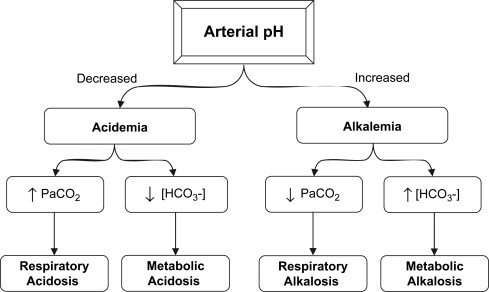
A patient's ABG results came back with the following values: pH 7.25, CO2 40, HCO3 22. How would you, as the nurse, interpret these results?
Metabolic acidosis
Respiratory acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a low pH and a normal or low HCO3. In this case, the pH is 7.25, which is below the normal range of 7.35-7.45, and the HCO3 is 22, which is at the lower end of the normal range of 22-26 mEq/L, indicating metabolic acidosis.
Choice B reason: Respiratory acidosis is characterized by a high CO2 level. However, in this scenario, the CO2 is 40, which is within the normal range of 35-45 mmHg, ruling out respiratory acidosis.
Choice C reason: Metabolic alkalosis would present with a high pH and a high HCO3 level. Since the pH is low, metabolic alkalosis is not the correct answer.
Choice D reason: Respiratory alkalosis is characterized by a low CO2 level and a high pH. Given that the CO2 is normal and the pH is low, respiratory alkalosis is not the condition indicated by these ABG results.
 |
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic that typically causes potassium loss, not hyperkalemia.
Choice B reason: Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic, which can lead to an increase in potassium levels, potentially causing hyperkalemia.
Choice C reason: Furosemide is a loop diuretic that usually results in potassium loss, not hyperkalemia.
Choice D reason: Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that does not typically cause hyperkalemia.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Increased length of stay is not a direct outcome of preoperative teaching and depends on many factors.
Choice B reason: Reduced postoperative respiratory function can be a concern, and preoperative teaching aims to mitigate this risk by educating on breathing exercises and mobilization.
Choice C reason: Preoperative teaching should help manage expectations and pain control strategies, not increase postoperative pain.
Choice D reason: Preoperative teaching should aim to reduce anxiety by providing information and reassurance, not induce it.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
