A nurse is preparing to develop a plan of care for a school-aged child who has been diagnosed with sickle cell anemia. Which of the following findings should the nurse include in the plan of care?
The child has a normal potassium level.
The child has a low hemoglobin level.
The child has a high platelet level.
The child has a low blood glucose level.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: The child has a normal potassium level, as it is within the reference range of 3.5 to 5 mEq/L. Potassium is an electrolyte that helps regulate the fluid balance, nerve impulses, and muscle contractions in the body.
Choice B reason: The child has a low hemoglobin level, as it is below the reference range of 10 to 15.5 g/dL. Hemoglobin is a protein in the red blood cells that carries oxygen to the tissues. Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that causes the red blood cells to have an abnormal shape and become rigid, sticky, and prone to clumping. This can lead to hemolysis, anemia, and reduced oxygen delivery.
Choice C reason: The child has a normal platelet level, as it is within the reference range of 150,000 to 450,000 mm^3^. Platelets are blood cells that help with clotting and prevent bleeding. Sickle cell anemia can cause thrombocytopenia, a low platelet count, due to increased destruction or sequestration of platelets in the spleen.
Choice D reason: The child has a normal blood glucose level, as it is within the reference range of 70 to 110 mg/dL. Blood glucose is the main source of energy for the cells in the body. Sickle cell anemia can cause hypoglycemia, a low blood glucose level, due to impaired glucose metabolism, increased glucose utilization, or decreased glucose production.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
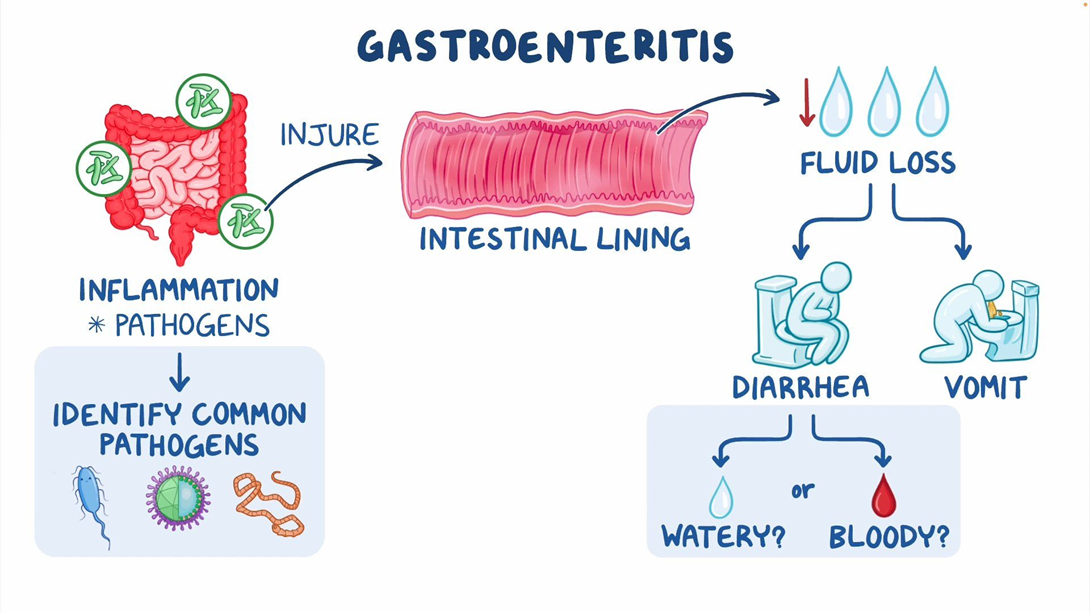
Choice A reason: Oral rehydration solution (ORS) is the best fluid for a child with acute gastroenteritis, as it contains the optimal balance of electrolytes and glucose to prevent dehydration and restore fluid balance. ORS is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) for the management of diarrhea in children.
Choice B reason: Water is not a good fluid for a child with acute gastroenteritis, as it does not contain any electrolytes or glucose and can dilute the blood sodium level, leading to hyponatremia. Water can also increase the osmotic load in the intestines and worsen diarrhea.
Choice C reason: Broth is not a good fluid for a child with acute gastroenteritis, as it is high in sodium and can cause hypernatremia and dehydration. Broth can also irritate the intestinal mucosa and increase diarrhea.
Choice D reason: Diluted apple juice is not a good fluid for a child with acute gastroenteritis, as it is high in fructose and can cause osmotic diarrhea. Apple juice can also lower the blood pH and cause metabolic acidosis.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is the best option to prevent the toddler from touching or injuring the surgical site. The nurse should apply soft padded restraints and check the circulation and skin integrity of the wrists frequently.
Choice B reason: Offering fluids through a straw is not recommended for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause suction and pressure in the mouth that can disrupt the sutures. The nurse should offer fluids with a cup or a spoon.
Choice C reason: Implementing a soft diet is not appropriate for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause irritation and infection in the mouth. The nurse should provide clear liquids for the first 24 hr and then advance to full liquids as tolerated.
Choice D reason: Administering opioids for pain is not the first choice for a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair, as it can cause respiratory depression and constipation. The nurse should use nonpharmacological methods such as distraction, comfort, and reassurance first, and then administer acetaminophen or ibuprofen as prescribed.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
