Maternal Newborn III
ATI Maternal Newborn III
Total Questions : 47
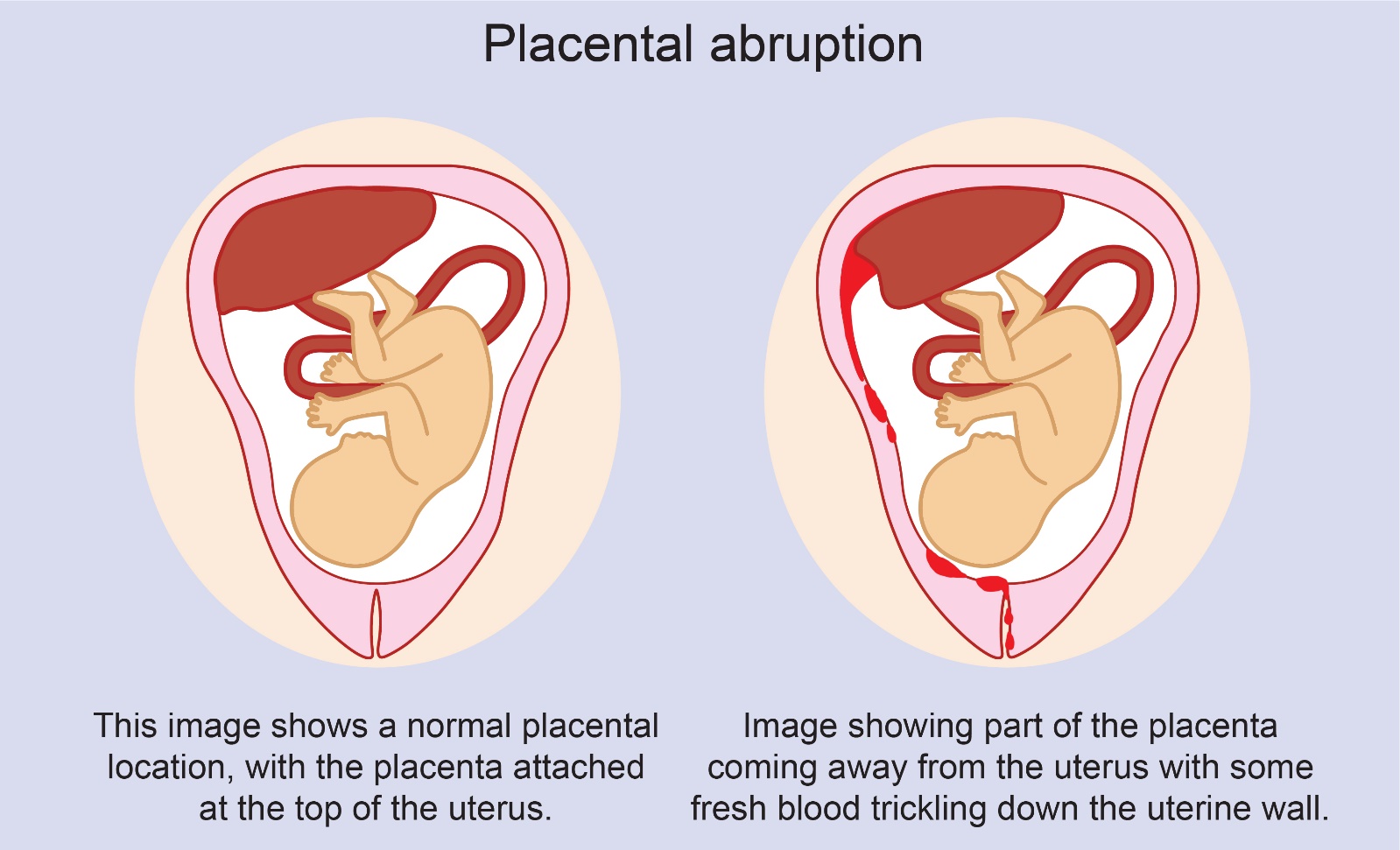
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse suspects that a pregnant client may be experiencing placenta abruption based on the assessment of which finding? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A: Absence of pain is not a sign of abruptio placenta. Abruption placenta is a condition where the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, causing bleeding and pain. The pain is usually severe and constant.
Choice B: Insidious onset is not a sign of abruptio placenta. Abruptio placenta is usually a sudden and acute event that occurs in the third trimester or during labor.
Choice C: Dark red vaginal bleeding is a sign of abruption placenta. The bleeding is caused by the rupture of blood vessels between the placenta and the uterus. The blood may be dark red because it is old or clotted.
Choice D: A rigid uterus is a sign of abruption placenta. The uterus becomes hard and tense as a result of the bleeding and contraction of the uterine muscles. This can impair the blood flow to the fetus and cause fetal distress.
Choice E: Absent fetal heart tones are a sign of abruption placenta. The loss of blood and oxygen to the fetus can cause fetal death or stillbirth. Fetal heart tones can be detected by using a Doppler device or a fetoscope.
A pregnant client in her second trimester has a hemoglobin level of 11 g/dL. The nurse interprets this as indicating
Explanation
Choice A: Hemodilution of pregnancy is a normal physiological phenomenon that occurs when the plasma volume increases more than the red blood cell mass, resulting in a lower hemoglobin concentration. The normal hemoglobin range for pregnant women in the second trimester is 10.5 to 14 g/dL.
Choice B: A multiple gestation pregnancy may cause a higher hemoglobin level due to increased erythropoietin production by the placenta. The normal hemoglobin range for pregnant women with twins in the second trimester is 12 to 16 g/dL.
Choice C: Greater-than-expected weight gain is not related to hemoglobin level. Weight gain during pregnancy depends on various factors such as pre-pregnancy weight, nutrition, activity level, and fetal growth.
Choice D: Iron deficiency anemia is a condition where the hemoglobin level is below the normal range due to inadequate iron intake or absorption, blood loss, or increased iron demand. The signs and symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia include fatigue, pallor, weakness, shortness of breath, and pica.
A nurse is providing prenatal care to a pregnant client. At which time would the nurse expect to screen the client for group B streptococcus infection?
Explanation
Choice A: 28 weeks' gestation is too early to screen for group B streptococcus infection. Group B streptococcus (GBS) is a type of bacteria that can cause serious infections in newborns if transmitted from the mother during labor and delivery. The optimal time to screen for GBS is between 35 and 37 weeks' gestation.
Choice B: 32 weeks' gestation is also too early to screen for GBS infection. Screening at this time may not reflect the true colonization status of the mother at the time of delivery, as GBS can be transient or intermittent.
Choice C: 16 weeks' gestation is much too early to screen for GBS infection. Screening at this time has no clinical value, as GBS colonization can change throughout pregnancy.
Choice D: 36 weeks' gestation is the appropriate time to screen for GBS infection. Screening at this time can identify mothers who are colonized with GBS and who need intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis.
A nurse is providing teaching about nutrition to a client at her first prenatal visit. Which of the following statements by the nurse should be included in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A: Vitamin E requirements do not decrease during pregnancy due to the increase in body fat. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that acts as an antioxidant and protects cell membranes from oxidative damage. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin E during pregnancy is 15 mg/day, which is the same as for non-pregnant women.
Choice B: Prenatal vitamins will meet your need for increased folic acid during pregnancy. Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for DNA synthesis and cell division. Folic acid deficiency can cause neural tube defects in the fetus, such as spina bifida and anencephaly. The RDA for folic acid during pregnancy is 600 mcg/day, which can be obtained from prenatal vitamins and fortified foods.
Choice C: You will not need to double your intake of protein during pregnancy. Protein is a macronutrient that provides amino acids for tissue growth and repair. The RDA for protein during pregnancy is 1.1 g/kg/day, which is only slightly higher than for non-pregnant women (0.8 g/kg/day).
Choice D: You will not need to increase your intake of calcium during pregnancy. Calcium is a mineral that is important for bone health and muscle contraction. Calcium absorption and retention are enhanced during pregnancy, so there is no need to increase the intake above the RDA of 1000 mg/day for women aged 19 to 50 years.
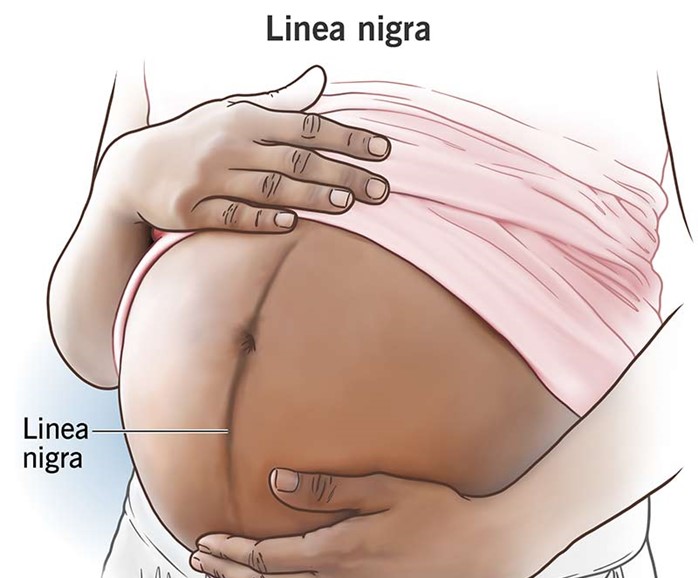
Assessment of a pregnant woman reveals a pigmented line down the middle of her abdomen. The nurse documents this as which finding?
Explanation
Choice A: Striae gravidarum are stretch marks that appear on the abdomen, breasts, or thighs during pregnancy. They are caused by the tearing of the connective tissue in the dermis due to rapid growth or weight gain.
Choice B: Linea nigra is a dark vertical line that runs from the umbilicus to the pubic area. It is caused by increased melanin production due to hormonal changes during pregnancy. This is the correct choice because it matches the description in the question.
Choice C: Vascular spiders are dilated blood vessels that appear on the skin as red or purple spider-like lesions. They are caused by increased estrogen levels and blood volume during pregnancy. They are usually found on the face, neck, chest, or arms.
Choice D: Melasma is a condition that causes brown or gray patches on the face, especially on the forehead, cheeks, nose, or upper lip. It is caused by increased melanin production due to sun exposure and hormonal changes during pregnancy. It is also known as chloasma or the mask of pregnancy.
Explanation
Choice A: A clear liquid diet is not appropriate for a client with hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a severe form of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy that can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and weight loss. A clear liquid diet does not provide adequate calories, protein, vitamins, or minerals for the client and the fetus.
Choice B: Administration of diethylstilbestrol is not indicated for a client with hyperemesis gravidarum. Diethylstilbestrol is a synthetic estrogen that was used in the past to prevent miscarriage and premature birth, but it was found to cause serious adverse effects such as vaginal cancer, infertility, and birth defects in the offspring.
Choice C: Total parenteral nutrition is the correct choice because it provides a complete and balanced source of nutrients through a central venous catheter. It is used for clients who cannot tolerate oral or enteral feeding due to severe gastrointestinal disorders such as hyperemesis gravidarum. It helps to prevent malnutrition, dehydration, and ketosis in the client and the fetus.
Choice D: Nothing by mouth is not a suitable option for a client with hyperemesis gravidarum. It can worsen the condition by causing starvation, acidosis, and ketosis. It can also increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia if the client vomits.
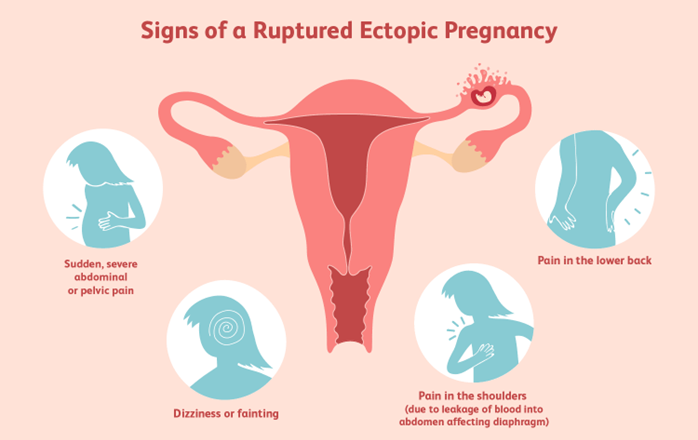
A client is suspected of having a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Which assessment would the nurse identify as the priority?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Hemorrhage is the most life-threatening complication of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, as it can lead to hypovolemic shock and death. The nurse should monitor the client's vital signs, blood loss, and level of consciousness, and administer fluids and blood products as ordered.
Choice B reason: Edema is not a common sign of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, and it is not a priority over hemorrhage. Edema may be caused by other conditions, such as heart failure, kidney disease, or venous insufficiency.
Choice C reason: Infection is a possible complication of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, but it is not as urgent as hemorrhage. Infection may manifest as fever, chills, malaise, or foul-smelling vaginal discharge. The nurse should administer antibiotics as ordered and monitor the client's temperature and white blood cell count.
Choice D reason: Jaundice is not a typical symptom of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, and it is not a priority over hemorrhage. Jaundice may indicate liver dysfunction or hemolytic anemia, which are unrelated to ectopic pregnancy. The nurse should assess the client's skin and sclera color, and check the liver enzymes and bilirubin levels.
Explanation
Choice B reason: This is an inappropriate answer because it implies that the nurse does not understand or care about the client's emotional state. It also suggests that the client has no reason to cry, which is invalidating and hurtful.
Choice C reason: This is an inappropriate answer because it focuses on the physical pain rather than the emotional pain of the client. It also implies that the nurse wants to avoid dealing with the client's feelings and just give them a medication to make them stop crying.
Choice D reason: This is an inappropriate answer because it is inaccurate and misleading. A spontaneous abortion, also known as a miscarriage, occurs when a pregnancy ends before 20 weeks of gestation. At this stage, the baby is already formed and has a heartbeat, organs, and limbs. Saying that a baby still wasn't formed in the womb is false and insensitive to the client's loss.
Assessment of a pregnant woman reveals that she compulsively craves ice. The nurse documents this finding as
Explanation
Choice A reason: Linea nigra is a dark vertical line that appears on the abdomen of some pregnant women. It is caused by increased melanin production and usually fades after delivery.
Choice B reason: Pica is a condition in which a person has an abnormal desire to eat substances that are not food, such as ice, clay, dirt, or chalk. It is more common in pregnant women and may indicate a deficiency in iron or other nutrients.
Choice C reason: Ballottement is a technique of palpating a floating structure by bouncing it gently and feeling it rebound. In obstetrics, it can be used to detect the presence of the fetus by feeling its head move when the cervix is tapped.
Choice D reason: Quickening is the first perception of fetal movements by the pregnant woman. It usually occurs between 16 and 20 weeks of gestation.

After reviewing the information provided in the client's medical record, which of the following complications should the nurse identify that the client is at risk of developing?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Preeclampsia is a condition in which a pregnant woman develops high blood pressure and proteinuria (protein in the urinE.. It can lead to serious complications such as eclampsia, which is seizures caused by preeclampsia, and HELLP syndrome, which is hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets. The main risk factor for preeclampsia is chronic hypertension, which means high blood pressure before pregnancy or before 20 weeks of gestation. Preeclampsia can be detected by measuring the blood pressure and urine protein level. Uric acid is not a reliable indicator of preeclampsia.
Choice C reason: Eclampsia is a severe complication of preeclampsia that causes seizures and can be fatal for both the mother and the baby. It usually occurs after 20 weeks of gestation or during labor or postpartum. The main risk factor for eclampsia is preeclampsia, which means high blood pressure and proteinuria during pregnancy. Eclampsia can be prevented by treating preeclampsia with antihypertensive drugs and magnesium sulfate, which is a medication that prevents seizures. Magnesium sulfate can also lower the serum magnesium level, which is the amount of magnesium in the blood. However, magnesium level is not a diagnostic criterion for eclampsia.
Choice D reason: Placenta previa is a condition in which the placenta covers part or all of the opening of the cervix. It can cause bleeding during pregnancy or delivery and can endanger both the mother and the baby. The main risk factor for placenta previa is previous cesarean section or other uterine surgery, which can cause scarring or damage to the uterine wall. Placenta previa can be detected by ultrasound, which is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the uterus and placenta. Hemoglobin is not a relevant factor for placenta previa. Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It can cause complications for both the mother and the baby, such as macrosomia, hypoglycemia, and birth trauma. The main risk factor for gestational diabetes is glucose intolerance, which means the body cannot use glucose effectively. Glucose intolerance can be detected by measuring the serum glucose level, which is the amount of glucose in the blood.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 47 questions on the ATI Maternal Newborn III Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



