The patient weighing 147 pounds with septic shock has a BP of 70/46 mm Hg, pulse 136, respirations 30, temperature 104° F, and blood glucose 391 mg/dL. Which intervention red by the health care provider should the nurse implement first?
Give a 2000mL normal saline bolus
Start insulin drip to maintain blood glucose at 110 to 150 mg/dL.
Give acetaminophen (Tylenol) 650 mg rectally.
Give prescribed Antibiotics
Start norepinephrine (Levophed) to keep systolic blood pressure >90 mm Hg.
The Correct Answer is D
In septic shock, prompt administration of antibiotics is crucial in order to target the underlying infection and prevent further progression of the septic process. Antibiotics help to eradicate the causative organisms and reduce the bacterial load, which can help improve patient outcomes.
While all the options mentioned are important interventions in the management of septic shock, initiating antibiotic therapy is considered a priority in order to address the underlying infection and prevent sepsis-related complications.
A. Giving a 2000 mL normal saline bolus in (option A) is incorrect because: Fluid resuscitation is important in septic shock to restore intravascular volume, but antibiotic therapy takes precedence as it directly targets the underlying infection.
B. Starting an insulin drip to maintain blood glucose at 110 to 150 mg/dL in (option B) is incorrect because Glycemic control is important in septic shock, but it is not the first priority compared to addressing the infection.
C. Giving acetaminophen (Tylenol) 650 mg rectally in (option C) is incorrect because Antipyretic medications can help reduce fever, but they do not address the underlying infection or stabilize the patient's condition.
E. Starting norepinephrine (Levophed) to keep systolic blood pressure >90 mm Hg in (option E) is incorrect because: Vasopressor support may be necessary in septic shock to maintain adequate blood pressure, but initiating antibiotics takes priority in order to address the underlying infection.
Therefore, in a patient with septic shock presenting with the given signs and symptoms, the nurse should first implement the intervention of giving the prescribed antibiotics to target the underlying infection.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
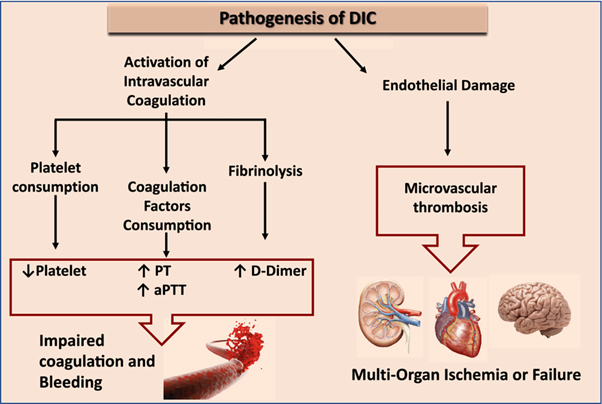
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by widespread activation of the coagulation system, leading to both excessive clot formation and consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This process can result in both bleeding and thrombosis.
The manifestations mentioned in option B are commonly seen in DIC:
Decreased platelet counts: DIC leads to platelet consumption and destruction, resulting in low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia).
Increased D-dimer: D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product, and its levels are increased DIC due to the breakdown of fibrin clots.
Increased prothrombin time (PT): DIC can lead to the depletion of clotting factors, resulting in prolonged prothrombin time, indicating impaired coagulation.
The other options mentioned do not represent the typical clinical manifestations of DIC:
A. Decreased hematocrit, increased platelet counts, and increased D-dimer in (option A) are incorrect because While platelet counts and D-dimer are increased in DIC, decreased hematocrit is not a characteristic finding.
C. Decreased Antithrombin III, increased platelet counts, and increased fibrinogen in (option C) is incorrect because: Decreased Antithrombin III can be seen in DIC, but increased platelet counts and fibrinogen levels are not specific to DIC.
D. Decreased D-dimer, increased platelet counts, and increased hemoglobin in (option D) is incorrect because Decreased D-dimer and increased hemoglobin are not typical findings in DIC, while increased platelet counts can be seen in some cases.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The characteristics described in the monitor strip analysis suggest ventricular tachycardia. The absence of a visible P wave and the wide and distorted QRS complex indicates that the electrical impulse is originating in the ventricles rather than the atria. The ventricular rate of 196 and regular R-R intervals further support the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia.
B. Atrial fibrillation in (option B) is incorrect because it is characterized by irregularly irregular R-R intervals and the absence of discernible P waves. The QRS complex is typically narrow
C. Atrial tachycardia in (option C) is incorrect because it would have a rapid atrial rate with regular R-R intervals, and P waves may or may not be discernible. The QRS complex is typically narrow.
D. Ventricular fibrillation in (option D) is incorrect because it would present as a chaotic, rapid, and irregular electrical activity with no discernible P waves, QRS complexes, or regular R-R intervals. It is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate defibrillation.
Therefore, based on the provided information, the nurse would interpret the patient's cardiac rhythm as ventricular tachycardia. However, it is important to note that an accurate interpretation should be made by a qualified healthcare professional, and the patient's clinical context should also be considered.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
