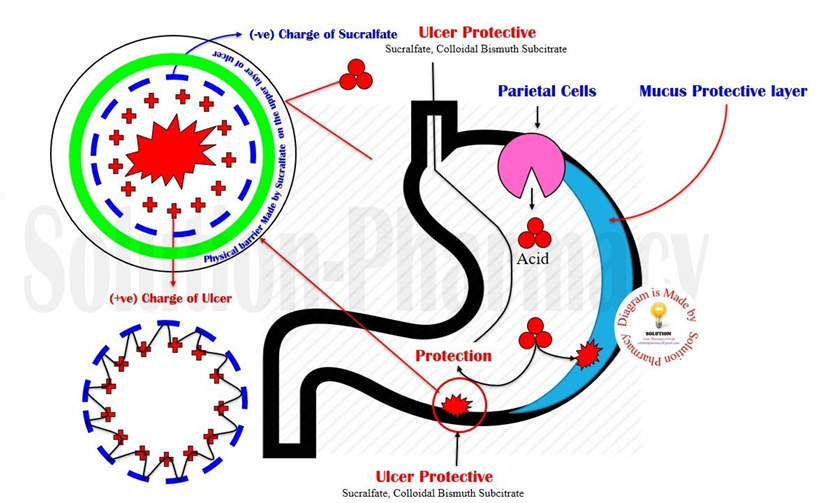
A patient with a gastric ulcer is ordered sucralfate (Carafate). How does this medication works?
calm the patient to reduce acid production
block the H2 receptors
neutralize the gastric acids
coat the gastric lining
The Correct Answer is D
A. Calm the patient to reduce acid production.
This description is not accurate for sucralfate. Calming the patient to reduce acid production is typically associated with medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers.
B. Block the H2 receptors.
Blocking H2 receptors is the mechanism of action for H2 receptor blockers, such as ranitidine. It is not the mechanism of action for sucralfate.
C. Neutralize the gastric acids.
Neutralizing gastric acids is the mechanism of action for antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate. Sucralfate works differently; it forms a protective coating on the gastric lining rather than directly neutralizing acids.
D. Coat the gastric lining.
This is the correct mechanism of action for sucralfate. It forms a protective coating on the gastric lining, adhering to the ulcer site and providing a barrier against gastric acid.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Before breakfast or lunch
Methylphenidate (Ritalin), a stimulant medication commonly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), is usually administered before breakfast or lunch for maximum effectiveness. This schedule helps align the peak concentration of the medication with the times when increased focus and attention are often needed, such as during school hours.
B. With meals
While it can be administered with meals, the goal is often to have the medication take effect before meals to help with focus and attention during activities like school or work.
C. After dinner
Administering methylphenidate after dinner may interfere with the patient's ability to fall asleep, as the medication can cause insomnia. It is generally recommended to avoid administering it in the late afternoon or evening.
D. At bedtime
Administering methylphenidate at bedtime is not appropriate due to the potential for insomnia. The stimulant effect of the medication is not aligned with the patient's sleep-wake cycle.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","E"]
Explanation
A. Bradycardia
Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of acetylcholine receptors can lead to bradycardia.
B. Rash
Rash is not typically associated with cholinergic crisis. Instead, it may be associated with other conditions or drug reactions.
C. Vomiting
Vomiting is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract by acetylcholine can lead to increased gastrointestinal motility and nausea/vomiting.
D. Fever
Fever is not typically associated with cholinergic crisis. Instead, it may suggest an infection or other inflammatory condition.
E. Drooling
Drooling is a symptom of cholinergic crisis. Excessive stimulation of salivary glands by acetylcholine can lead to increased salivation and drooling.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
