign compared with the difficulty in breathing.
Choice C rationale: difficulty in swallowing is an indicator of airway edema which may compromise the patients breathing and oxygenation which may result in death. Therefore, the healthcare provider should be notified to assess the need for intubation.
Choice D rationale: Pain of 6 on a scale of 0 to 10 is moderate and is expected due to burns and can be managed with analgesics and nonpharmacological interventions.
A nurse is teaching a class about the epidermis. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: the epidermis which is the most superficial layer of the skin relies on the dermis for nutrition since it lacks its own blood supply.
Choice B rationale: adipose tissue is contained in the hypodermis which is part of the dermis layer of the skin and not the epidermis.
Choice C rationale: nerve fibers are contained in the dermis layer of the skin and not the epidermis.
Choice D rationale: blood vessels are contained in the dermis layer of the skin and not the epidermis.
A nurse is preparing to administer hydrocortisone 100 mg IM daily to a client. Available is hydrocortisone 250 mg/2 mL. How many ml should the nurse administer per dose?
(Round the answer to the nearest tenth number. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
Explanation
The amount to be administered = desired dose/ dose at hand X quantity of the solution
= 100/250 x 2
= 0.8 mL
A nurse in an emergency room is caring for a client who sustained partial-thickness burns to both lower legs, chest, face, and both forearms Which of the following is the priority action the nurse should take?
Explanation
Choice A rationale: this is important to assess the individual’s blood level and risk of infection but it is not a priority action compared to airway management.
Choice B rationale: The insertion of an indwelling urinary catheter is crucial for urine output monitoring but is not a priority action to take.
Choice C rationale: Inspection of the mouth for signs of inhalation injuries is a priority action for burns patients, especially those who have sustained facial burns since they can result in airway compromise and subsequent respiratory failure. The signs to look out for include; soot in the mouth and mouth, hoarseness, stridor, wheezes, or singed nasal hairs. In cases of suspected inhalation injuries, the nurse should inform the healthcare provider to assess for the need for intubation.
Choice D rationale: administration of analgesics is crucial for pain relief for all burn patients. However, this is not a priority action to take compared to airway management.
A nurse is preparing to start an IV infusion of lactated Ringer's for a client who sustained a burn injury. The client is prescribed 5,200 mL of fl over the first 24 hr. How many mL/hr should the nurse set the pump to infuse for the first 8 hr?
Explanation
In burns, half the total fluids required within 24 hours should be given within 8 hours and the other half distributed over the remaining 16 hours to prevent hypovolemic shock and electrolyte imbalance.
Therefore, half the fluid that should be given within 8 hours is 5200/2= 2600
We will use the formula: drip rate= total volume of fluid to be administered/total duration
= 2600/8
=325 mL/hr
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 40 questions on the ATI Medical Surgical integ/burns Exam Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



