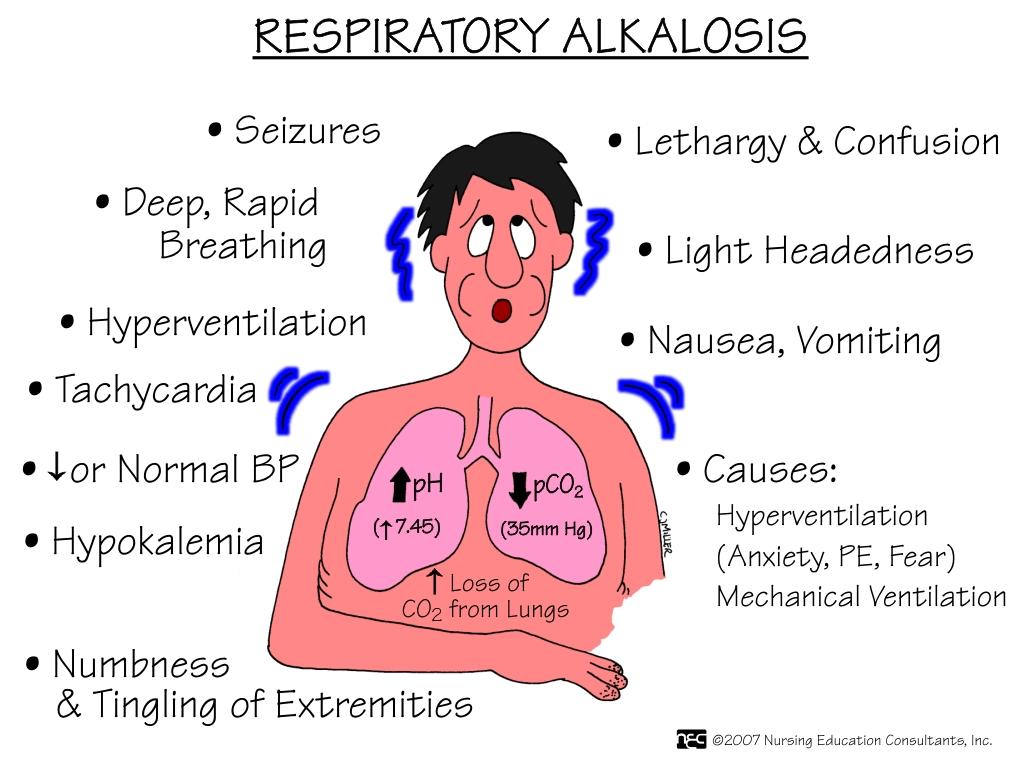
A client in the beginning stages of an asthma attack has arterial blood gases that reveal the following results: pH 7.51, PaCO2 28 mmHg, PaO2 75 mmHg, O2 saturation 92%, HCO3 24 mEq/L. The nurse interprets this blood gas result as:
Metabolic alkalosis.
Metabolic acidosis.
Respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory acidosis.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated pH and an increased bicarbonate (HCO3) level. In this case, the pH is elevated (7.51), but the bicarbonate level is within the normal range (24 mEq/L), indicating that the alkalosis is not metabolic in origin.
Choice B reason: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decreased pH and a decreased bicarbonate (HCO3) level. In this scenario, the pH is elevated, not decreased, and the bicarbonate level is normal, ruling out metabolic acidosis.
Choice C reason: Respiratory alkalosis is characterized by an elevated pH and a decreased partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2). The given values show a pH of 7.51 (elevated) and a PaCO2 of 28 mmHg (decreased), which are indicative of respiratory alkalosis. This condition often occurs in the early stages of an asthma attack due to hyperventilation, which causes excessive exhalation of CO2.
Choice D reason: Respiratory acidosis is characterized by a decreased pH and an increased PaCO2. In this case, the pH is elevated, and the PaCO2 is decreased, which is the opposite of what is seen in respiratory acidosis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A reason: Albuterol is a bronchodilator used to treat conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is not typically used in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). TB treatment focuses on antibiotics that target the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria.
Choice B reason: Isoniazid is one of the primary medications used in the treatment of tuberculosis. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of mycolic acids, which are essential components of the bacterial cell wall. Isoniazid is usually part of the initial treatment regimen for TB and is taken for several months to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria.
Choice C reason: Pyrazinamide is another key medication in the treatment of tuberculosis. It is particularly effective during the initial phase of treatment and helps to reduce the duration of therapy. Pyrazinamide works by disrupting the bacterial cell membrane metabolism and transport functions.
Choice D reason: Tiotropium is a long-acting bronchodilator used to manage COPD. It is not used in the treatment of tuberculosis. The focus of TB treatment is on antibiotics that specifically target the TB bacteria.
Choice E reason: Rifampin is a critical antibiotic in the treatment of tuberculosis. It works by inhibiting the RNA synthesis of the bacteria, effectively killing the TB bacteria. Rifampin is usually taken in combination with other TB medications to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of the bacteria.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: A decreased anteroposterior diameter of the chest is not typically associated with COPD and emphysema. In fact, patients with COPD often have an increased anteroposterior diameter, known as a “barrel chest,” due to hyperinflation of the lungs. This change in chest shape is a compensatory mechanism to accommodate the increased lung volume and is a common physical finding in advanced COPD.
Choice B reason: Oxygen saturation level below 95% is a common finding in patients with COPD and emphysema. These conditions impair the lungs’ ability to oxygenate the blood effectively, leading to lower oxygen levels. Chronic hypoxemia is a hallmark of COPD, and monitoring oxygen saturation is crucial in managing these patients. Normal oxygen saturation levels typically range from 95% to 100%, so levels below 95% indicate a need for supplemental oxygen or other interventions.
Choice C reason: Petechiae on the chest are not a typical finding in COPD or emphysema. Petechiae are small, red or purple spots caused by bleeding into the skin and are usually associated with conditions affecting blood clotting or platelet function. They are not related to the respiratory pathology seen in COPD and emphysema.
Choice D reason: Respiratory alkalosis is not commonly associated with COPD and emphysema. These conditions are more likely to cause respiratory acidosis due to chronic retention of carbon dioxide (CO2). In COPD, the damaged alveoli and airways lead to impaired gas exchange, resulting in elevated CO2 levels and a decrease in blood pH. Respiratory alkalosis, characterized by low CO2 levels and increased pH, is more often seen in conditions causing hyperventilation, such as anxiety or acute asthma attacks.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
