A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
Hypomagnesemia
Hypocalcemia
Hyponatremia
Hypokalemia
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A Reason:
Hypomagnesemia is incorrect. Lithium therapy itself is not a direct cause of hypomagnesemia. While exercise can affect magnesium levels to some extent, it's not a primary electrolyte imbalance that is typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
Choice B Reason:
Hypocalcemia is incorrect. Similarly, lithium therapy is not a direct cause of hypocalcemia. Exercise can affect calcium metabolism, but it's not a primary electrolyte imbalance typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
When a client taking lithium begins a new exercise program, the nurse should primarily assess for the risk of:
Choice C Reason:
Hyponatremia is correct. Lithium can affect the body's regulation of sodium, and excessive sweating due to increased exercise can lead to sodium loss. This combination can potentially contribute to the development of hyponatremia (low sodium levels). Therefore, when a client on lithium starts a new exercise regimen that may induce sweating, monitoring for signs of hyponatremia becomes crucial. Symptoms of hyponatremia can include confusion, headaches, nausea, and in severe cases, seizures or coma.
Choice D Reason:
Hypokalemia is incorrect. Lithium itself does not commonly cause hypokalemia. Exercise can lead to potassium loss through sweating, but hypokalemia is not the primary electrolyte imbalance typically associated with lithium use or considered a significant concern specifically due to lithium.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Oxygen saturation within this range is generally considered adequate and might not directly correlate with the administration of albumin.
Choice B Reason:
Decrease in protein is incorrect. Albumin infusions are meant to supplement protein levels in the blood, so a decrease in protein wouldn't be an expected finding.
Choice C Reason:
Increase in blood pressure is correct. Albumin infusions can potentially help increase blood volume, leading to an increase in blood pressure. In shock, where there's a significant decrease in blood pressure due to reduced circulating volume, administering albumin or other intravenous fluids can help restore blood volume and consequently raise blood pressure towards a more stable range.
Choice D Reason:
PaCO2 of 30 mm Hg is incorrect. PaCO2 levels are related to respiratory function and the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. While shock can impact various physiological parameters, a PaCO2 level of 30 mm Hg alone might not be directly tied to the administration of albumin in shock.
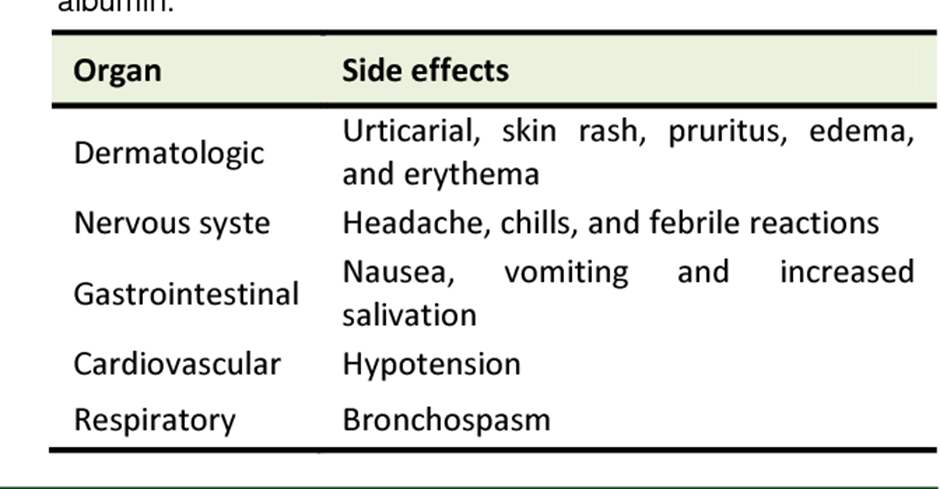
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Decreased respiratory rate is incorrect. Heparin administration and an elevated aPTT typically do not directly cause a decrease in respiratory rate. Respiratory rate changes might occur due to other factors such as respiratory conditions, pain, or medications affecting the respiratory center, but they are not commonly linked to heparin therapy.
Choice B Reason:
Increased blood pressure is incorrect. Heparin therapy and an elevated aPTT do not typically result in increased blood pressure. Heparin's primary effect is on preventing blood clotting, and while it can indirectly affect blood pressure by preventing clot formation, it doesn't typically cause a significant increase in blood pressure.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased temperature is incorrect. Heparin therapy and an elevated aPTT do not generally cause a decrease in body temperature. Changes in body temperature might occur due to various reasons such as infection, environmental factors, or certain medications, but they are not directly linked to heparin administration.
Choice D Reason:
Increased pulse rate is correct. An increased pulse rate can be an early indicator of bleeding or a potential side effect of heparin administration. Heparin's anticoagulant effect might predispose individuals to bleeding, so an increased pulse rate could indicate a response to potential bleeding complications rather than a direct effect of heparin itself.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
