A patient presents with a blood pH of 7.29, bicarbonate (HCO2) level of 25 mmol/L, and partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) of 55 mmHg. Which cause is consistent with these lab values?
Excessive H+ ion loss due to severe vomiting
Hyperventilation secondary to a panic attack
Shallow and decreased breathing secondary to COPD
Increased renal HCO3 excretion due to kidney disease
The Correct Answer is C
A. Excessive H⁺ ion loss due to severe vomiting: Severe vomiting typically leads to metabolic alkalosis, not acidosis.
B. Hyperventilation secondary to a panic attack: Hyperventilation leads to respiratory alkalosis due to low PaCO2 levels.
C. Shallow and decreased breathing secondary to COPD: COPD can cause respiratory acidosis due to hypoventilation, leading to a high PaCO2 and a low pH.
D. Increased renal HCO3 excretion due to kidney disease: Increased renal excretion of bicarbonate would lead to metabolic acidosis, not respiratory acidosis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
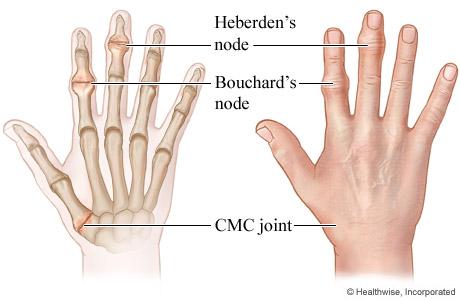
A. Rickets: Typically related to Vitamin D deficiency, leading to softening of bones in children, not joint pain.
B. Osteomalacia: Refers to softening of bones in adults due to Vitamin D deficiency, but it does not present with Heberden's or Bouchard's nodes.
C. Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune condition that causes symmetrical joint pain, but Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes are not characteristic of it.
D. Osteoarthritis: The description of morning stiffness, swelling, limited range of motion, and symmetrical joint pain in the hips, along with Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes, is characteristic of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis often worsens with physical exertion and in cold weather.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Blocking the arterial walls from absorbing electrolytes: The respiratory system does not affect the absorption of electrolytes in this manner.
B. Preventing the absorption of sodium and potassium: The respiratory system does not regulate sodium and potassium absorption directly.
C. Regulating the excretion or reabsorption of H and HCO3: This function is performed by the kidneys, not the respiratory system.
D. Increasing ventilation to drop the H ion level: The respiratory system compensates for acid-base imbalances by increasing ventilation (hyperventilation) to lower the hydrogen ion (H⁺) level and reduce acidity.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
