Karen, 35, comes in with recurring skin rashes and joint pain. The physician suspects an autoimmune disorder and orders an ELISA test to detect specific antibodies.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Celiac disease
Multiple sclerosis
Lupus
The Correct Answer is D
A. Rheumatoid arthritis typically presents with joint pain and inflammation but is not commonly associated with recurring skin rashes.
B. Celiac disease primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract and is characterized by an immune reaction to gluten ingestion. It does not typically present with joint pain or recurring skin rashes.
C. Multiple sclerosis is a neurological disorder characterized by demyelination of the central nervous system, leading to various neurological symptoms. It is not commonly associated with recurring skin rashes or joint pain.
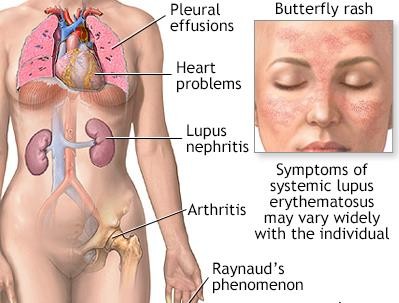
D. Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can affect multiple organs and systems, including the skin and joints. Recurring skin rashes and joint pain are common manifestations of lupus, and ELISA testing may be used to detect specific antibodies associated with the condition.
 |
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. TCR Gene Rearrangement testing is not used to identify bacterial infections.
B. TCR Gene Rearrangement testing is used to detect clonality in lymphoid cells, aiding in the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative disorders such as lymphoma.
C. This testing is not primarily used to evaluate genetic disorders.
D. TCR Gene Rearrangement testing does not measure electrolyte imbalance.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. This vaccine is recommended for adults over 50 years old to prevent shingles, but it is not typically administered annually.
B. There is no routine annual immunization for Hepatitis C.
C. Annual influenza vaccination is strongly recommended for patients with COPD to reduce the risk of influenza-related complications.
D. While pneumococcal vaccination is important for patients with COPD, it is not administered annually in most cases.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
