Respiratory
- The respiratory system undergoes significant changes to meet the increased oxygen requirements of pregnancy and to facilitate gas exchange between the maternal and fetal blood
- The main respiratory changes include:
- Increased oxygen consumption: The amount of oxygen used by the body per minute increases by 15% to 20% during pregnancy. This is due to increased metabolic rate (the rate at which chemical reactions occur in the body) and increased fetal oxygen demand. The oxygen consumption peaks at 32 weeks of gestation and then remains stable until term. The normal range of oxygen consumption in pregnancy is 250 to 300 mL/min.
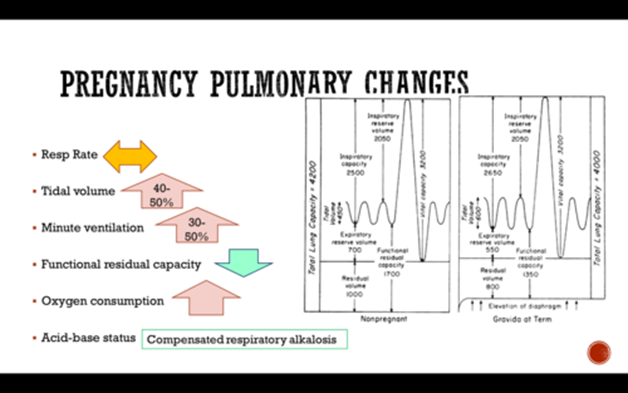
- Increased tidal volume: The amount of air breathed in or out per breath increases by 30% to 40% during pregnancy. This is due to increased progesterone levels that stimulate the respiratory center in the brain and increase the sensitivity to carbon dioxide. The tidal volume peaks at 28 weeks of gestation and then remains stable until term. The normal range of tidal volume in pregnancy is 500 to 700 mL.
-
- Decreased functional residual capacity: The amount of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration decreases by 20% during pregnancy. This is due to elevation of the diaphragm (the muscle that separates the chest and abdomen) by the gravid uterus and increased chest wall compliance (the ease of expansion of the chest). The functional residual capacity decreases progressively throughout pregnancy and reaches its lowest point at term. The normal range of functional residual capacity in pregnancy is 1.5 to 2 L.
- Increased minute ventilation: The amount of air breathed in or out per minute increases by 40% to 50% during pregnancy. This is due to increased tidal volume and increased respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute). The minute ventilation peaks at 28 weeks of gestation and then remains stable until term. The normal range of minute ventilation in pregnancy is 7 to 10 L/min.
- Decreased partial pressure of carbon dioxide: The pressure exerted by carbon dioxide in the arterial blood decreases by 15% during pregnancy. This is due to increased minute ventilation that removes more carbon dioxide from the body. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide reaches its lowest point at mid-pregnancy and then remains stable until term. The normal range of partial pressure of carbon dioxide in pregnancy is 27 to 32 mmHg.
- Increased partial pressure of oxygen: The pressure exerted by oxygen in the arterial blood increases by 5% during pregnancy. This is due to increased minute ventilation that brings more oxygen into the body. The partial pressure of oxygen reaches its highest point at mid-pregnancy and then remains stable until term. The normal range of partial pressure of oxygen in pregnancy is 95 to 105 mmHg.
- The respiratory changes result in increased alveolar ventilation (the amount of air reaching the alveoli or air sacs in the lungs) and decreased physiological dead space (the amount of air that does not participate in gas exchange) that enhance gas exchange between the maternal and fetal blood
- The respiratory changes may cause symptoms such as dyspnea (difficulty breathing), nasal congestion, epistaxis (nosebleed), or voice changes that are normal or abnormal depending on the severity, duration, and frequency
Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Respiratory
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Increased tidal volume and respiratory rate are the consequences of increased oxygen consumption during pregnancy, not the causes. Tidal volume increases by 40% and respiratory rate increases by 15% during pregnancy . These changes result in an increase in minute ventilation by 50% .
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Asthma is not a normal respiratory change in pregnancy, but a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the airways.
Asthma can cause symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Asthma can worsen or improve during pregnancy depending on various factors such as hormonal changes, allergen exposure, and stress.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Cocaine use is not a likely cause of nasal congestion and epistaxis in pregnancy.
Cocaine can cause damage to the nasal septum and mucosa, but it would also cause other symptoms such as agitation, tachycardia, hypertension, and fetal distress. Cocaine use in pregnancy is associated with increased risks of miscarriage, preterm labor, placental abruption, and fetal growth restriction.
The nurse should ask about substance use history and offer counseling and treatment if
Wrong because these symptoms are not indicative of a cardiovascular complication, unless there are other signs such as chest pain, palpitations, edema, or cyanosis.
A reduced iron level. This is because ingesting white clay dirt from the backyard, also known as calabash chalk or nzu, can bind iron and other minerals in the intestine and prevent their absorption. This can lead to iron deficiency anemia and other complications for the pregnant woman and the unb
Search Here
Related Topics
- Hypoglycemia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Preterm birth - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Macrosomia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Post-term birth - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Hyperbilirubinemia - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Cardiovascular Changes in Pregnancy - Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
