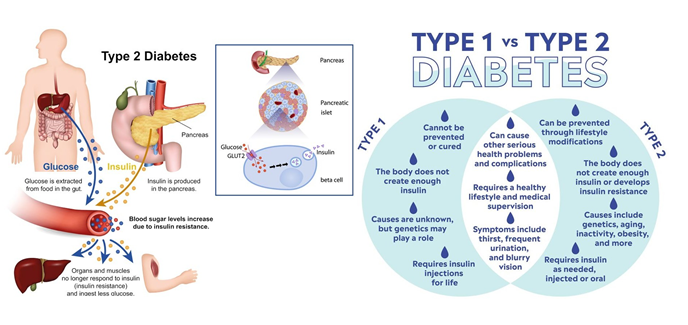
Mr. G was newly diagnosed with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, he asks the nurse what "type 2” means in relation to diabetes. The nurse to the patient that type 2 diabetes differs from type 1 diabetes in that with type 2 diabetes:
The patient is totally dependent on an outside source of insulin.
The insulin precursor that is secreted by the pancreas is not activated by the liver.
There is decreased insulin secretion and cellular resistance to insulin that is produced.
The immune system destroys the pancreatic insulin-producing cells.
The Correct Answer is C
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from decreased insulin secretion and/or increased insulin resistance. In type 2 diabetes, the body's cells become resistant to insulin, which is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate for the increased demand, but over time, the pancreas may not be able to keep up, and blood sugar levels rise.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, people with type 2 diabetes still produce insulin, but their body is not able to use it effectively. Therefore, type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and/or medication, such as oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin therapy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
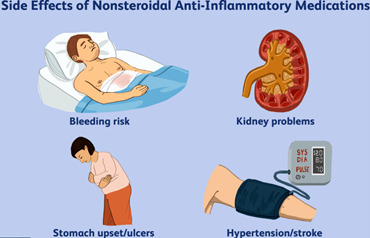
NSAIDs are known to be a common cause of acute gastritis. Therefore, it is essential for the nurse to ask the patient about their frequency of NSAID use to determine if this may have caused their current symptoms. Other options such as family history of gastric problems, recent weight gain or loss, and amount of fat in the diet, may also be relevant to the patient's overall health status, but they are not as important as the potential cause of their current condition.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Counting sponges, needles, and surgical instruments is an intraoperative activity that is specific to the circulating function of the perioperative nurse. The nurse is responsible for maintaining an accurate count of all surgical items to prevent leaving any foreign objects inside the patient after the surgery. This is a crucial task to ensure patient safety and prevent any potential complications that may arise from such errors.
Option a. admitting, identifying, and assessing the patient, is a preoperative function that is usually performed by the preoperative nurse.
Option c. passing instruments to the surgeon and assistants, is a scrub nurse function that requires knowledge of the surgical procedure and a sterile technique.
Option d. preparing the instrument table and sterile equipment is also a scrub nurse function that requires expertise in sterile technique, knowledge of surgical procedures, and the ability to maintain a sterile environment.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.