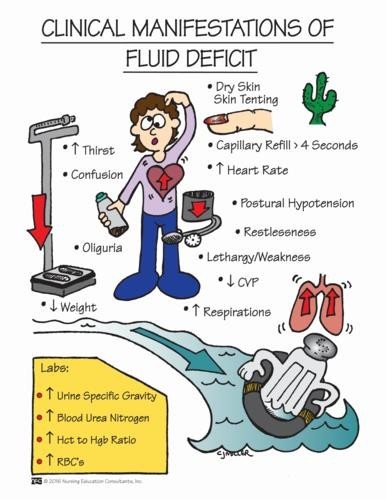
A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative and is experiencing nausea and vomiting. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as indications that the client has fluid volume deficit. (Select all that apply.)
Full bounding pulse
Cool extremities
Moist crackles in the lungs
Orthostatic hypotension
Flat neck veins
Correct Answer : B,D,E
A: A full bounding pulse is a sign of increased fluid volume or fluid overload, not fluid volume deficit.
B: Cool extremities can be an indication of decreased peripheral perfusion, which may occur in fluid volume deficit.
C: Moist crackles in the lungs are an indication of fluid volume excess or pulmonary congestion, not fluid volume deficit.
D: Orthostatic hypotension, which is a drop in blood pressure when changing from lying to standing, can be a sign of fluid volume deficit due to inadequate blood volume.
E: Flat neck veins are an indication of decreased venous return and can occur in fluid volume deficit.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A: Incorrect. Leaning on the crutches for support while standing still is not the correct way to use crutches. It can lead to discomfort and instability.
B: Correct. The client should advance the unaffected leg first while climbing stairs when using crutches. This technique ensures better stability and safety during stair ascent.
C: Incorrect. Standing 5 cm (2 in) from the front of a chair before sitting is not directly related to the use of crutches.
D: Incorrect. Bearing weight on the axilla while standing in the tripod position is not the correct way to use crutches. The tripod position is used for resting, not weight bearing.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Body regulation of heat and cold increases with age: This statement is incorrect. Age-related changes can lead to decreased efficiency in regulating body temperature, making older adults more susceptible to extreme temperatures.
B. Circulation becomes less efficient with age: Correct. With age, blood vessels can lose some of their elasticity, leading to decreased efficiency in circulating blood throughout the body. This can impact the ability to respond to temperature changes effectively.
C. Increased metabolic rate occurs with age, and increasing body temperature: This statement is incorrect. In general, metabolic rate tends to decrease with age, which can contribute to decreased heat production in older adults.
D. Sweat gland activity is increased with age: This statement is incorrect. Sweat gland activity tends to decrease with age, leading to decreased sweating and potential challenges in cooling the body during hot conditions.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
