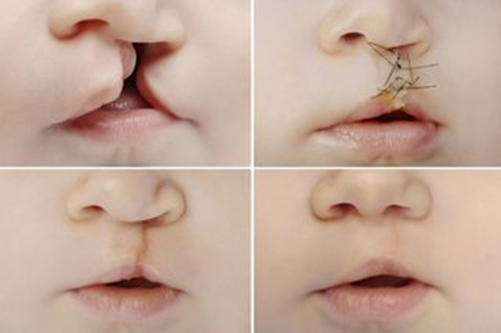
A nurse is planning care for a 10-month-old infant who is 8 hours postoperative following cleft palate repair. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the infant's plan of care?
Apply and release elbow restraints every hour
Keep the infant supine
Feed the infant with a spoon for 48 hours
Suction the mouth with an oral suction tube
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: Applying and releasing elbow restraints every hour prevents the infant from touching or injuring the surgical site, while allowing some movement and circulation. This is a standard nursing intervention for infants who have undergone cleft palate repair.
Choice B reason: Keeping the infant supine is not recommended, as it increases the risk of aspiration and bleeding. The infant should be placed in a side-lying or upright position to facilitate drainage and prevent pressure on the suture line.
Choice C reason: Feeding the infant with a spoon for 48 hours is not necessary, as it may cause discomfort and trauma to the palate. The infant can be fed with a special nipple or a syringe with a rubber tip that delivers small amounts of formula or breast milk to the side of the mouth.
Choice D reason: Suctioning the mouth with an oral suction tube is contraindicated, as it may damage the palate and cause bleeding or infection. The nurse should use a bulb syringe to gently suction the nose and mouth if needed.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is the best option to prevent the toddler from touching or injuring the surgical site. The nurse should apply soft padded restraints and check the circulation and skin integrity of the wrists frequently.
Choice B reason: Offering fluids through a straw is not recommended for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause suction and pressure in the mouth that can disrupt the sutures. The nurse should offer fluids with a cup or a spoon.
Choice C reason: Implementing a soft diet is not appropriate for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause irritation and infection in the mouth. The nurse should provide clear liquids for the first 24 hr and then advance to full liquids as tolerated.
Choice D reason: Administering opioids for pain is not the first choice for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause respiratory depression and constipation. The nurse should use nonpharmacological methods such as distraction, comfort, and reassurance first, and then administer acetaminophen or ibuprofen as prescribed.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Half-strength infant formula is not a clear liquid and should not be given to an infant with intussusception. Infant formula contains proteins, fats, and carbohydrates that can increase the risk of bowel obstruction, infection, and perforation.
Choice B reason: Half-strength orange juice is not a clear liquid and should not be given to an infant with intussusception. Orange juice contains fructose, citric acid, and potassium that can irritate the bowel, cause osmotic diarrhea, and worsen dehydration.
Choice C reason: Sterile water is a clear liquid, but it is not the best choice for an infant with intussusception. Sterile water does not contain any electrolytes or glucose and can dilute the blood sodium level, leading to hyponatremia and seizures.
Choice D reason: Oral electrolyte solution is the best fluid for an infant with intussusception, as it contains the optimal balance of electrolytes and glucose to prevent dehydration and restore fluid balance. Oral electrolyte solution is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) for the management of dehydration in children.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
