_RN_Fundamentals_2019_with_NGN
ATI_RN_Fundamentals_2019_with_NGN
Total Questions : 71
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreWhile assessing the client's abdomen, you note that the Jackson-Pratt drain's reservoir is expanded and half full of blood. Which is the appropriate action for you to take at this time?.
Explanation
Leaving the drain until the end of the shift is not appropriate because it could lead to complications such as:
- Hematoma formation:Blood accumulation in the tissues surrounding the drain can put pressure on surrounding structures,potentially impairing blood flow and causing tissue damage.
- Infection:A reservoir containing blood provides a favorable environment for bacterial growth,increasing the risk of infection.
- Drain occlusion:Clotted blood can block the drain,preventing effective drainage and leading to fluid buildup and potential infection.
- Decreased wound healing:Excessive blood loss can delay wound healing by depriving the tissues of necessary oxygen and nutrients.
Removing the drain without the surgeon's order is not appropriate because:
- Premature removal:It could disrupt the healing process and lead to complications such as fluid collection or infection.
- Assessment limitation:Removing the drain would eliminate the ability to monitor ongoing blood loss and could mask potential complications.
A Jackson-Pratt drain works by creating suction when the bulb is squeezed and emptied¹. The bulb should be emptied before it is more than half full to avoid the discomfort of the weight of the drain pulling on the internal tubing and to maintain the suction
Notifying the surgeon about the blood loss is wrong because it is not an urgent situation unless there are signs of excessive bleeding, such as bright red blood, clots, or a sudden increase in the amount of drainage²³. The surgeon should be notified if the drainage is more than 100 ml in 24 hours or if the color changes from serosanguineous (pink) to sanguineous (red)
A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for a 250 mL IV fluid bolus. The nurse administers a 500 mL IV bolus.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Notify the healthcare provider.
The nurse should first notify the healthcare provider of the error in administering the IV bolus.
This is important because the healthcare provider can assess the situation and provide guidance on how to proceed.
Choice A is not the correct answer because obtaining the client’s vital signs is important but not the first action the nurse should take.
Choice C is not the correct answer because documenting the incident in the client’s medical record is important but not the first action the nurse should take.
Choice D is not the correct answer because assessing the client for adverse reactions is important but not the first action the nurse should take.
A nurse is documenting client care.
Which of the following abbreviations should the nurse use?
Explanation
The nurse should use the abbreviation “BRP” for bathroom privileges.
This is a commonly accepted abbreviation in the medical field and is used to indicate that a client has permission to use the bathroom.
Choice A is not the correct answer because “SC” is not a commonly accepted abbreviation for subcutaneous.
Instead, “SQ” or “SubQ” are more commonly used.
Choice B is not the correct answer because “SS” is not a commonly accepted abbreviation for sliding scale.
Instead, “Sliding Scale” should be written out in full to avoid confusion.
Choice D is not the correct answer because “OJ” is not a commonly accepted medical abbreviation for orange juice.
Instead, “orange juice” should be written out in full to avoid confusion.
A nurse is caring for a client.
Exhibit 1 Vital Signs 0800: Exhibit 2 Temperature 37.6° C (99.7° F) Blood pressure 108/56 mm Hg Heart rate 66/min Respiratory rate 18/min Pulse oximetry 97% on room air 0830: Temperature 37.5° C (99.5° F) Blood pressure 88/56 mm Hg Heart rate 104/min Respiratory rate 24/min Pulse oximetry 93% on room air Select the 4 findings that require immediate follow-up.
Explanation
The blood pressure has dropped significantly from 108/56 mm Hg to 88/56 mm Hg.
The pulse oximetry has decreased from 97% to 93%, indicating a decrease in oxygen saturation.
The heart rate has increased from 66/min to 104/min.
The level of consciousness is always an important factor to monitor in a patient.
A. Temperature: The temperature has only changed slightly and is within the normal range.
C. Respiratory rate: The respiratory rate has increased but is still within normal range.
G. Skin color and temperature: This information is not provided in the exhibit.
A nurse is preparing to insert an IV catheter for an adult client.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
The nurse should place the extremity in a dependent position before inserting an IV catheter.
This helps to dilate the veins and make them more visible and easier to access.
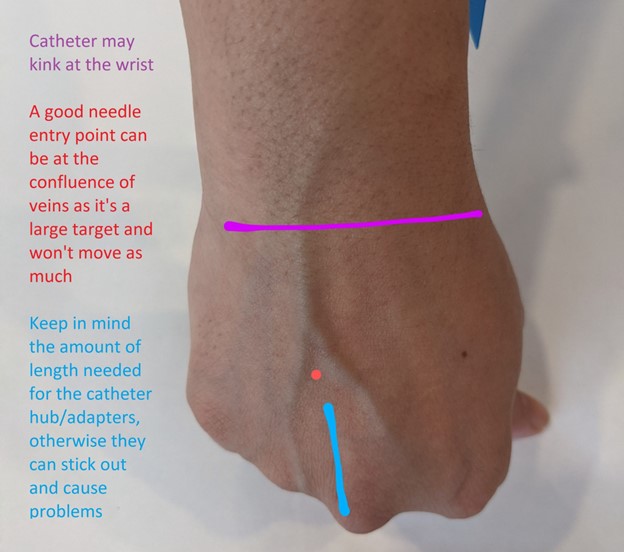
Choice A is wrong because the nurse should choose a site that is distal to the most proximal site on the extremity selected.
This helps to preserve more proximal sites for future use if needed.
Choice B is wrong because applying a cool compress before insertion of an IV catheter can cause vasoconstriction and make it more difficult to access the vein.
Instead, a warm compress can be applied to help dilate the veins.
Choice C is wrong because the tourniquet should be placed above, not below, the proposed insertion site to help dilate the vein and make it easier to access.
A nurse is implementing seizure precautions for a client who has a seizure disorder.
Which of the following equipment should the nurse place at the client's bedside? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
An oral airway can help maintain an open airway during a seizure.
Supplemental oxygen supplies can be used to provide oxygen if the client’s breathing is compromised.
Oral suction equipment can be used to clear secretions from the client’s mouth and prevent aspiration.
Limb restraints: Restraints should not be used during a seizure as they can cause injury.
Blood glucose monitor: While it is important to monitor blood glucose levels in clients with seizures, it is not a priority during a seizure.
A nurse is teaching a group of newly licensed nurses about the Braden scale.
Which of the following responses by a newly licensed nurse indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The Braden scale measures six elements: sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, and friction/shear.
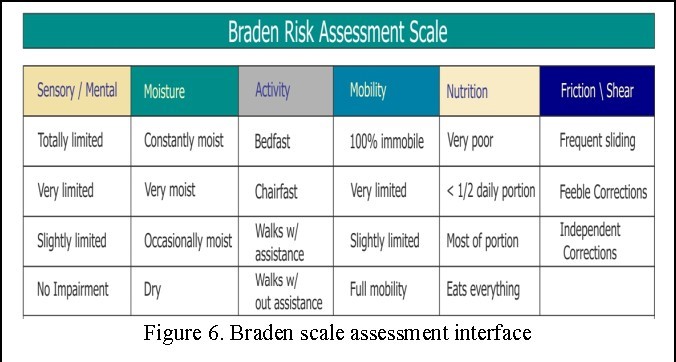
“The higher the score, the higher the pressure injury risk”: This statement is incorrect.
The lower the score on the Braden scale, the higher the risk for pressure injury.
“Each element has a range from one to five points”: This statement is incorrect.
Each element has a range from one to four points, except for friction/shear which has a range from one to three points.
“The client’s age is part of the measurement”: This statement is incorrect. Age is not one of the elements measured by the Braden scale.
A nurse is planning care for a female client who has an indwelling urinary catheter.
Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan?
Explanation
This is important to prevent urine from flowing back into the bladder, which can cause infection 1.
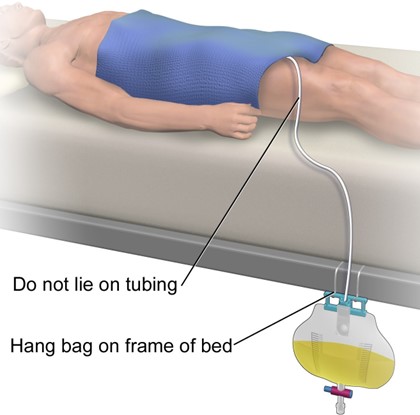
Choice A is incorrect because the catheter should be secured to the outer side of the thigh, not taped to the lower abdomen 2.
Choice B is incorrect because attaching the drainage bag to the side rails of the bed can cause it to be above the level of the bladder.
Choice C is incorrect because it is important to empty the drainage bag regularly, not just when it is three-quarters full.
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving continuous enteral feeding via NG tube.
Which of the following is an unexpected finding?
Explanation
Gastric residual of 300 mL at the end of the shift is an unexpected finding.
Gastric residual volume refers to the volume of fluid remaining in the stomach during enteral feeding.
A gastric residual volume of less than or equal to 500 mL every 6 hours is considered safe and indicates that the gastrointestinal tract is functioning.
Choice B is wrong because weight gain is expected during enteral feeding.
Choice C is wrong because a blood glucose level of 110 mg/dL is within the normal range.
Choice D is wrong because diarrhea can be a common side effect of enteral feeding.
A nurse is caring for a client who has a tracheostomy.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Secure the tracheostomy ties to allow one finger to fit snugly underneath. This is important to ensure that the tracheostomy tube is secure and in place.
Choice B is wrong because normal saline is not typically used to cleanse the skin around the stoma.
Choice C is wrong because soaking the outer cannula in warm, soapy tap water is not a recommended method of cleaning.
Choice D is wrong because a cotton tip applicator should not be used to clean inside the inner cannula.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 71 questions on the ATI_RN_Fundamentals_2019_with_NGN Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



