A nurse formulates the problem of ineffective airway clearance for a client who has pneumonia. Which assessment data best supports this problem?
Respiratory rate of 24/min.
Weak, nonproductive cough.
Pulse oximetry (SpO2) of 90%.
Shortness of breath with activity.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason:
A respiratory rate of 24/min is slightly elevated, which can be expected in a client with pneumonia due to the body's attempt to increase oxygen intake and carbon dioxide elimination. However, this rate does not directly indicate ineffective airway clearance.
Choice B reason:
A weak, nonproductive cough is a key indicator of ineffective airway clearance. In pneumonia, the presence of secretions in the airways is common, and an effective cough is necessary to clear these secretions. A weak cough that does not produce sputum suggests that the client is unable to clear their airways effectively, which can lead to impaired gas exchange and worsening of symptoms.
Choice C reason:
Pulse oximetry (SpO2) of 90% indicates that the client's oxygen saturation is below the normal range, which is typically between 95-100% for healthy individuals. While this finding is concerning and warrants intervention, it is a result of ineffective airway clearance rather than a direct indicator of it.
Choice D reason:
Shortness of breath with activity is common in clients with pneumonia and can result from various factors, including impaired gas exchange, decreased lung compliance, and increased work of breathing. While it may be associated with ineffective airway clearance, it is not as specific as a weak, nonproductive cough for indicating this particular problem.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason
While hypertension can contribute to the development of PAD, it does not directly cause fats to deposit in the arteries. Hypertension can damage the arterial walls, making them more susceptible to atherosclerosis, but it is not the primary mechanism of PAD development.
Choice B Reason
Excess fats in the diet can contribute to atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of plaques in the arterial walls. However, the fats do not simply get stored; they combine with other substances, including calcium and inflammatory cells, to form plaques that can restrict blood flow.
Choice C Reason
This statement is the most accurate. PAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaques formed by fats, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. These plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the extremities. The process can be exacerbated by factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Arterial spasms can occur, but they are not the typical cause of chronic PAD. Spasms are more often associated with conditions like Raynaud's phenomenon or can be a response to stress or cold temperatures. PAD is usually a result of progressive atherosclerosis rather than intermittent spasms.
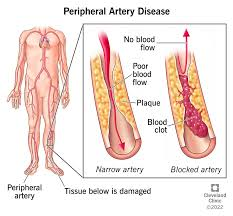
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason
A hemoglobin level of 7.1 g/dL is significantly lower than the normal range, which is typically around 13.8 to 17.2 g/dL for men and 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL for women. This finding is concerning as it indicates severe anemia, which can be a life-threatening condition requiring immediate intervention. Anemia can lead to tissue hypoxia as the blood's capacity to carry oxygen is diminished. In the context of peripheral arterial disease, where blood flow is already compromised, anemia can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of ischemic events.
Choice B Reason
Ecchymosis, or bruising, on the client's upper extremities could be a result of the antiplatelet effects of aspirin, which inhibits platelet aggregation and prolongs bleeding time. While this is a concern and warrants monitoring, it is not as immediately life-threatening as severe anemia. However, it does indicate a risk of bleeding complications, which should be addressed by the healthcare provider.
Choice C Reason
A platelet count of 148,000/uL is at the lower end of the normal range, which is approximately 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. This finding should be monitored, especially in the context of aspirin therapy, which can affect platelet function. However, it is not as critical as the low hemoglobin level.
Choice D Reason
Gastrointestinal discomfort is a common side effect of aspirin due to its irritation of the stomach lining. While this symptom can be uncomfortable and may lead to more serious gastrointestinal issues such as ulcers or bleeding, it is typically not as urgent as severe anemia. The client should be evaluated for potential gastrointestinal complications of aspirin therapy.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
