A nurse is discussing with a client who knows someone taking metoprolol for blood pressure management. The client inquires whether metoprolol would be suitable for her as well. Based on the client's medical record, which of the following should the nurse recognize as a contraindication to metoprolol?
Recently treated bilateral pneumonia
A concurrent prescription for tadalafil
Diet-controlled diabetes mellitus Type 2
A history of sinus bradycardia
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason : Recently treated bilateral pneumonia is not a contraindication to metoprolol. Metoprolol is a beta-blocker used primarily for the management of hypertension and is not affected by a history of pneumonia.
Choice B reason : While tadalafil is known to interact with medications that lower blood pressure, it is not a direct contraindication to metoprolol. However, caution is advised when they are used concurrently due to the potential for additive blood pressure-lowering effects.
Choice C reason : Diabetes mellitus Type 2, especially when diet-controlled, is not a contraindication to metoprolol. Beta-blockers like metoprolol can mask hypoglycemic symptoms, so patients with diabetes should be monitored closely, but it does not preclude the use of the medication.
Choice D reason : A history of sinus bradycardia is a contraindication to metoprolol. Metoprolol can exacerbate bradycardia, leading to hemodynamic instability and is therefore contraindicated in patients with a history of significant bradycardia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: A barrel chest is typically not associated with mitral valve stenosis. It is more commonly seen in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to hyperinflation of the lungs. Mitral valve stenosis affects the heart and not the lung structure.
Choice B reason: Clubbing of the fingers is a sign that can be associated with chronic hypoxia and certain types of congenital heart disease. While it can be seen in some heart conditions, it is not a specific finding for mitral valve stenosis.
Choice C reason: A heart murmur, specifically a diastolic murmur, is a classic finding in mitral valve stenosis. As the stenotic mitral valve obstructs blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, a pressure gradient is created, which produces a murmur that can be heard upon auscultation.
Choice D reason: Bradycardia, or a slower than normal heart rate, is not a direct finding associated with mitral valve stenosis. Mitral valve stenosis may lead to arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation due to atrial enlargement, but bradycardia is not typically induced by this condition.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason : The statement that warfarin dissolves clots in the bloodstream is incorrect. Warfarin does not dissolve existing clots. Instead, it is an anticoagulant that works by decreasing the production of certain clotting factors in the blood, which helps prevent the formation of new clots.
Choice B reason : This statement is not accurate regarding the action of warfarin. Warfarin does not affect the electrical impulses of the heart. Medications that slow the response of the ventricles to fast atrial impulses are typically antiarrhythmic drugs, not anticoagulants like warfarin.
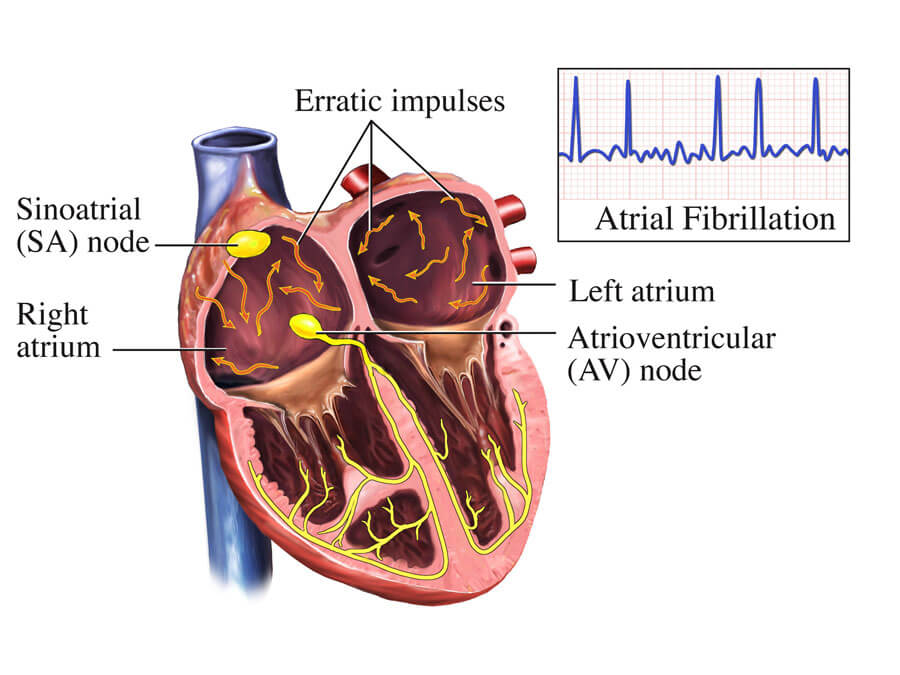
Choice C reason : This is the correct statement. Warfarin is prescribed for clients with atrial fibrillation to reduce the risk of stroke. Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of forming blood clots in the heart, which can then travel to the brain, causing a stroke. Warfarin's anticoagulant effect helps to prevent these clots from forming.
Choice D reason : Warfarin does not help maintain a normal heart rhythm. It is not an antiarrhythmic drug but an anticoagulant. The purpose of warfarin in atrial fibrillation is to prevent stroke by reducing the risk of clot formation, not to correct the heart rhythm.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
