A nurse is preparing to administer diphenhydramine to a client who is to receive a blood transfusion. The nurse should explain that the purpose diphenhydramine is to prevent which of the following manifestations of a transfusion reaction?
Low-back pain
Fever
Dyspnea
Urticaria
The Correct Answer is D
A) Low-back pain:
Low-back pain is not typically associated with transfusion reactions. While certain complications of blood transfusions, such as transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) or hemolytic reactions, can cause back pain, diphenhydramine is not specifically administered to prevent this manifestation.
B) Fever:
Fever can be a manifestation of various transfusion reactions, including febrile non-hemolytic reactions or bacterial contamination of blood products. However, diphenhydramine is not typically administered to prevent fever associated with transfusion reactions. Instead, measures such as leukoreduction of blood products or premedication with acetaminophen may be used to reduce the risk of febrile reactions.
C) Dyspnea:
Dyspnea, or difficulty breathing, can occur in severe transfusion reactions such as transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) or anaphylaxis. While diphenhydramine may be part of the treatment for anaphylaxis, it is not specifically administered to prevent dyspnea associated with transfusion reactions.
D) Urticaria.
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a common manifestation of an allergic transfusion reaction. Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine medication that can help prevent or alleviate allergic reactions, including urticaria, by blocking the action of histamine, a substance released during allergic reactions. Administering diphenhydramine before a blood transfusion is a preventive measure to reduce the risk of allergic transfusion reactions, including urticaria.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
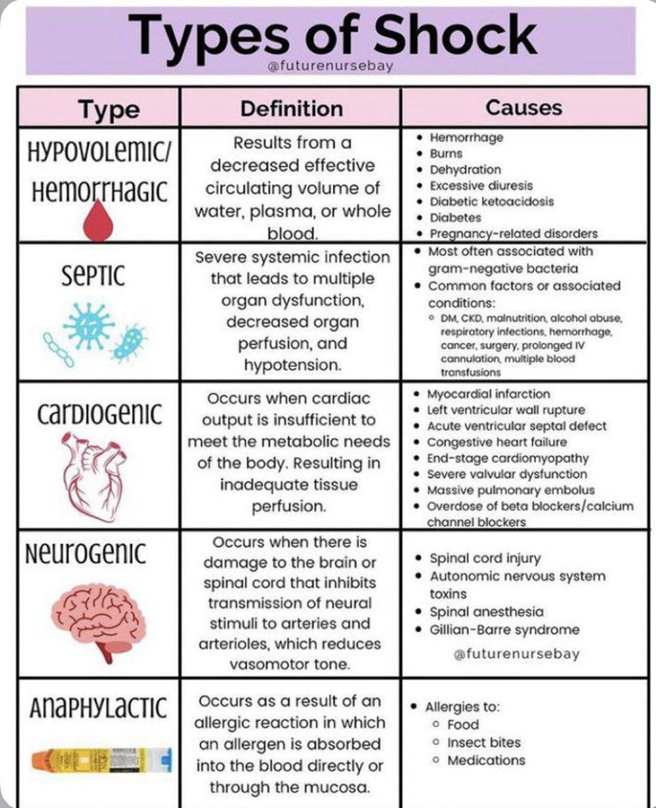
A) Cardiogenic shock:
Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, often due to myocardial infarction (heart attack) or other conditions affecting the heart's function. The client's history of a recent infection does not align with the etiology of cardiogenic shock.
B) Neurogenic shock:
Neurogenic shock occurs due to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, typically as a result of spinal cord injury or severe brain injury. It is characterized by widespread vasodilation and bradycardia. The client's history of a recent infection does not align with the etiology of neurogenic shock.
C) Hypovolemic shock:
Hypovolemic shock occurs due to a significant loss of blood volume, such as from trauma, hemorrhage, or dehydration. While infection can lead to fluid loss and dehydration in some cases, the client's history of a recent infection suggests a different etiology, specifically septic shock, which is driven by the systemic inflammatory response to infection.
D) Septic shock.
Septic shock is a type of distributive shock caused by a systemic response to infection. It occurs when an infection triggers a widespread inflammatory response, leading to vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, fluid loss from the bloodstream, and impaired tissue perfusion. The client's history of a recent infection suggests that the shock may be septic in nature.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","E"]
Explanation
A. The inside surface of the lungs is small, and the dose is concentrated in that area: Inhalation medications are delivered directly to the lungs, where they are rapidly absorbed due to the small surface area and the close proximity of the medication to the lung tissue.
B. There is a large surface area inside the lungs: The lungs have a large surface area for gas exchange, allowing for efficient absorption of inhaled medications into the bloodstream.
C. Inhaled medications are given at very high doses: Inhaled medications are typically given at therapeutic doses appropriate for the patient's condition. While they may be given in higher doses compared to oral medications in some cases, the dosage is carefully adjusted based on factors such as the patient's age, weight, and severity of the condition.
D. Inhaled medications are given with food: Inhaled medications are typically administered separately from meals. Food can interfere with the absorption of inhaled medications and may affect their effectiveness.
E. There is a rich blood supply to the lungs: The lungs have a rich network of blood vessels, known as pulmonary capillaries, which allows for rapid absorption of inhaled medications into the bloodstream.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
