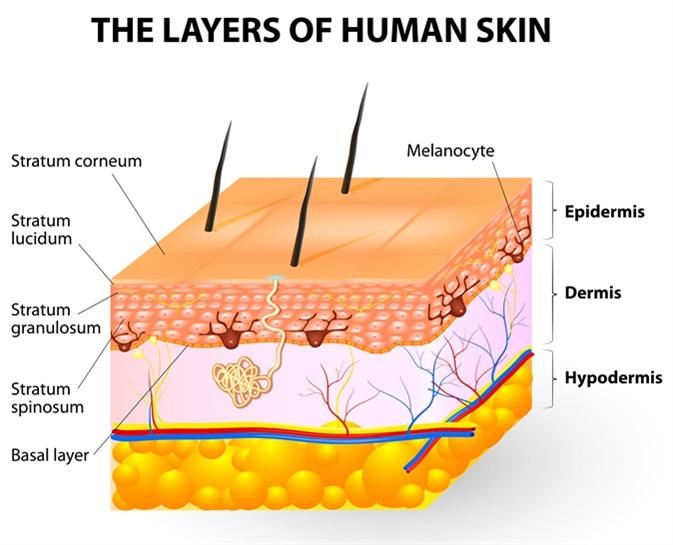
Melanocytes give rise to the pigment melanin, which is responsible for skin color. Where can the melanocytes be found?
Loose connective tissue
Epidermis
Dermis
Superficial fascia
The Correct Answer is B
A. Loose connective tissue:
Melanocytes are not typically found in loose connective tissue. Their primary location is within the epidermis, specifically in the basal layer, where they interact with keratinocytes to produce melanin and contribute to skin color. Loose connective tissue contains collagen and elastin fibers, as well as fibroblasts, but it does not house melanocytes.
B. Epidermis:
This is the correct answer. Melanocytes are primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation and determines skin color. Melanocytes are interspersed among keratinocytes in the epidermis and transfer melanin to keratinocytes to provide skin pigmentation.
C. Dermis:
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. While the dermis plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the epidermis, melanocytes are not primarily located in the dermis. They are confined to the basal layer of the epidermis.
D. Superficial fascia:
The superficial fascia, also known as the subcutaneous tissue or hypodermis, lies beneath the dermis and consists of adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue. It provides insulation, energy storage, and cushioning for underlying structures. However, melanocytes are not typically found in the superficial fascia. They are restricted to the epidermis, specifically the basal layer, where they carry out their function of melanin production.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Metabolic acidosis:
Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a low pH (<7.35) and a low bicarbonate level (<22 mEq/L) due to an excess of acids in the body or a loss of bicarbonate. However, in the given ABG values, the pH is low (7.22), but the bicarbonate level is elevated (28 mEq/L), which does not align with metabolic acidosis. Therefore, metabolic acidosis is not the correct interpretation in this case.
B. Respiratory acidosis:
Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is inadequate removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) by the lungs, leading to an accumulation of CO2 in the blood and a decrease in pH. In the ABG values provided, the pH is low (7.22), and the PaCO2 is elevated (68 mm Hg), indicating respiratory acidosis as the primary disturbance. This interpretation is supported by the elevated PaCO2 and the low pH, making it the correct choice based on the given data.
C. Respiratory alkalosis:
Respiratory alkalosis results from hyperventilation, leading to excessive elimination of CO2 and a decrease in PaCO2 levels. However, in the ABG values presented, the PaCO2 is elevated (68 mm Hg), which contradicts the expected decrease seen in respiratory alkalosis. Therefore, respiratory alkalosis is not the correct interpretation of the ABG values in this case.
D. Metabolic alkalosis:
Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by a high pH (>7.45) and a high bicarbonate level (>26 mEq/L) due to excessive loss of acids or an increase in bicarbonate levels. However, in the ABG values provided, the pH is low (7.22), and the bicarbonate level is elevated (28 mEq/L), which is not consistent with metabolic alkalosis. Therefore, metabolic alkalosis is not the correct interpretation based on the given data.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Electrical burns can have small amounts of skin damage, but more extensive damage beneath the skin.
This response is the best choice because it educates the client about the potential for deeper tissue damage associated with electrical burns. It acknowledges that while the burn on the skin may appear small, the damage underneath could be more extensive, affecting muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
B. Electrical burns commonly cause reddened/purplish skin without blistering.
This statement is not the best response because it focuses solely on the appearance of the skin without addressing the potential for deeper tissue damage. While it is true that electrical burns can present with reddened or purplish skin without blistering, this response does not provide comprehensive information about the nature and severity of electrical burns.
C. Electrical burns typically are minor.
This response is incorrect because it downplays the seriousness of electrical burns. While some electrical burns may indeed be minor, others can cause significant tissue damage and complications. It's important for the nurse to educate the client about the range of severity that electrical burns can present.
D. Electrical burns usually cause much more skin damage than what can be seen on your skin.
This statement is partially accurate but does not provide as much information as choice A. While it acknowledges that electrical burns can cause more damage than what is visible on the skin's surface, it doesn't emphasize the potential for deeper tissue damage as effectively as choice A does.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
