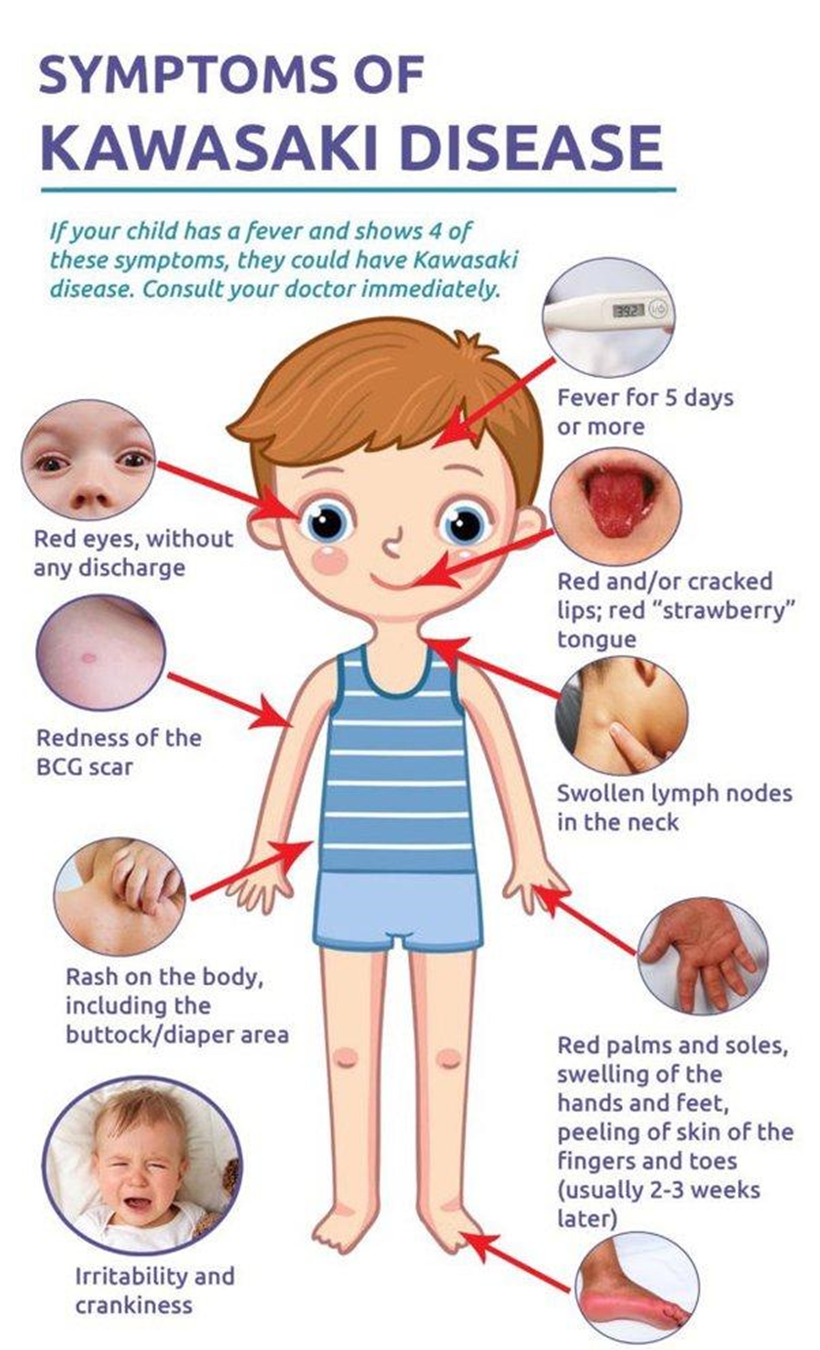
On assessment of a child admitted with a diagnosis of acute-stage Kawasaki disease, the nurse expects to note which clinical manifestation of the acute stage of the disease?
Cracked lips
Desquamation of the skin
Normal appearance
Conjunctival hyperemia
The Correct Answer is D
A. Cracked lips:
Incorrect: While red, cracked lips are part of the mucous membrane changes seen in Kawasaki disease, they are not specific to the acute stage. Mucous membrane changes can occur in both the acute and subacute stages.
B. Desquamation of the skin:
Incorrect: Desquamation, or peeling of the skin, is more characteristic of the subacute or convalescent stages of Kawasaki disease, particularly on the fingers and toes.
C. Normal appearance:
Incorrect: In the acute stage, the child with Kawasaki disease typically exhibits signs of illness, including fever and other clinical manifestations. A "normal appearance" would not be expected in the acute stage.
D. Conjunctival hyperemia.
Explanation: Conjunctival hyperemia, or redness of the eyes, is a common clinical manifestation of the acute stage of Kawasaki disease. Other typical signs and symptoms during this stage include fever, mucous membrane changes (such as red, cracked lips), changes in the extremities, rash, and cervical lymphadenopathy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
A.Reduce exposure to environmental organisms.
Explanation: Minimizing the child's exposure to environmental organisms helps reduce the risk of infections. This includes practices such as maintaining a clean environment and promoting good hygiene.
B. Maintain the child in a semiprivate room.
Explanation: The type of room (semiprivate or private) may not be directly related to infection control. However, maintaining a clean and controlled environment is important.
C.Use strict aseptic technique for all procedures.
Explanation: Strict aseptic technique is crucial to prevent the introduction of pathogens during procedures. This involves maintaining a sterile field and using appropriate infection control measures during medical interventions.
D.Ensure that anyone entering the child's room wears a mask.
Explanation: Wearing a mask helps prevent the spread of respiratory infections, which can be particularly risky for immunocompromised children. It is a measure to protect the child from potential airborne pathogens.
E. Apply firm pressure to a needlestick area for at least 10 minutes.
Explanation: Applying firm pressure to a needlestick area is relevant in the context of preventing bleeding or hematoma formation but is not directly related to infection control.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
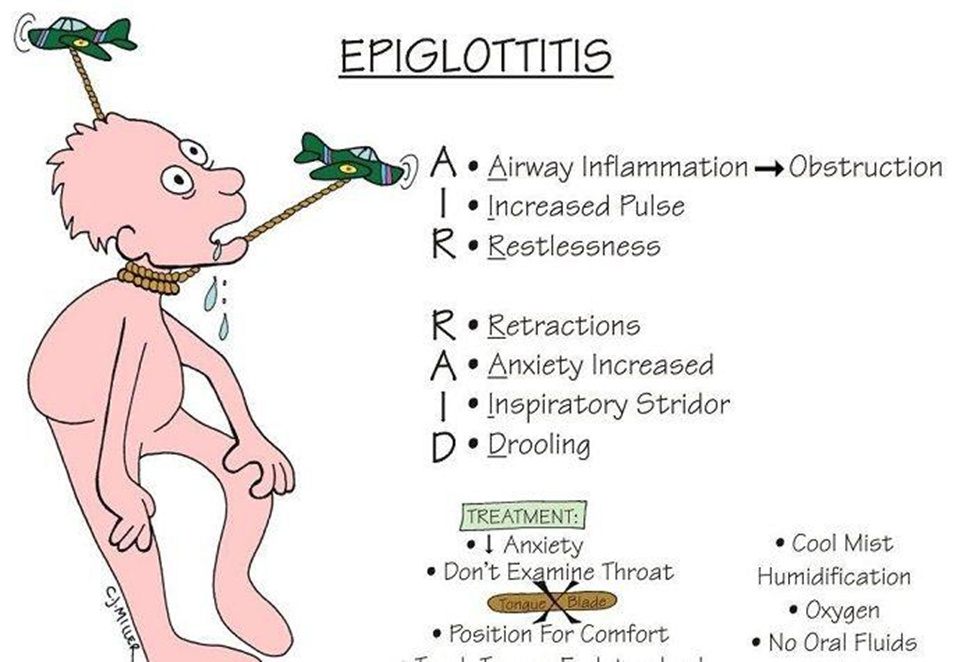
A. Contact the assigned emergency room physician to evaluate the need for an advanced airway
Explanation:
Epiglottitis is a medical emergency that can rapidly progress to airway obstruction. The classic signs and symptoms include a high fever, difficulty swallowing, voice hoarseness, inspiratory stridor, and sternal retractions. Immediate intervention may be necessary to secure the airway. Therefore, contacting the emergency room physician to evaluate the need for an advanced airway (such as intubation) is a priority.
B. Administer intravenous corticosteroids
Explanation: While corticosteroids may be used in the management of epiglottitis to reduce airway inflammation, securing the airway is the priority in the acute phase. Corticosteroids would typically be administered after securing the airway.
C. Obtain a throat culture
Explanation: Obtaining a throat culture is not the immediate priority in the case of suspected epiglottitis. Prompt intervention to secure the airway takes precedence over diagnostic tests.
D. Inspect the throat to obtain further data to support the diagnosis
Explanation: Direct visualization of the throat (inspection) may exacerbate the airway obstruction and is not recommended in the acute management of suspected epiglottitis. The priority is to secure the airway while minimizing agitation and discomfort for the child. Diagnostic procedures, such as obtaining a throat culture, can be considered after the airway is stabilized.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
