A male client weighing 175 pounds is to receive an intramuscular injection into his deltoid of two milliliters (2 mL) of a viscous fluid.
Which needle size should a nurse use?
1/2 inch, 25 gauge.
1 inch, 23 gauge.
1-1/2 inches, 21 gauge.
2 inches, 16 gauge.
The Correct Answer is B
This needle size is appropriate for an intramuscular injection into the deltoid of a 175-pound adult male with a viscous fluid.
The needle length should be long enough to reach the muscle through the subcutaneous tissue, and the needle gauge should be suitable for the viscosity of the fluid. A 23-gauge needle is a common choice for intramuscular injections.
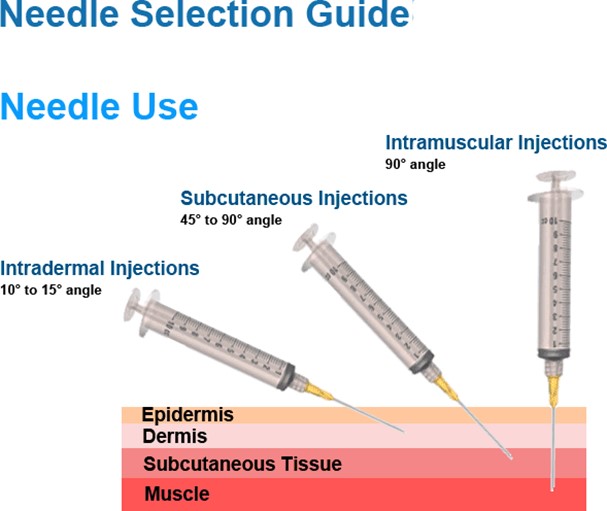
Choice A is wrong because a 1/2 inch needle is too short to reach the deltoid muscle in an adult male.
Choice C is wrong because a 1-1/2 inch needle is too long and may cause injury to the underlying nerves or blood vessels.
Choice D is wrong because a 16-gauge needle is too large and may cause excessive tissue trauma and pain.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
This is because spinach and salads contain a lot of vitamin K, which can make warfarin less effective at preventing blood clots.

Vitamin K helps the blood to clot, so eating foods high in vitamin K can counteract the effect of warfarin.
Choice A is wrong because wheat bread and butter do not contain a lot of vitamin K and do not affect warfarin.
Choice B is wrong because mangoes and tomatoes do not contain a lot of vitamin K and do not affect warfarin.
Choice D is wrong because aged cheeses and wine do not contain a lot of vitamin K and do not affect warfarin.
It is important to keep a stable diet while taking warfarin and avoid sudden changes in the amount of vitamin K intake. Foods that are high in vitamin K include green leafy vegetables, chickpeas, liver, egg yolks, avocado, and olive oil.
These foods should be limited but not eliminated from the diet. Do not drink cranberry or grapefruit juice while taking warfarin as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This is because the recovery position helps maintain the airway and prevent aspiration, and loosening the necktie prevents breathing restriction.
The other choices are wrong because:
Choice A is wrong because placing a stick or any object in the person’s mouth can cause injury to the teeth, gums, tongue or jaw and obstruct the airway. The person cannot swallow or bite their tongue during a seizure.
Choice B is wrong because recording the time of the seizure is not the first priority. The first priority is to ensure the safety and comfort of the person.
Choice C is wrong because restraining the limbs can cause injury or fracture, increase agitation and prolong the seizure. The nurse should protect the person from injury by moving furniture away and padding the head.
Normal ranges for seizure duration are usually less than 5 minutes for generalized tonic-clonic seizures and less than 15 seconds for absence seizures. If the seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes, or if the person has repeated seizures without regaining consciousness, it is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
