When the nurse checks the patient for orthodontic hypotension, what did the nurse have the patient do?
Physical exertion
Eat
Stand up
D. Lie down
The Correct Answer is C
Orthostatic hypotension is a drop in blood pressure that occurs when a person stands up from a sitting or lying down position. To check for orthostatic hypotension, the nurse typically takes the patient's blood pressure and heart rate while the patient is lying down, then has the patient stand up for a few minutes and takes the blood pressure and heart rate again. If the blood pressure drops significantly (usually a drop of 20 mm Hg or more) and the heart rate increases, it may indicate orthostatic hypotension.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Atherosclerosis is a complex disease process that involves the gradual buildup of plaques (fatty deposits) in the walls of arteries, leading to narrowing and reduced blood flow. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors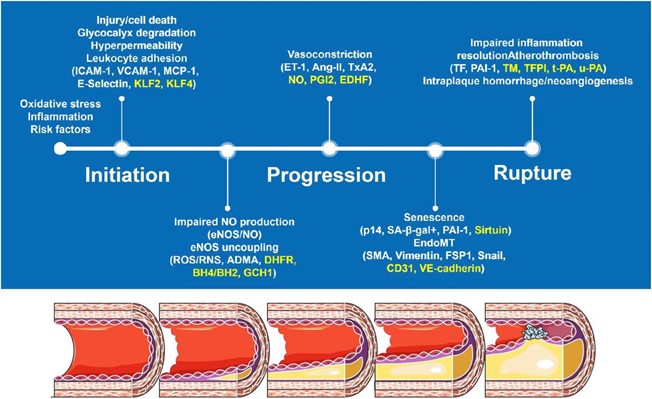
One of the key contributing factors to atherosclerosis is damage to the endothelial cells that line the walls of arteries. This damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, high levels of lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and other inflammatory factors. When the endothelial cells are damaged, they release chemicals that attract white blood cells to the area. These white blood cells then migrate into the arterial wall, where they begin to accumulate and form fatty deposits called plaques.
Over time, these plaques can grow and calcify, leading to further narrowing of the artery and reducing blood flow to the affected tissue. In addition, plaques can rupture and form blood clots, which can completely block blood flow to the affected area and cause a heart attack or stroke.
While high serum cholesterol levels are a risk factor for atherosclerosis, they are not the sole cause. Similarly, an increase in antithrombotic substances (substances that prevent blood clots) and congenital heart disease are not primary causes of atherosclerosis, although they may contribute to the disease process in some cases.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
In the normal electrocardiogram, the PR interval represents
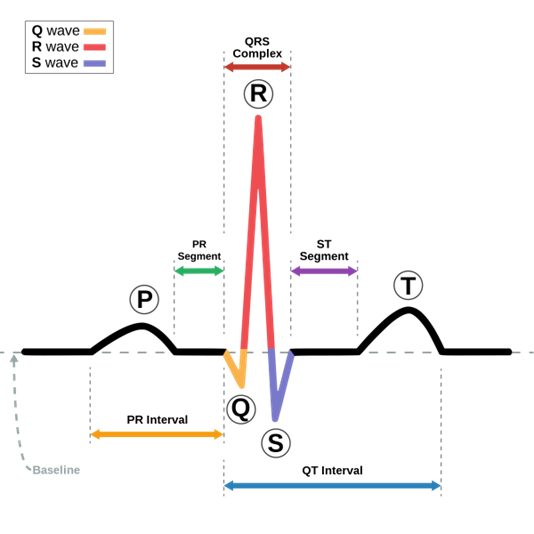
The PR interval represents the time from the onset of atrial activation to the onset of ventricular activity. During this time, the electrical impulse travels through the atria, the atrioventricular (AV) node, and the bundle of His before entering the ventricles and initiating ventricular depolarization. Option A is incorrect because the atrial depolarization is represented by the P wave. Option B is incorrect because the ventricular depolarization is represented by the QRS complex. Option D is incorrect because there is no such term as “electrical systole” of the ventricles in ECG interpretation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
