A nurse is preparing to administer acetaminophen 10 mg/kg/dose to a child who weighs 28 lb. The amount available is acetaminophen 120 mg/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer?
(Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trailing zero.)
The Correct Answer is ["5.3."]
To calculate the dose of acetaminophen for a child, the nurse needs to convert the child's weight from pounds to kilograms and then multiply it by the prescribed dose per kilogram. The formula is:
Weight in kg = Weight in lb / 2.2
Dose in mg = Weight in kg x Dose per kg
Dose in mL = Dose in mg / Concentration in mg/mL
Using the given information, the nurse can plug in the values and solve for the dose in mL:
Weight in kg = 28 / 2.2 = 12.73
Dose in mg = 12.73 x 10 = 127.3
Dose in mL = 127.3 / 120 x 5 = 5.3
Therefore, the nurse should administer 5.3 mL of acetaminophen to the child.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse should expect to find irritability in an infant who is dehydrated. Dehydration in infants can lead to changes in behavior and irritability due to the imbalance in fluid and electrolytes. Other common signs of dehydration in infants may include:
Poor skin turgor (skin tenting)
Sunken fontanelles (soft spots on the baby's head)
Dry mucous membranes (dry mouth and tongue)
Decreased urine output or concentrated urine
Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
Increased respiratory rate
Sunken eyes
Decreased tears when crying
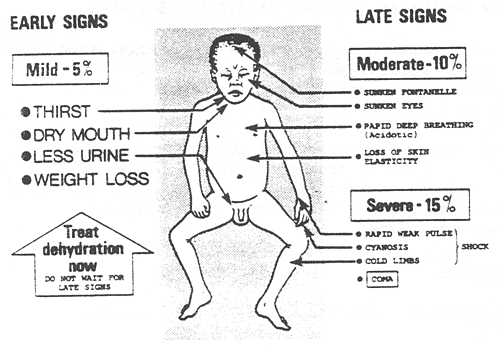
B. Tetany is a condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and is more commonly associated with hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) rather than dehydration.
C. A slow, bounding pulse is not typically associated with dehydration. Dehydration often leads to a rapid heart rate (tachycardia) as the body attempts to compensate for the loss of fluid.
D. Decreased temperature is not a typical finding in dehydration. Dehydration can lead to fever in some cases due to an underlying infection, but it does not cause a decrease in body temperature on its own.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Children with sickle cell anemia are prone to dehydration, which can worsen the sickling of red blood cells and trigger a sickle cell crisis. Therefore, it is essential to maintain good hydration to prevent crises. Offering fluids to the child multiple times every day helps to keep them well-hydrated.
Option B is not necessary unless there is a specific medical reason to restrict outdoor play. Regular play is essential for a child's physical and emotional development.
Option C is important, but it is not specific to discharge teaching after an acute crisis episode. Monitoring the child's temperature daily is essential to detect early signs of infection, which can be a trigger for sickle cell crises.
Option D is not recommended because applying cold compresses can cause vasoconstriction and may worsen pain in children with sickle cell anemia. Heat therapy, warm compresses, or a warm bath are more appropriate for pain relief during a sickle cell crisis. However, pain management should be discussed with the healthcare provider to ensure the most appropriate approach for the individual child's needs.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
