A college student decides to go to a party the night before a major exam instead of studying. After receiving a low score on the exam, the student tells a fellow student, "I have to work too much and don't have time to study." which defense mechanism is the student using?
Rationalization
Denial
Regression
Suppresion
The Correct Answer is A
A. Rationalization:
Rationalization involves providing logical or rational explanations to justify one's behavior or actions, especially when faced with anxiety or guilt. In this scenario, the student is rationalizing their decision to go to the party instead of studying by attributing their low exam score to having to work too much. This rationalization serves as a way to lessen feelings of guilt or responsibility for not studying adequately. In this scenario, the most applicable defense mechanism is A. Rationalization, as the student is providing a logical explanation to justify their behavior and avoid taking full responsibility for their actions or decisions.
B. Denial:
Denial is a defense mechanism where an individual refuses to accept or acknowledge reality or facts that are too painful or distressing. If the student were in denial, they would outright reject or refuse to believe that their decision to attend the party had any impact on their exam performance, despite evidence suggesting otherwise.
C. Regression:
Regression involves reverting to earlier, more childlike behaviors or coping mechanisms in response to stress or anxiety. If the student were exhibiting regression, they might engage in behaviors characteristic of a less mature or responsible approach to handling academic challenges, such as avoiding responsibility or blaming external factors without taking personal accountability.
D. Suppression:
Suppression is a defense mechanism where an individual consciously pushes aside or ignores thoughts, feelings, or impulses that are distressing or unacceptable. If the student were suppressing their feelings of guilt or regret about attending the party instead of studying, they would be deliberately trying to ignore or push away these emotions rather than addressing them directly.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
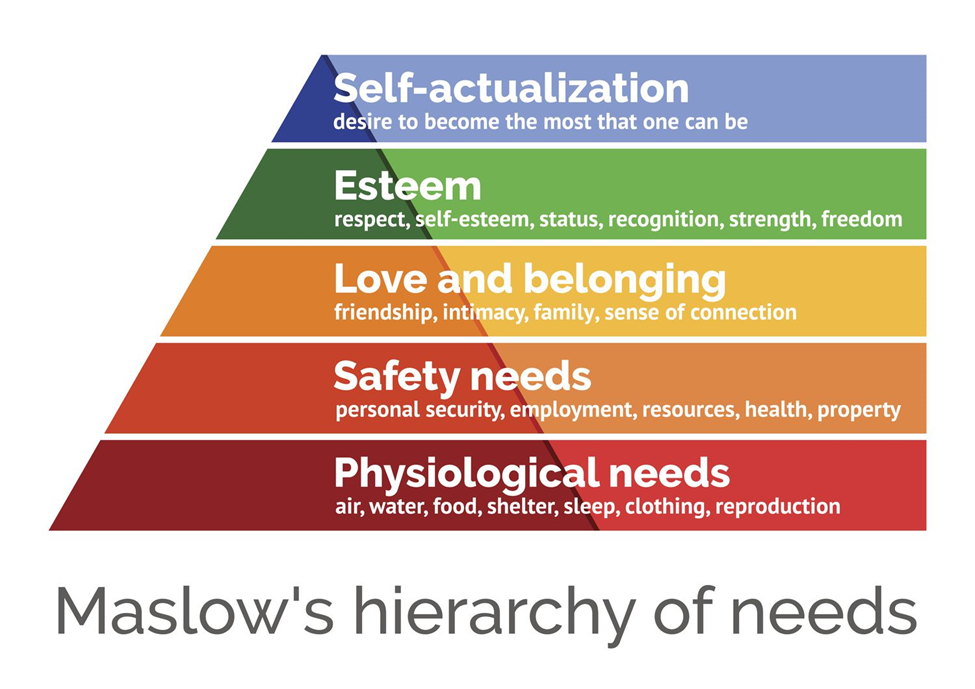
A. Needs to be taught about medication action and side effects: This problem relates to the client's need for information and understanding about their medication regimen, including its action and potential side effects. While education about medication is important, it may not be the top priority when considering Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
B. Refuses to eat or bathe: This problem directly impacts the client's physiological needs for food and hygiene, which are foundational in Maslow's hierarchy. Therefore, addressing the client's refusal to eat or bathe would take priority over other concerns.
C. Is reluctant to participate in unit social activities: This problem pertains to the client's social and emotional needs, which are higher-level needs in Maslow's hierarchy. While social activities can contribute to the client's well-being, they are not as critical as addressing immediate physiological needs.
D. Reports feelings of alienation from family: This problem relates to the client's sense of belongingness and love, which are also higher-level needs in Maslow's hierarchy. While addressing feelings of alienation is important for the client's overall well-being, it is not as urgent as addressing physiological needs.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Akathisia: Akathisia is a side effect of antipsychotic medications characterized by restlessness, agitation, and a strong urge to move. It is not typically associated with tongue protrusion, lip smacking, or rapid eye blinking.
B. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is a rare but serious reaction to antipsychotic medications, characterized by fever, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and autonomic dysfunction. It is not associated with the specific symptoms described in the scenario.
C. Dystonia: Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained or repetitive muscle contractions, leading to abnormal postures or repetitive movements. It can occur as a side effect of antipsychotic medications but typically presents differently from the symptoms described in the scenario.
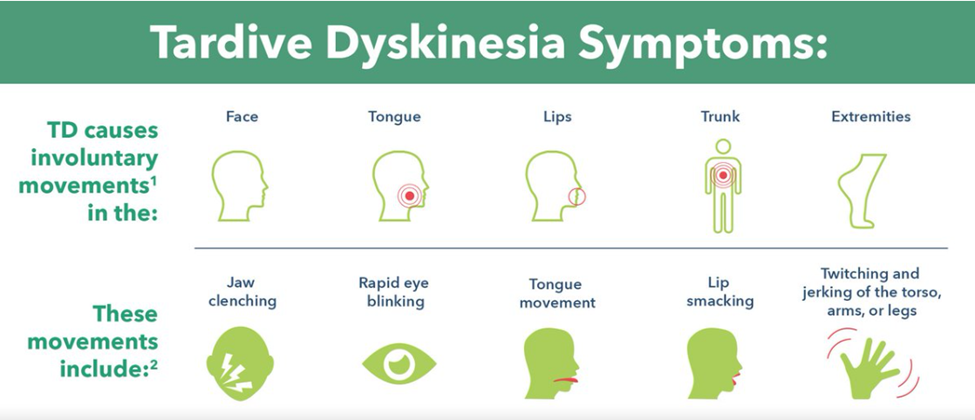
D. Tardive dyskinesia: Tardive dyskinesia is a chronic syndrome characterized by involuntary, repetitive movements of the face, tongue, and other body parts. It is associated with long-term use of conventional, first-generation antipsychotic medications. Symptoms can include tongue protrusion, lip smacking, rapid eye blinking, and other abnormal movements.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
