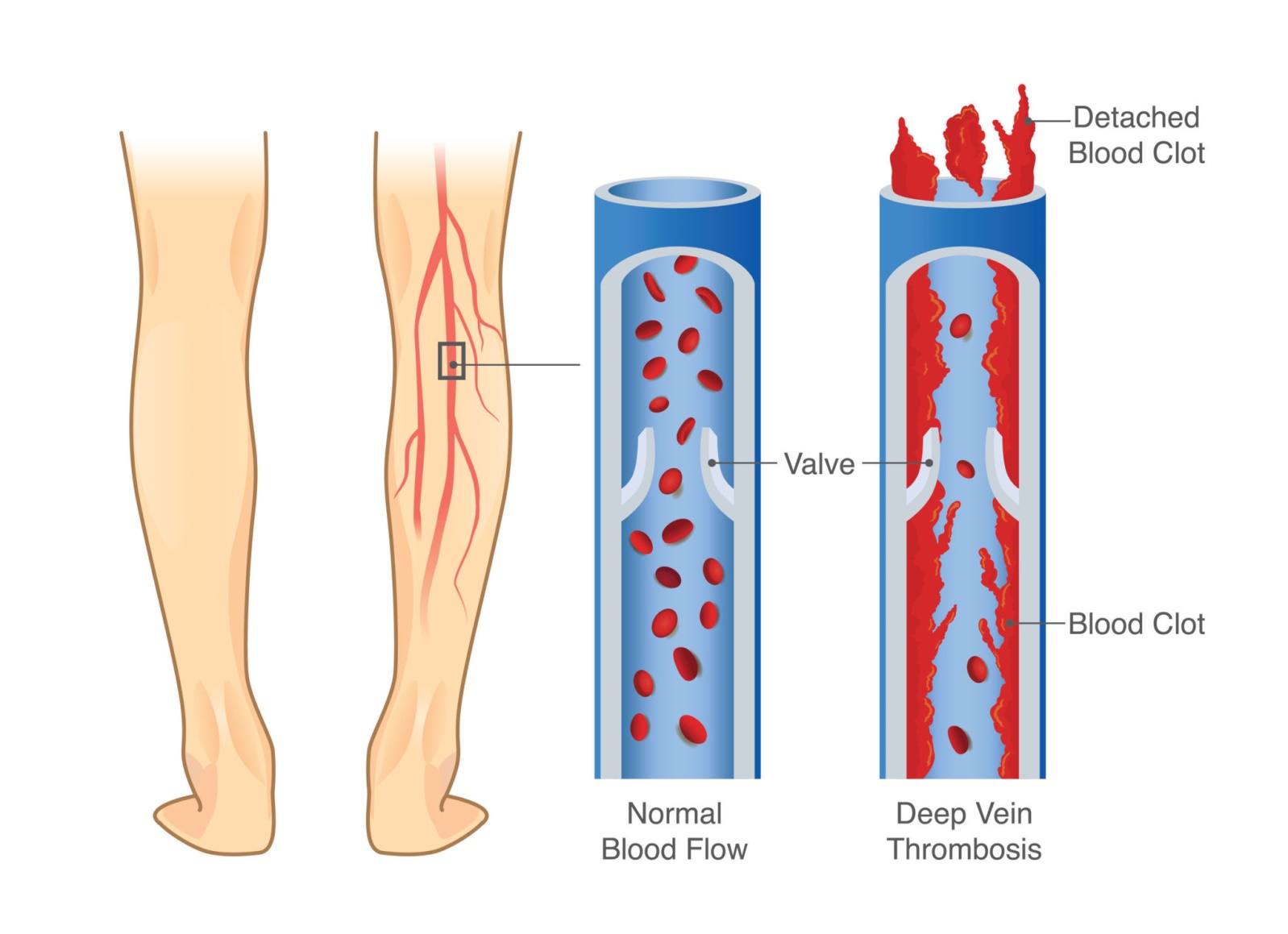
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving warfarin therapy to prevent deep vein thrombosis. Which of the following medications should the nurse have available in the event of an overdose?
Epinephrine
Vitamin K
Atropine
Protamine
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason : Epinephrine is an adrenergic agonist primarily used in the management of cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, and severe asthma attacks. It is not used to reverse the effects of warfarin overdose. Warfarin acts as an anticoagulant by inhibiting vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, and epinephrine has no role in this mechanism.
Choice B reason : Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin toxicity. Warfarin works by inhibiting the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X. In the event of an overdose, vitamin K is administered to reverse the anticoagulant effects of warfarin and restore the clotting factor levels to normal. The administration can be oral or intravenous, depending on the severity of the overdose and the urgency of the situation.
Choice C reason : Atropine is an anticholinergic drug used to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate) and as an antidote for organophosphate poisoning. It does not have a role in reversing warfarin overdose as it does not affect the clotting cascade or vitamin K metabolism.
Choice D reason : Protamine is used to reverse the effects of heparin, another anticoagulant, but not warfarin. Protamine sulfate binds to heparin, forming a stable complex and neutralizing its anticoagulant effects. Since warfarin's mechanism of action is different from heparin's, protamine is not effective in reversing warfarin toxicity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason : A fixed volume deficit, or hypovolemia, is not a direct finding associated with bradycardia. Bradycardia refers to a slower than normal heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute in adults⁸. Hypovolemia can cause various compensatory mechanisms to activate, including an increase in heart rate to maintain cardiac output, which is the opposite of bradycardia. Therefore, a fixed volume deficit is not a typical finding in bradycardia unless it is part of a broader clinical picture⁹.
Choice B reason : Anxiety is a condition that can sometimes lead to an increased heart rate, known as tachycardia, rather than a decreased heart rate as seen in bradycardia. While anxiety can coexist with bradycardia, especially if the patient is anxious about their health, it is not a direct symptom or finding of bradycardia itself⁹.
Choice C reason : Lightheadedness is a common symptom of bradycardia. When the heart rate is too slow, it may lead to inadequate cerebral perfusion, which can cause a feeling of lightheadedness or dizziness. This symptom can be particularly evident when the patient changes positions, such as standing up quickly, which can exacerbate the effects of reduced cardiac output on cerebral blood flow⁸⁹.
Choice D reason : An elevated temperature is not typically associated with bradycardia. Fever can actually lead to an increased heart rate as the body attempts to manage the higher metabolic demands associated with a raised temperature. Bradycardia in the presence of fever might indicate a more complex clinical scenario, such as myocarditis or central nervous system infections, but it is not a direct finding of bradycardia⁹.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason : A low sodium diet is often prescribed for patients with heart conditions to help manage blood pressure and fluid retention. It is not typically something that would need to be questioned in the context of recent pacemaker surgery.
Choice B reason : Checking serum cardiac enzyme levels is a common practice after heart surgery to monitor for any signs of damage to the heart muscle. This would not typically be questioned unless there were specific contraindications for the patient.
Choice C reason : An MRI of the chest should be questioned because MRI machines use strong magnetic fields that can interfere with the functioning of a pacemaker. Unless the pacemaker is specifically labeled as MRI-safe, this type of imaging could be dangerous for the patient.
Choice D reason : Physical therapy is a standard part of recovery after many types of surgery, including pacemaker insertion, to help the patient regain strength and mobility. It would not typically be questioned unless the patient had specific restrictions.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
