A client presents with shock in the hospital, and has a history of a recent infection. What does the nurse suspect that this client is experiencing?
Cardiogenic shock
Neurogenic shock
Hypovolemic shock
Septic shock
The Correct Answer is D
A) Cardiogenic shock:
Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, often due to myocardial infarction (heart attack) or other conditions affecting the heart's function. The client's history of a recent infection does not align with the etiology of cardiogenic shock.
B) Neurogenic shock:
Neurogenic shock occurs due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, typically as a result of spinal cord injury or severe brain injury. It is characterized by widespread vasodilation and bradycardia. The client's history of a recent infection does not align with the etiology of neurogenic shock.
C) Hypovolemic shock:
Hypovolemic shock occurs due to a significant loss of blood volume, such as from trauma, hemorrhage, or dehydration. While infection can lead to fluid loss and dehydration in some cases, the client's history of a recent infection suggests a different etiology, specifically septic shock, which is driven by the systemic inflammatory response to infection.
D) Septic shock.
Septic shock is a type of distributive shock caused by a systemic response to infection. It occurs when an infection triggers a widespread inflammatory response, leading to vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, fluid loss from the bloodstream, and impaired tissue perfusion. The client's history of a recent infection suggests that the shock may be septic in nature.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A) Respirations rate:
Respiratory rate is an important vital sign to monitor in patients with shock, as respiratory distress can indicate inadequate oxygenation. However, blood pressure is generally considered more critical to assess initially in the context of shock because it directly reflects tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery.
B) Heart rate:
Heart rate is an important vital sign to monitor in patients with shock, as tachycardia (rapid heart rate) may indicate the body's compensatory response to maintain cardiac output and tissue perfusion. However, blood pressure is generally considered more critical to assess initially in the context of shock because it directly reflects tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery.
C) Blood pressure.
In shock, the body's vital organs are not receiving adequate blood flow and oxygen, leading to a life-threatening condition. While all vital signs are important to monitor in a patient experiencing shock, blood pressure is typically considered the most critical because it reflects the perfusion pressure—the force driving blood through the circulatory system to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues. A decrease in blood pressure can indicate inadequate tissue perfusion and impending organ failure. Therefore, timely assessment and monitoring of blood pressure are essential for identifying and managing shock effectively.
D) Temperature:
Temperature monitoring is important in assessing for signs of infection or other systemic issues that may contribute to shock, such as sepsis. However, blood pressure is generally considered more critical to assess initially in the context of shock because it directly reflects tissue perfusion and oxygen delivery.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
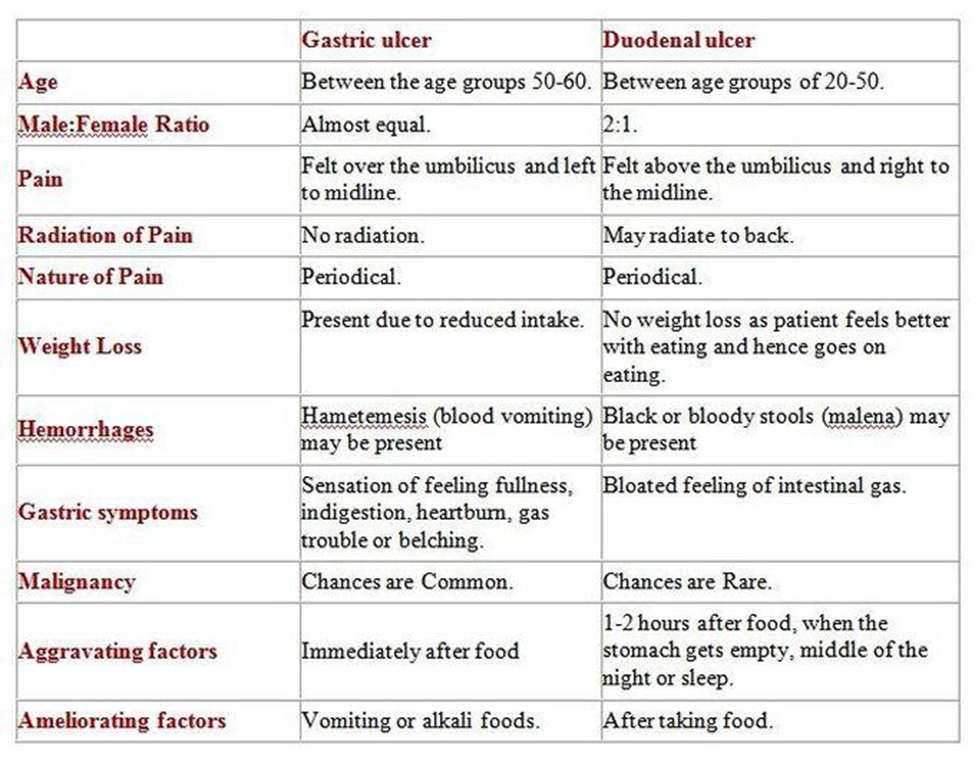
A) Nighttime pain:
Nighttime pain, also known as nocturnal pain, is a symptom associated with both duodenal and gastric ulcers. It occurs when the stomach or duodenal lining is empty and no food is present to buffer the effect of gastric acid. While nighttime pain can occur in both types of ulcers, it is not more specific to duodenal ulcers compared to gastric ulcers.
B) Anorexia:
Anorexia, or loss of appetite, can occur in both duodenal and gastric ulcers due to factors such as pain, discomfort, and inflammation. It is not a symptom that is more commonly associated with one type of ulcer over the other.
C) Postprandial pain (occurring after a meal).
Postprandial pain, which occurs after a meal, is more commonly associated with duodenal ulcers than gastric ulcers. This pain typically occurs 2 to 3 hours after eating, as it is often triggered by the release of gastric acid and duodenal contractions stimulated by food intake. Duodenal ulcers tend to cause this type of pain because they are located in the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, which is exposed to gastric acid and bile after a meal.
D) Nausea and vomiting:
Nausea and vomiting can occur in both duodenal and gastric ulcers, particularly if the ulcer is accompanied by complications such as obstruction or perforation. These symptoms are not more specific to duodenal ulcers compared to gastric ulcers.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
