The experienced nurse understands that the student nurse may require additional instruction regarding proper respiratory assessment techniques when the nurse observes the student: (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
Listening to at least one full respiration in each location.
Instructing the client to breathe in and out rapidly while listening to breath sounds.
Listening to breath sounds through the hospital gown or clothing.
Instructing the client to take slow deep breaths through his or her nose.
Listening as the client inhales, then goes to the next site during exhalation.
Correct Answer : B,C
Choice A reason: Listening to at least one full respiration in each location is a proper technique for respiratory assessment. It ensures that the nurse can accurately assess the breath sounds and identify any abnormalities. This method allows for a thorough evaluation of the respiratory system, ensuring that no areas are missed.
Choice B reason: Instructing the client to breathe in and out rapidly while listening to breath sounds is incorrect. Rapid breathing can lead to hyperventilation and may not provide an accurate representation of the client’s normal breath sounds. The proper technique is to instruct the client to take slow, deep breaths through their mouth, which allows for a more accurate assessment of the breath sounds and any potential abnormalities.
Choice C reason: Listening to breath sounds through the hospital gown or clothing is incorrect. Clothing can interfere with the sounds and may lead to inaccurate assessments. The proper technique is to place the stethoscope directly on the client’s skin to ensure that the breath sounds are heard clearly and accurately.
Choice D reason: Instructing the client to take slow deep breaths through his or her nose is partially correct but not ideal. While slow deep breaths are appropriate, they should be taken through the mouth to ensure that the breath sounds are more pronounced and easier to assess. Breathing through the nose can sometimes muffle the sounds and make it harder to detect abnormalities.
Choice E reason: Listening as the client inhales and then moving to the next site during exhalation is incorrect. The nurse should listen to both the inhalation and exhalation phases of respiration at each site. This ensures a complete assessment of the breath sounds and helps in identifying any abnormalities that may be present during either phase of respiration.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Exercise is a well-known trigger for asthma, particularly exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB). During physical activity, especially in cold or dry air, the airways can narrow, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing. Proper management and pre-exercise medication can help mitigate these effects.
Choice B reason:
Pollen is a common allergen that can trigger asthma symptoms. Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can cause allergic reactions that lead to asthma exacerbations. Seasonal variations in pollen levels can significantly impact individuals with asthma, making it important to monitor pollen counts and take preventive measures.
Choice C reason:
Animal dander, which consists of tiny flakes of skin shed by cats, dogs, and other animals, is a frequent asthma trigger. Proteins found in the dander, saliva, and urine of pets can cause allergic reactions and asthma symptoms. Reducing exposure to pets and maintaining a clean environment can help manage this trigger.
Choice D reason:
Emotional stress can also trigger asthma symptoms. Stress and strong emotions can lead to hyperventilation and changes in breathing patterns, which can exacerbate asthma. Stress management techniques and relaxation exercises can be beneficial in controlling asthma symptoms related to emotional stress.
Choice E reason:
Recent travel abroad is not typically considered a common trigger for asthma. While travel can expose individuals to different environmental factors and allergens, it is not a direct trigger like the other options listed. However, it is important for individuals with asthma to plan and prepare for travel to manage their condition effectively.
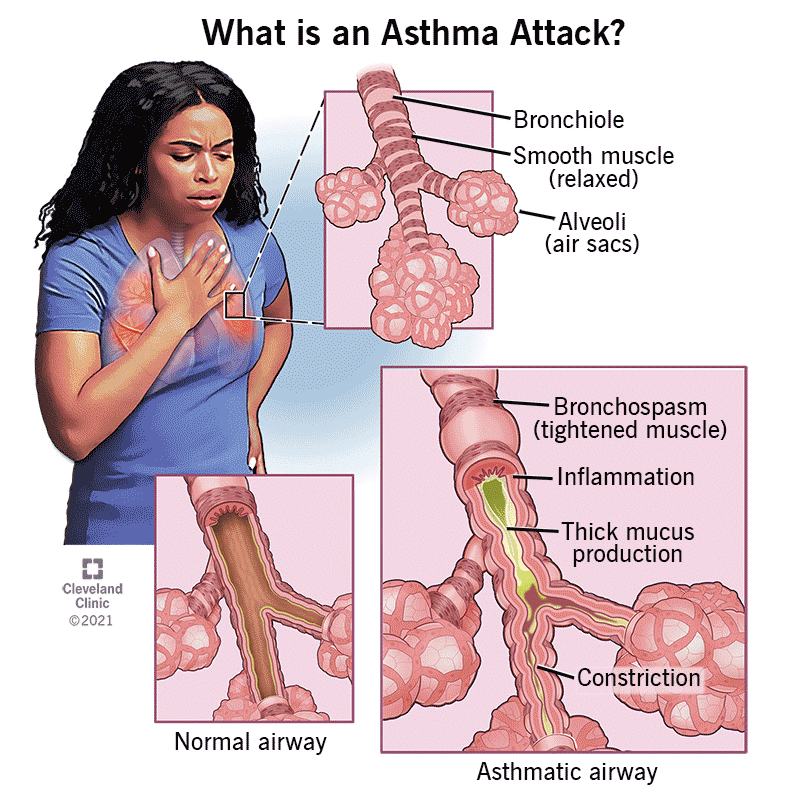
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Maintaining adequate oxygenation is the primary goal for a client with impaired gas exchange due to an asthma exacerbation. Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method to monitor the oxygen saturation of a patient’s blood, and values above 94% indicate sufficient oxygenation.
Choice A reason:
The client will demonstrate decreased episodes of coughing at night is important but not the priority goal. While reducing coughing can improve comfort and sleep quality, it does not directly address the critical issue of impaired gas exchange. The primary concern in an asthma exacerbation is ensuring that the client maintains adequate oxygen levels.
Choice B reason:
The client’s pulse oximetry values will remain above 94% on room air for the majority of the time is the priority goal. This goal directly addresses the issue of impaired gas exchange by ensuring that the client maintains adequate oxygenation. Pulse oximetry values above 94% indicate that the client’s blood is sufficiently oxygenated, which is crucial for preventing hypoxemia and ensuring that the body’s tissues receive enough oxygen to function properly.
Choice C reason:
The client’s breath sounds will only have slight wheezing by discharge is a relevant goal but not the priority. While reducing wheezing is an indicator of improved airway function, it is not as directly measurable or critical as maintaining adequate oxygen saturation. Wheezing can persist even when oxygen levels are adequate, so it is not the most reliable indicator of improved gas exchange.
Choice D reason:
The client will correctly demonstrate the use of a peak flow meter is an important educational goal but not the priority in an acute setting. Proper use of a peak flow meter can help the client monitor their asthma and prevent future exacerbations, but it does not directly address the immediate issue of impaired gas exchange. The priority in an acute asthma exacerbation is to ensure that the client is adequately oxygenated.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
