The nurse must administer 1600 mL of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) over 24 hours. The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver how many mL/hr? (Round to the nearest tenth, do not use trailing zeros, use a leading zero if it applies)
The Correct Answer is ["66.7"]
Step 1: Determine the total volume to be administered. Total volume = 1600 mL
Step 2: Determine the total time in hours. Total time = 24 hours
Step 3: Calculate the rate in mL/hr. Rate = Total volume ÷ Total time Rate = 1600 mL ÷ 24 hours Rate = 66.6667 mL/hr
Step 4: Round to the nearest tenth. Rounded rate = 66.7 mL/hr
The nurse should set the IV pump to deliver 66.7 mL/hr.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
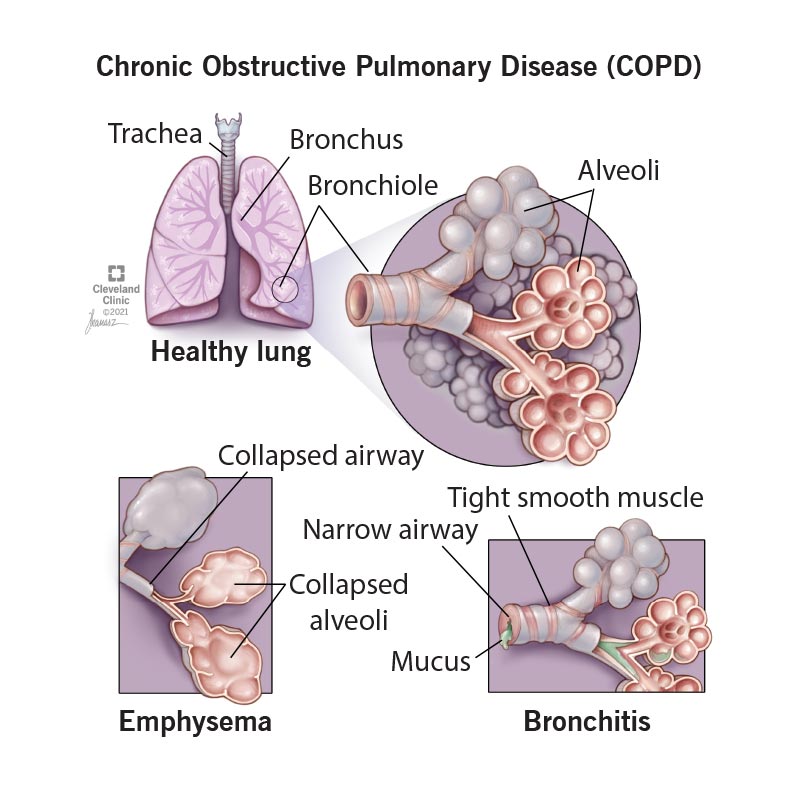
Choice A reason: Elevating the client’s head of the bed to 45 degrees is important for promoting optimal lung expansion and reducing the risk of aspiration. However, it is not the first priority when preparing for tracheostomy care. Ensuring adequate oxygenation is more critical in the immediate preparation phase.
Choice B reason: Hyper-oxygenating the client using an Ambu bag is the first priority. This step is crucial to ensure that the client has sufficient oxygen reserves before the tracheostomy care procedure begins. Hyper-oxygenation helps prevent hypoxia during suctioning, which can be particularly important for clients with COPD who may already have compromised respiratory function.
Choice C reason: Opening the suction and tracheostomy kits is necessary for the procedure, but it should be done after ensuring the client is adequately oxygenated. Preparing the equipment is important, but patient safety and oxygenation take precedence.
Choice D reason: Suctioning the client using aseptic technique is a critical part of tracheostomy care to maintain a patent airway and prevent infection. However, this should be done after the client has been hyper-oxygenated to ensure they are stable and to minimize the risk of hypoxia during the procedure.
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
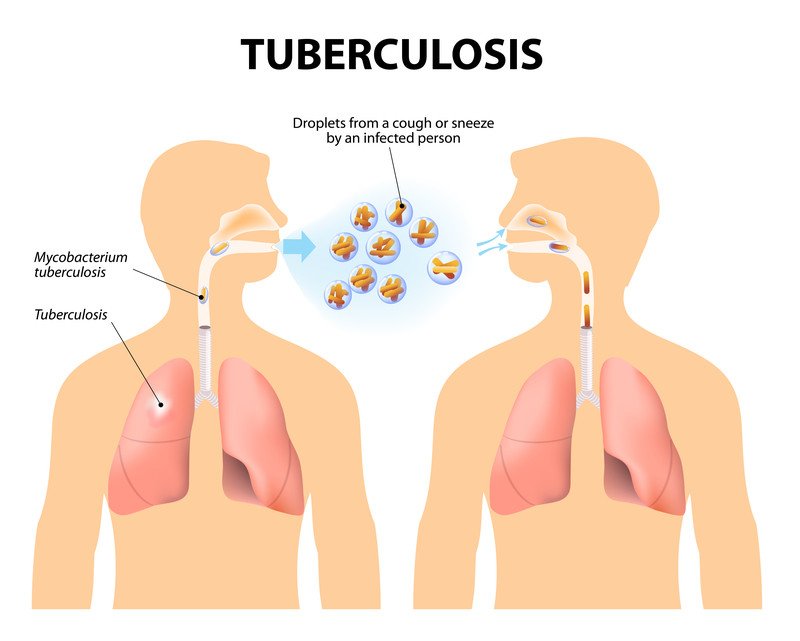
Choice A reason: Albuterol is a bronchodilator used to treat conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is not typically used in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). TB treatment focuses on antibiotics that target the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria.
Choice B reason: Isoniazid is one of the primary medications used in the treatment of tuberculosis. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of mycolic acids, which are essential components of the bacterial cell wall. Isoniazid is usually part of the initial treatment regimen for TB and is taken for several months to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria.
Choice C reason: Pyrazinamide is another key medication in the treatment of tuberculosis. It is particularly effective during the initial phase of treatment and helps to reduce the duration of therapy. Pyrazinamide works by disrupting the bacterial cell membrane metabolism and transport functions.
Choice D reason: Tiotropium is a long-acting bronchodilator used to manage COPD. It is not used in the treatment of tuberculosis. The focus of TB treatment is on antibiotics that specifically target the TB bacteria.
Choice E reason: Rifampin is a critical antibiotic in the treatment of tuberculosis. It works by inhibiting the RNA synthesis of the bacteria, effectively killing the TB bacteria. Rifampin is usually taken in combination with other TB medications to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of the bacteria.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
