The nurse is caring for a client admitted to the hospital with a tentative diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Which diagnostic procedure should the nurse prepare the client for the healthcare provider?
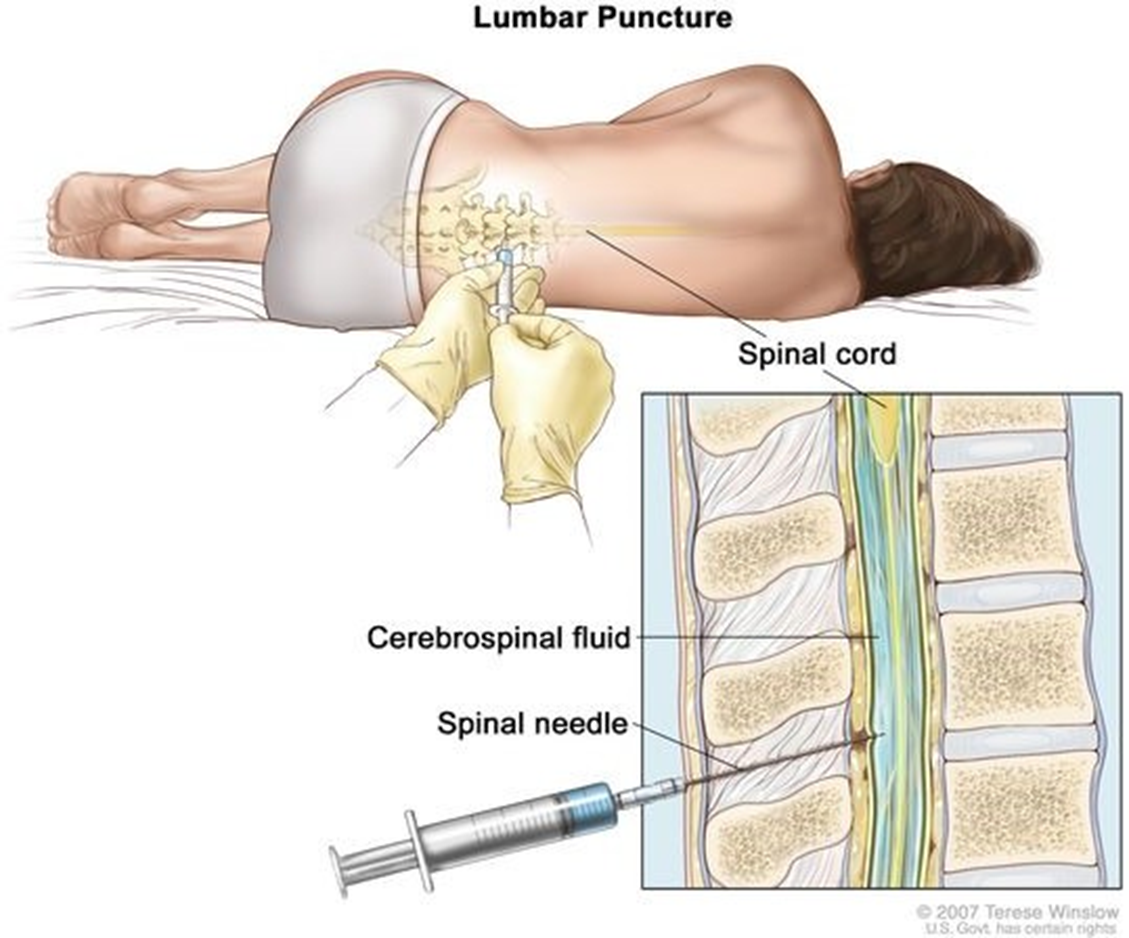
Lumbar puncture.
Skull radiography.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Computerized tomography (CT) scan.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale
A lumbar puncture is a key diagnostic procedure for suspected bacterial meningitis. It allows for the collection of cerebrospinal fluid, which can be analyzed for signs of bacterial infection.
Choice B rationale
Skull radiography is not typically used to diagnose bacterial meningitis. While it can help identify abnormalities in the structure of the skull or brain, it cannot detect the presence of bacteria.
Choice C rationale
While an MRI can provide detailed images of the brain and surrounding tissues, it is not the primary tool for diagnosing bacterial meningitis. It may be used in conjunction with other tests, but a lumbar puncture is more definitive.
Choice D rationale
A CT scan can be used to detect abnormalities in the brain, such as swelling or inflammation, which could be indicative of meningitis. However, it cannot definitively diagnose bacterial meningitis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["42"]
Explanation
Step 1: Convert the volume from liters to milliliters. 1 liter = 1000 mL. Step 2: Convert the time from hours to minutes. 4 hours = 240 minutes.
Step 3: Calculate the rate in mL per minute. Rate = Volume ÷ Time = 1000 mL ÷ 240 min = 4.17 mL/min.
Step 4: Calculate the drops per minute. Drops per minute = Rate × Drop factor = 4.17 mL/min
× 10 gtt/mL = 41.7 gtt/min.
Step 5: Round off the result to the nearest whole number. 41.7 gtt/min rounds off to 42 gtt/min.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Rubbing painful areas gently until the pain subsides is not typically recommended for managing pain in Raynaud’s disease. This could potentially cause more harm than good19.
Choice B rationale
Wearing gloves when handling cold items can help guard against painful spasms in Raynaud’s disease. Cold temperatures can trigger Raynaud’s attacks, so protecting the hands from cold is a key part of managing the condition19.
Choice C rationale
The need for return appointments for IV pain medication is not typically a primary component of pain management in Raynaud’s disease. Pain in Raynaud’s disease is usually managed through lifestyle modifications and medications19.
Choice D rationale
While enrolling in a pain clinic can provide pain relief alternatives, it’s not the first line of management for pain in Raynaud’s disease. The primary management strategies include avoiding cold exposure and using medications to improve blood flow19.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
