A nurse in an emergency department is assessing a 2-year-old child who has a high fever, severe dyspnea, and is drooling. Which of the following actions is the nurse's priority?
Obtain blood culture specimens.
Administer an antipyretic.
Prepare for nasotracheal intubation.
Insert an IV catheter.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: Obtaining blood culture specimens is important to identify the causative organism and guide antibiotic therapy, but it is not the priority action for a child who is in respiratory distress. The nurse should first secure the airway and stabilize the child's condition.
Choice B reason: Administering an antipyretic may help lower the fever and reduce discomfort, but it does not address the cause of the dyspnea and drooling, which may indicate epiglottitis. This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate airway management.
Choice C reason: Preparing for nasotracheal intubation is the priority action for a child who has signs of epiglottitis, as it can prevent airway obstruction and respiratory failure. The nurse should have the equipment and personnel ready for intubation and avoid any stimulation or manipulation of the throat that can trigger laryngeal spasm.
Choice D reason: Inserting an IV catheter is necessary to administer fluids and medications, but it is not the first priority for a child who is in respiratory distress. The nurse should focus on the airway before the circulation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This statement is normal, as an infant who is 2 months old should be alert and responsive to stimuli. The nurse should assess the infant's level of consciousness and responsiveness using the AVPU scale (alert, voice, pain, unresponsive).
Choice B reason: This statement is normal, as an infant who is 2 months old should have warm and dry skin and a tone that is appropriate for their ethnicity. The nurse should assess the infant's skin color, temperature, moisture, and turgor.
Choice C reason: This statement is abnormal, as an infant who is 2 months old should not have a distended abdomen or a visible mass in the right upper quadrant. This could indicate a serious condition such as a liver tumor, a bowel obstruction, or a hernia. The nurse should report this finding to the provider and monitor the infant for signs of pain, vomiting, or jaundice.
Choice D reason: This statement is normal, as an infant who is 2 months old should have full range of motion in their extremities and no clicks noted. The nurse should assess the infant's muscle strength, tone, and symmetry, and check for any signs of hip dysplasia, such as a positive Barlow or Ortolani test.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
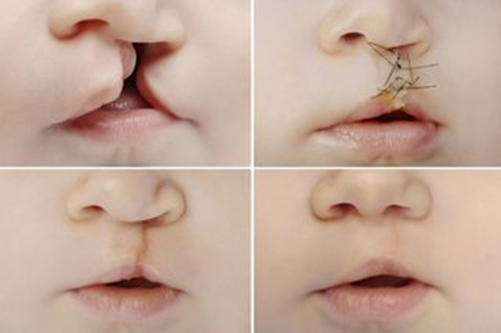
Choice A reason: Applying and releasing elbow restraints every hour prevents the infant from touching or injuring the surgical site, while allowing some movement and circulation. This is a standard nursing intervention for infants who have undergone cleft palate repair.
Choice B reason: Keeping the infant supine is not recommended, as it increases the risk of aspiration and bleeding. The infant should be placed in a side-lying or upright position to facilitate drainage and prevent pressure on the suture line.
Choice C reason: Feeding the infant with a spoon for 48 hours is not necessary, as it may cause discomfort and trauma to the palate. The infant can be fed with a special nipple or a syringe with a rubber tip that delivers small amounts of formula or breast milk to the side of the mouth.
Choice D reason: Suctioning the mouth with an oral suction tube is contraindicated, as it may damage the palate and cause bleeding or infection. The nurse should use a bulb syringe to gently suction the nose and mouth if needed.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
