A male inpatient client who is experiencing depression has no interest in eating. He skips meals frequently and has been losing weight. What is the best nursing action in this situation?
Leave food with the client at mealtime and offer snacks frequently
Give the client information on the benefits of good nutrition
Ask the client to "Please eat one meal for me."
Remove client privileges every time the client doesn't eat
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale: this is correct since it provides the patient with an opportunity to eat his meals freely whenever they are ready to eat without feeling pressured or threatened.
Choice B rationale: the patient already knows about the benefits of good nutrition but still lacks the motivation to eat owed of his depression hence this may not be very helpful in this situation.
Choice C rationale: this may make the patient feel manipulated and guilty for not eating hence may not be helpful in addressing the underlying situation.
Choice D rationale: this may worsen the patient’s depression and lower their self-esteem since they will receive punishment for their condition rather than being offered the necessary help.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale: transitioning clients out of the facility as quickly as possible is not a goal of a therapeutic environment but instead the therapeutic environment focuses on providing maximum support and an appropriate level of care to clients until they are ready to transition to a less restrictive setup.
Choice B rationale: this is essential for client safety and the safety of individuals surrounding them while promoting effective crisis management.
Choice C rationale: this is appropriate since it enhances the client’s self-worth and confidence which is crucial in boosting their self-esteem and motivation.
Choice D rationale: this is correct since effective adaptive skills enable clients to cope with their challenges and improve their functioning.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Akathisia refers to restlessness and agitation and is a common side effect of antipsychotic medications. This condition can be reversed by reducing the dose of antipsychotic medication taken by the client.
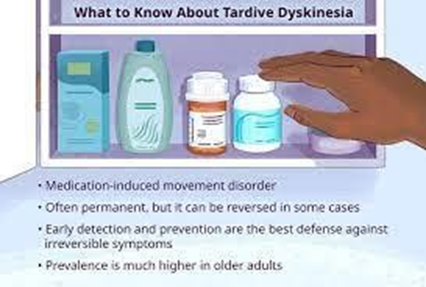
Choice B rationale: Tardive dyskinesia refers to the involuntary movement of body parts such as the limbs, face, jaw, and tongue and is a common side effect of long-term use of first-generation antipsychotic medications which work by blocking dopamine receptors. This condition is irreversible, especially when not detected early.
Choice C rationale: Dystonia which refers to muscle spasms affecting the jaw, eyes, and limbs can be reversed by the use of anticholinergic medications or botulin toxin.
Choice D: Akinesia refers to the absence of movement and can be managed by adjusting the dosage of the antipsychotic medications being taken by the patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
