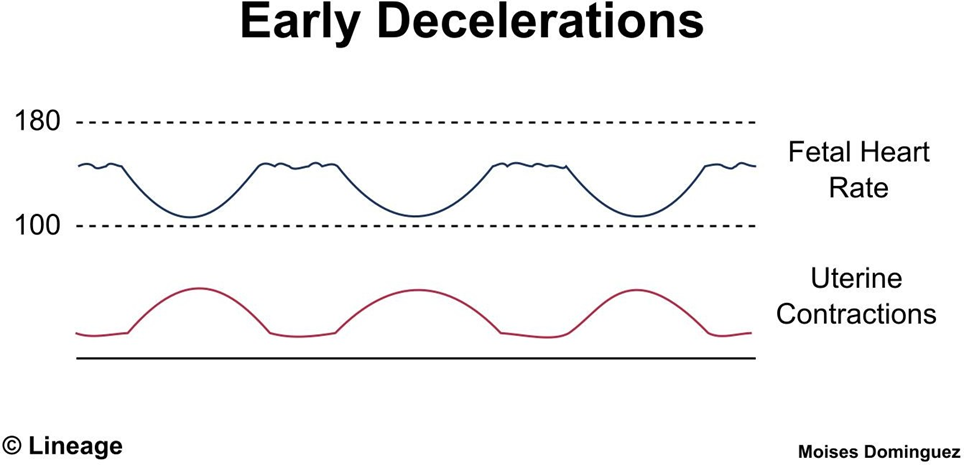
A nurse is caring for a client who is in labor and receiving electronic fetal monitoring. The nurse is reviewing the monitor tracing and notes early decelerations. Which of the following should the nurse expect?
Head compression
Fetal hypoxia
Abruptio placentae
Postmaturity
The Correct Answer is A
A.
A. Early decelerations are typically benign and occur in response to head compression during contractions. They mirror the uterine contractions and are not associated with fetal distress.
B. Fetal hypoxia is associated with variable or late decelerations, not early decelerations.
C. Abruptio placentae is a medical emergency characterized by premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall, which can lead to late decelerations due to fetal hypoxia.
D. Postmaturity is a term used to describe a pregnancy that extends beyond 42 weeks gestation and is not directly related to fetal heart rate patterns during labor.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Encourage the client to ambulate in the hallway 1 hr before bedtime - While light exercise during the day can promote better sleep, exercising close to bedtime can actually disrupt sleep.
B. Tell the client to avoid drinking fluids 1 hr before bedtime - While limiting fluids close to bedtime can reduce nighttime awakenings to urinate, it may not directly address difficulty falling asleep.
C. Schedule routine care tasks during hours when the client is awake - This action ensures that the client can maximize restful sleep during the night by minimizing disruptions from care
activities.
D. Advise the client to leave the television in the room on when trying to fall asleep - Screen
time before bed can interfere with falling asleep due to the stimulating effect of light and content.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. A flexible activity schedule may increase overstimulation; structured activities with set limits are more appropriate for clients in acute mania.
B. Clients experiencing acute mania often have increased energy expenditure and may neglect meals; providing high-calorie nutritional supplements helps prevent weight loss and maintains adequate nutrition.
C. Eating alone may increase the risk of inadequate intake due to distraction or hyperactivity; supervised or structured meal times are safer.
D. Allowing unrestricted choice of clothing may lead to inappropriate or disorganized attire; guidance is needed to maintain safety and appropriate appearance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
