Ati rn Gerontology
Ati rn Gerontology
Total Questions : 35
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse is teaching a client who has constipation. Which of the following statements should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Try to defecate at different times of the day
This statement is not advisable for clients with constipation. Regularity is key in managing constipation. Encouraging the client to try to defecate at the same time each day can help establish a routine and improve bowel regularity. The body’s natural circadian rhythms can aid in this process, making it easier to have a bowel movement at a consistent time.
Choice B Reason: Consume a low-fiber diet
A low-fiber diet is not recommended for clients with constipation. Fiber adds bulk to the stool and helps it pass more easily through the intestines. Foods high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Increasing dietary fiber intake is a common and effective strategy for managing constipation. The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men.
Choice C Reason: Reduce your daily activity
Reducing daily activity is not beneficial for managing constipation. Physical activity helps stimulate intestinal function and can promote regular bowel movements. Encouraging clients to engage in regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help alleviate constipation. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Choice D Reason: Increase your daily fluid intake
Increasing daily fluid intake is a key recommendation for managing constipation. Fluids help soften the stool, making it easier to pass. Water is the best choice, but other fluids like herbal teas and clear soups can also be beneficial. It is generally recommended to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day, though individual needs may vary based on factors such as age, sex, and activity level.

A nurse is providing education to a client who needs a cholecystectomy due to a build-up of calculi or gallstones. Which of the following is the best response from the nurse to explain what caused this problem?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
This option suggests that the gallbladder is blocked by a tumor. While tumors can cause blockages, they are not the most common cause of gallbladder inflammation requiring a cholecystectomy. Gallstones are a more frequent cause of such issues.
Choice B Reason:
This is the correct answer. Gallstones can block the common bile duct, leading to inflammation of the gallbladder, a condition known as cholecystitis. This blockage prevents bile from flowing out of the gallbladder, causing pain and potentially leading to infection.
Choice C Reason:
While cholesterol is a component of many gallstones, the inflammation of the gallbladder is typically due to the physical blockage caused by the stones rather than the cholesterol itself. The blockage leads to bile buildup and subsequent inflammation.
Choice D Reason:
Gallbladder infections caused by viruses are extremely rare. Most gallbladder infections are bacterial and occur secondary to blockages caused by gallstones.
A nurse is caring for a hospitalized client at risk for complications of immobility. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include to prevent complications?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Instruct the client to wear a hospital gown every day, even when out of bed
This intervention does not directly address the prevention of complications related to immobility. Wearing a hospital gown may be necessary for medical reasons, but it does not promote mobility or prevent complications such as pressure ulcers, muscle atrophy, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Encouraging the client to wear regular clothes when out of bed might actually promote a sense of normalcy and encourage more movement.
Choice B Reason: Have the client remain in bed for self-care activities
Keeping the client in bed for self-care activities is counterproductive in preventing complications of immobility. Prolonged bed rest can lead to muscle atrophy, decreased joint mobility, and increased risk of pressure ulcers and DVT. Encouraging the client to get out of bed and perform self-care activities while standing or sitting can help maintain muscle strength and joint flexibility.
Choice C Reason: Encourage the client to sit in the chair for all meals
Encouraging the client to sit in a chair for meals is an effective intervention to prevent complications of immobility. Sitting up helps improve digestion and respiratory function and reduces the risk of pressure ulcers by changing the pressure points on the body. It also promotes muscle activity and circulation, which are crucial in preventing DVT and maintaining overall physical health.
Choice D Reason: Elevate the head of the bed to 30° to 45° for medication administration
While elevating the head of the bed can be beneficial for certain medical conditions and for medication administration, it does not significantly contribute to preventing complications of immobility. This position can help with respiratory function and prevent aspiration during medication administration, but it does not promote overall mobility or prevent muscle atrophy and pressure ulcers.
A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about wearing medical masks. Which of the following statements should the nurse include?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
This option suggests removing the mask before removing gloves. However, the correct procedure is to remove gloves first, followed by the mask, to prevent contamination from the gloves to the face.
Choice B Reason:
This is the correct answer. Medical masks should be discarded after each use to prevent contamination and ensure effectiveness. Reusing masks can lead to the spread of pathogens.
Choice C Reason:
While positioning the mask correctly is important, the statement contains an error. The flexible metal piece should be at the top of the mask, not the bottom.
Choice D Reason:
Touching the front of the mask while wearing it is incorrect as it can lead to contamination. The front of the mask is considered contaminated, and touching it can transfer pathogens to the hands.
A nurse is preparing to admit a client who has a new diagnosis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The nurse should plan to place the client in which of the following types of transmission-based precautions?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Contact precautions are recommended for patients with MRSA to prevent the spread of the bacteria. This includes measures such as placing the patient in a single room, using personal protective equipment (PPE) like gowns and gloves, and ensuring proper hand hygiene. These precautions help to minimize the risk of transmission through direct or indirect contact with the patient or their environment.
Choice B Reason:
Protective precautions, also known as reverse isolation, are used to protect immunocompromised patients from infections. This is not applicable for MRSA patients, as the goal is to prevent the spread of MRSA to others, not to protect the patient from external infections.
Choice C Reason:
Airborne precautions are used for diseases that are transmitted through the air, such as tuberculosis or measles. MRSA is not transmitted through airborne particles, so this type of precaution is not appropriate.
Choice D Reason:
Droplet precautions are used for diseases that are spread through large respiratory droplets, such as influenza or pertussis. MRSA is primarily spread through direct contact, not through respiratory droplets, making droplet precautions unnecessary.
An infection control nurse is teaching a class about the transmission of infectious agents. The nurse should include that which of the following diseases is transmitted via airborne transmission? (Select All that Apply.)
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Rubeola, also known as measles, is highly contagious and spreads through airborne transmission. The virus can remain infectious in the air for up to two hours after an infected person coughs or sneezes. This makes it one of the most easily spread diseases through airborne particles.
Choice B Reason:
Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route, not through airborne transmission. It spreads via spores that can survive on surfaces and be ingested, leading to infection.
Choice C Reason:
Varicella, or chickenpox, is transmitted through airborne particles. The virus can spread through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters or through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. This makes it an airborne disease.
Choice D Reason:
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, speaks, or sings. The bacteria can remain suspended in the air for several hours, making TB an airborne disease.
Choice E Reason:
Staphylococcus aureus is not typically transmitted through airborne means. It spreads through direct contact with infected wounds, contaminated surfaces, or through respiratory droplets in some cases. However, it is not considered an airborne disease.
A preoperative nurse is caring for a client who is being prepped for emergency surgery related to a small bowel obstruction. The client is anxious and doesn’t understand what the surgeon means by “adhesions” causing the blockage. Which of the following statements is the best response from the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A Reason: The most important thing is that now you are here, and it is going to get taken care of
While this statement is reassuring, it does not provide the client with the specific information they are seeking about adhesions. Clients often feel more at ease when they understand the cause of their condition. Providing clear and accurate information helps reduce anxiety and empowers the client to be more involved in their care.
Choice B Reason: This means that scar tissue formed from the healing of a past abdominal surgery is now constricting the opening in your intestine
This statement is the best response because it directly addresses the client’s question about adhesions. Adhesions are bands of scar tissue that can form after abdominal surgery, causing organs or tissues to stick together. These adhesions can constrict the intestines, leading to a blockage. Providing this explanation helps the client understand the cause of their condition and the reason for the surgery.
Choice C Reason: I will be happy to go and get you some reading materials about this procedure to explain it further
Offering reading materials can be helpful, but it does not immediately address the client’s anxiety or their specific question about adhesions. While additional information can be beneficial, the nurse should first provide a clear and direct explanation to help the client understand their condition.
Choice D Reason: It’s okay. It happens all the time and I’ve seen a lot of clients with this issue
This statement may come across as dismissive and does not provide the client with the information they need. While it is important to reassure the client, it is equally important to provide specific information about their condition. Understanding the cause of their symptoms can help reduce anxiety and improve the client’s overall experience.
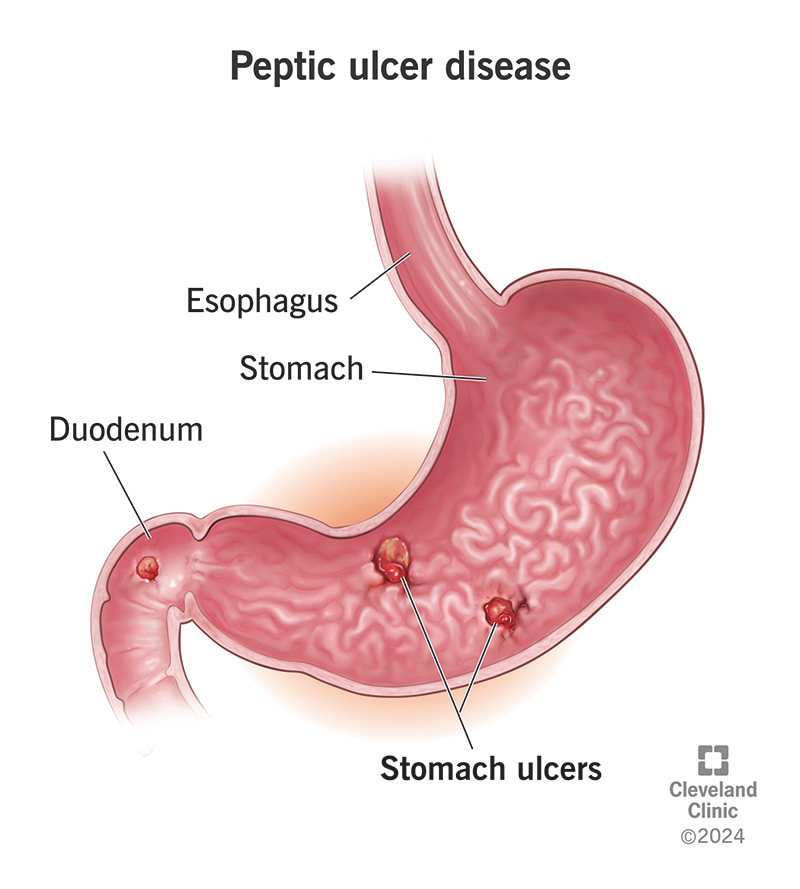
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has a peptic ulcer. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Monitoring for changes in urine color, such as maroon or red-colored urine, is not typically associated with peptic ulcers. These changes could indicate other conditions, such as urinary tract infections or kidney issues.
Choice B Reason:
Ecchymosis, or bruising, on the sides of the abdomen or pelvic areas is not a common symptom of peptic ulcers. This could be related to other medical conditions, such as trauma or bleeding disorders.
Choice C Reason:
This is the correct answer. Dark or black-colored stool, known as melena, can indicate gastrointestinal bleeding, which is a serious complication of peptic ulcers. It is crucial for patients to monitor their stool color and report any changes to their healthcare provider immediately.
Choice D Reason:
Monitoring for unintentional weight gain is not directly related to peptic ulcers. While weight changes can be a sign of various health issues, they are not specific indicators of complications from peptic ulcers.
A nurse is preparing to perform an abdominal assessment on a child. Identify the sequence the nurse should follow. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the selected order of performance. Use all the steps.)
Explanation
Choice A Reason: Superficial palpation
Superficial palpation is typically performed after auscultation to avoid altering bowel sounds. It involves gently pressing on the abdomen to detect tenderness, masses, or other abnormalities. This step helps in identifying areas that may require deeper examination.
Choice B Reason: Auscultation
Auscultation is performed after inspection and before palpation to listen to bowel sounds without interference. Using a stethoscope, the nurse listens for the presence, frequency, and character of bowel sounds. This step is crucial as palpation can stimulate bowel activity, potentially leading to inaccurate findings.
Choice C Reason: Inspection
Inspection is the first step in an abdominal assessment. The nurse visually examines the abdomen for any abnormalities such as distension, scars, or discoloration. This step provides initial information about the child’s abdominal health and helps guide the subsequent steps of the assessment.
Choice D Reason: Deep palpation
Deep palpation is performed last to assess the deeper structures of the abdomen. This step involves applying more pressure to feel for masses, organ size, and tenderness. It is important to perform this step last to avoid causing discomfort or altering the findings of the other assessment steps.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of Clostridium difficile and is placed on contact precautions. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Removing the protective gown before removing gloves is incorrect. The correct procedure is to remove gloves first, followed by the gown, to prevent contamination from the gown to the hands.
Choice B Reason:
Using an electronic thermometer is not recommended for clients with Clostridium difficile. Disposable thermometers or dedicated equipment should be used to prevent cross-contamination.
Choice C Reason:
This is the correct answer. The protective gown should be removed before leaving the client’s room to prevent the spread of Clostridium difficile spores to other areas of the healthcare facility. Proper removal and disposal of PPE are crucial in infection control.
Choice D Reason:
Shaking bed linens is incorrect as it can aerosolize Clostridium difficile spores, increasing the risk of spreading the infection. Linens should be carefully handled and placed in a linen bag without shaking.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 35 questions on the Ati rn Gerontology Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



