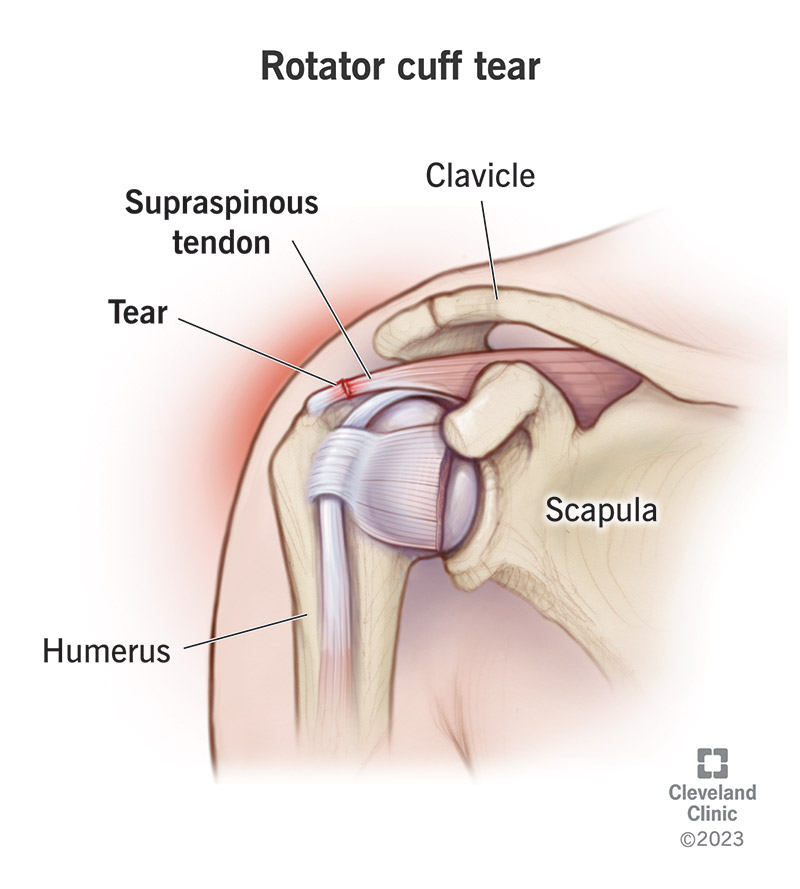
A nurse in a provider's office is assessing a client who reports shoulder pain. Which of the following findings by the nurse indicates a rotator cuff injury?
Inability to abduct the arm at the shoulder.
Negative drop arm test.
Alteration in the contour of the joint.
A positive Tinel's sign.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason:
The inability to abduct the arm at the shoulder is a classic sign of a rotator cuff injury. The rotator cuff is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint and aiding in various movements, including abduction. When there is a tear or significant weakness in the rotator cuff muscles, especially the supraspinatus muscle, the patient may be unable to lift the arm away from the body or may experience pain while doing so.
Choice B reason:
A negative drop arm test would actually indicate that there is no rotator cuff injury. The drop arm test is performed by asking the patient to fully abduct the arm to 90 degrees and then slowly lower it. If the patient can control the motion and lower the arm smoothly, the test is negative. A positive drop arm test, where the patient cannot control the descent of the arm, would suggest a rotator cuff tear.
Choice C reason:
While an alteration in the contour of the joint may indicate some form of shoulder pathology, it is not specific to a rotator cuff injury. Changes in the contour could be due to various conditions, including dislocation, arthritis, or other musculoskeletal disorders.
Choice D reason:
A positive Tinel's sign is used to diagnose nerve compression or nerve damage, not rotator cuff injuries. It is performed by tapping over the course of a nerve to elicit a tingling sensation or pain in the distribution of the nerve. This sign is commonly associated with conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
The inability to move toes can be an early sign that a cast is too tight. This symptom may indicate that the cast is impinging on nerves or blood vessels, leading to decreased motor function. It is essential to address this immediately to prevent further complications such as permanent damage or compartment syndrome.
Choice B reason:
Edema, or swelling of the toes, can occur if a cast is too tight, but it may not be the first sign observed. Swelling is a response to increased pressure in the tissues and can develop over time as fluid accumulates. While it is a concern, it often follows other symptoms such as changes in sensation or movement.
Choice C reason:
Pallor of the toes, indicating reduced blood flow, can be a sign of a cast that is too tight. However, pallor may not be as immediately noticeable as the inability to move toes or changes in sensation. It is still a critical sign that requires prompt evaluation and possible adjustment of the cast.
Choice D reason:
A change in the temperature of the toes, such as them becoming cooler to the touch, can suggest impaired blood flow due to a tight cast. This sign, along with pallor, may develop after other symptoms such as numbness or motor impairment.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
The location of the burn is crucial in assessing the severity because burns to the face, neck, and upper extremities can compromise vital functions. For example, burns to the face may affect the airway and respiratory system, while burns to the hands can impair mobility and the ability to perform daily tasks. The depth of the burn at these locations also affects the severity assessment, as deeper burns can damage underlying tissues and structures.
Choice B reason:
While the age of the client can influence the healing process and the risk of complications, it is not the primary factor in assessing the initial severity of the burn. However, age is considered when planning treatment and rehabilitation, as children and the elderly may have different healing rates and responses to therapy.
Choice C reason:
The cause of the burn can provide context for potential complications, such as inhalation injury from a fire or chemical exposure. However, the immediate assessment of severity is more focused on the observable damage to the skin and underlying tissues rather than the cause of the burn.
Choice D reason:
The client's associated medical history is important for understanding potential risks and complications during the healing process, but it is not the primary factor in assessing the severity of the burn. The medical history will be more relevant when considering the client's overall prognosis and planning long-term care.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
