A client 80 years of age experienced dysphagia (impaired swallowing) in the weeks following a recent stroke, but the care team wishes to now begin introducing minced and pureed food. How should the nurse best position the client?
Protective Supine
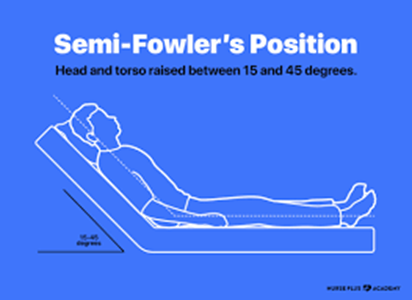
Semi-Fowlers
Low-Fowlers
Fowlers
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A rationale: Protective supine positioning is not ideal for managing dysphagia or facilitating swallowing.
Choice B rationale: Semi-Fowlers positioning, with the head of the bed elevated at a 30 to 45-degree angle, is often recommended for clients with dysphagia. This position helps prevent aspiration during eating and promotes effective swallowing.
Choice C rationale: Low-Fowlers and Fowlers positions may not be as effective in preventing aspiration during eating as the Semi-Fowlers position.
Choice D rationale: Fowlers positioning alone may not be sufficient for managing dysphagia; Semi-Fowlers is a more specific recommendation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The client who is 92 years old, uses a walker, is incontinent, and has an extensive cardiac history is at higher risk for the development of pressure injuries due to age, immobility, and additional risk factors.
Choice B rationale: A client with paraplegia may be at risk for pressure injuries, but the combination of age, walker use, incontinence, and cardiac history increases the risk in Choice A.
Choice C rationale: A comatose client with a traumatic brain injury is at risk, but other factors in Choice A contribute to a higher overall risk.
Choice D rationale: A client who uses a cane and has dementia may be at risk, but the combination of age, walker use, incontinence, and cardiac history increases the risk in Choice A.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The stool test for occult blood is not primarily designed to detect bacteria.
Choice B rationale: Parasites are not typically detected through a stool test for occult blood.
Choice C rationale: Steatorrhea refers to the presence of excess fat in the stool and is not the primary focus of a stool test for occult blood.
Choice D rationale: The purpose of the stool test for occult blood is to check for the presence of blood in the stool, which may not be visible to the naked eye. This can be an indicator of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
