Renal Changes in pregnancy
- The renal system undergoes significant changes to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, excrete metabolic wastes, and regulate blood pressure during pregnancy
- The main renal changes include:
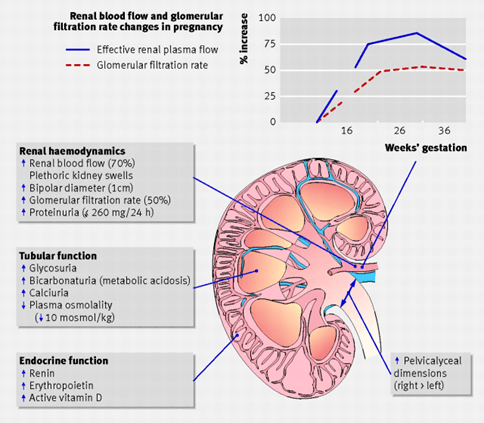
- Increased renal blood flow: The amount of blood flowing through the kidneys per minute increases by 50% to 80% during pregnancy. This is due to increased cardiac output and decreased renal vascular resistance. The renal blood flow peaks at mid-pregnancy and then declines slightly until term. The normal range of renal blood flow in pregnancy is 1200 to 1500 mL/min.
- Increased glomerular filtration rate: The rate at which the kidneys filter blood and produce urine increases by 40% to 60% during pregnancy. This is due to increased renal blood flow and increased glomerular permeability (the ability of the glomeruli or clusters of capillaries in the kidneys to allow substances to pass through). The glomerular filtration rate peaks at mid-pregnancy and then declines slightly until term. The normal range of glomerular filtration rate in pregnancy is 120 to 150 mL/min.
- Increased urinary output: The amount of urine produced per day increases by 25% to 50% during pregnancy. This is due to increased glomerular filtration rate and decreased tubular reabsorption (the process by which the kidneys return substances from the urine back to the blood). The urinary output peaks at mid-pregnancy and then declines slightly until term. The normal range of urinary output in pregnancy is 1200 to 1500 mL/day.
- Decreased serum creatinine and urea: The concentration of creatinine and urea in the blood decreases by 25% to 50% during pregnancy. This is due to increased glomerular filtration rate and increased plasma volume. The serum creatinine and urea reach their lowest point at mid-pregnancy and then remain stable until term. The normal range of serum creatinine in pregnancy is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/dL and the normal range of serum urea in pregnancy is 9 to 21 mg/dL.
- Increased urinary protein: The amount of protein excreted in the urine increases by 50% to 100% during pregnancy. This is due to increased glomerular permeability and increased protein intake. The urinary protein reaches its highest point at term and then returns to pre-pregnancy levels by the postpartum period. The normal range of urinary protein in pregnancy is less than 300 mg/day or less than 1+ on dipstick.
- Increased urinary glucose: The amount of glucose excreted in the urine increases by 100% to 200% during pregnancy. This is due to decreased tubular reabsorption and increased insulin resistance (the reduced ability of the body to respond to insulin). The urinary glucose reaches its highest point at mid-pregnancy and then declines slightly until term. The normal range of urinary glucose in pregnancy is less than 100 mg/dL or negative on dipstick.
- The renal changes result in increased renal clearance (the rate at which the kidneys remove substances from the blood) and decreased serum osmolality (the concentration of solutes in the blood) that maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, excrete metabolic wastes, and regulate blood pressure during pregnancy
- The renal changes may cause symptoms such as frequency, urgency, nocturia (urination at night), or glycosuria (glucose in the urine) that are normal or abnormal depending on the severity, duration, and frequency
Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Renal Changes in pregnancy
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Decreased serum osmolality and increased renal clearance are not the main causes of increased urine production during pregnancy. Decreased serum osmolality is a consequence of increased plasma volume and decreased thirst threshold, not a cause.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Urinary specific gravity 1.015 is within the normal range of 1.005 to 1.030.
Specific gravity measures how concentrated the urine is. A high specific gravity indicates dehydration or kidney dysfunction.
Taking iron supplements does not compensate for the decreased red blood cell count during pregnancy.
Less than 400 mg/dL or 2+ on dipstick indicates a severe glycosuria, which is almost certainly a sign of diabetes. A GTT is also recommended to diagnose diabetes.
Search Here
Related Topics
- Hypoglycemia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Preterm birth - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Macrosomia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Post-term birth - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Hyperbilirubinemia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Cardiovascular Changes in Pregnancy - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
