Rn Mental Health 2023 Exam 3
ATI Rn Mental Health 2023 Exam 3
Total Questions : 65
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreFor which of the following clients is a nurse considered a mandated reporter to the appropriate agency?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
A client lying about suicidal ideation to their provider does not fall under mandatory reporting unless there is evidence or suspicion of harm to self or others. In this case, the client has reported lying, which indicates there is no actual suicidal ideation or intent.
Choice B reason:
While smoking marijuana may be illegal in some jurisdictions, it does not typically require mandatory reporting by a nurse unless it directly affects patient care or involves minors.
Choice C reason:
Theft from an employer is a legal issue but does not require mandatory reporting by a nurse unless it involves stealing medication or other actions that could harm patients.
Choice D reason:
This choice clearly involves child abuse, which is a reportable offense. Nurses are mandated reporters for any suspected child abuse or neglect. Tying a child to a bed as punishment can cause physical and emotional harm, and it is the nurse's duty to report this to the appropriate agency to ensure the child's safety.
A nurse is leading a crisis intervention group for adolescents who witnessed the suicide of a classmate. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
When leading a crisis intervention group, especially for adolescents who have witnessed the traumatic event of a classmate's suicide, it is crucial to first identify the individuals' prior coping skills. This initial step is essential because it helps the nurse to understand the baseline coping mechanisms each adolescent has previously employed. Adolescents may have varying levels of resilience and different strategies for dealing with stress and trauma. By identifying these skills early on, the nurse can tailor the intervention to reinforce these existing skills while introducing new coping strategies. This personalized approach ensures that each adolescent's unique needs are addressed, which is particularly important in the aftermath of a suicide, where feelings of guilt, confusion, and grief can be overwhelming. Moreover, understanding their prior coping skills can help the nurse to predict potential challenges and provide targeted support to those who may be more vulnerable or at risk of negative outcomes.
Choice B reason:
Reviewing community resources is an important action but not the first one that should be taken. Community resources can provide additional support and services to the adolescents after the initial crisis intervention. These resources might include mental health services, support groups, or educational programs. However, before directing adolescents to these resources, it is essential to assess their current psychological state and coping abilities. This ensures that the resources recommended are appropriate and beneficial for each individual's specific situation.
Choice C reason:
Discussing the importance of confidentiality is a critical component of any therapeutic intervention, particularly in a group setting. It creates a safe space where adolescents feel secure to share their thoughts and feelings without fear of judgment or breach of privacy. However, this is not the first action to take. Establishing confidentiality is part of setting the ground rules for the group intervention, which typically occurs after initial assessments and once a rapport has been established.
Choice D reason:
Initiating referrals may be necessary for adolescents who require more specialized care or individual therapy. Referrals are an important part of the continuum of care and ensure that adolescents have access to the appropriate level of support. However, this action is typically taken after the initial crisis intervention session, where the nurse has had the opportunity to assess each adolescent's needs and determine who might benefit from additional services.
A nurse is providing discharge teaching about the manifestations of relapse to the family of a client who has schizophrenia. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Excessive sleep or a significant change in sleep patterns can be an indicator of a relapse in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia can disrupt the regular sleep-wake cycle, leading to either insomnia or hypersomnia (excessive sleep). When a client with schizophrenia begins sleeping more than usual, it may suggest a worsening of symptoms or an impending relapse. It's essential for the nurse to include this information in the discharge teaching so that the family can monitor and seek help if the client's sleep patterns change significantly.
Choice B reason:
An inability to concentrate is another potential sign of a relapse in schizophrenia. Cognitive difficulties, including problems with concentration, are common in schizophrenia and can worsen during a relapse. This symptom can affect the client's ability to function daily and adhere to treatment plans. Therefore, it is crucial for the nurse to educate the family about this sign so they can recognize it early and consult with healthcare providers.
Choice C reason:
Exhibiting an inflated sense of self is not typically associated with schizophrenia relapse. While some individuals with schizophrenia might experience grandiose delusions, an inflated sense of self is not a common or specific sign of relapse. The family should be aware of more characteristic symptoms such as changes in sleep, concentration, mood, or behavior.
Choice D reason:
Increasing participation in social activities is generally not a sign of relapse in schizophrenia; in fact, it is often encouraged as part of the recovery process. Social withdrawal, rather than increased participation, would be more concerning and could indicate a relapse. It's important for families to support the client's social engagement as it can be beneficial for their overall well-being.
A nurse in a mental health facility is caring for a group of clients. After assessing the clients, which of the following clients requires an update to their plan of care to ensure client safety?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
A client with anorexia nervosa expressing a fear of gaining weight does require careful monitoring and intervention, but this does not typically pose an immediate risk to their safety. The treatment plan should focus on addressing the eating disorder and any associated psychological issues, but it may not necessitate an urgent change in the plan of care regarding safety concerns.
Choice B reason:
While a client with schizophrenia exhibiting tangential associations in speech indicates a need for ongoing psychiatric care, it does not inherently suggest an immediate risk to safety that would require an urgent update to the care plan. These speech patterns are a symptom of schizophrenia and should be addressed through appropriate therapeutic and medication management strategies.
Choice C reason:
A client with bipolar disorder exhibiting poor impulse control presents an immediate safety concern. Poor impulse control can lead to risky behaviors, self-harm, or harm to others. This situation requires an urgent update to the care plan to include safety measures such as close supervision, environmental modifications, and possibly medication adjustments to manage impulsivity.
Choice D reason:
A client with Alzheimer's disease having difficulty remembering the names of family members is experiencing a symptom of their condition. While this is distressing and requires a compassionate approach to care, it does not typically pose an immediate safety risk that would necessitate an urgent update to the care plan.
A nurse observes the caregiver of a client who has Alzheimer's disease throwing magazines on the floor and crying. Which of the following actions should the case manager take first?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Discussing relaxation techniques with the caregiver is a beneficial action that can help manage stress. However, it may not be the most immediate need for a caregiver who is in the midst of an emotional crisis. Relaxation techniques are more preventive and are best introduced when the caregiver is receptive and not overwhelmed by acute distress.
Choice B reason:
Referring the caregiver to a local support group is an excellent long-term strategy for providing support and resources. Support groups can offer a sense of community and shared experience, which is invaluable. Nonetheless, this action does not address the caregiver's immediate emotional needs and should follow after providing immediate emotional support.
Choice C reason:
Consulting social services to explore counseling options is an important step in supporting the caregiver's mental health. Counseling can provide professional assistance and coping strategies for the caregiver's stress and emotional burden. However, this is a step that should be taken after addressing the caregiver's immediate emotional distress.
Choice D reason:
Offering to talk with the caregiver about their feelings is the most immediate and direct way to provide support. It addresses the caregiver's current emotional state and provides an outlet for their feelings. Active listening and empathetic communication can help alleviate the caregiver's distress and serve as a bridge to further support and resources.
A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing a situational crisis following the sudden loss of their adolescent child. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Providing teaching on the use of coping skills is an important part of helping a client manage a situational crisis. Coping skills can include stress management techniques, relaxation methods, and problem-solving strategies. These skills are vital for the client to regain a sense of control and begin the healing process. However, this is not the immediate action to take when a client is experiencing a crisis following a significant loss.
Choice B reason:
Assisting the client to identify a friend or a support system is beneficial for providing emotional support and reducing feelings of isolation. Social support is a key factor in improving outcomes for individuals in crisis. However, this step comes after ensuring the client's immediate safety and addressing any potential risks.
Choice C reason:
Planning regular follow-up visits is crucial for ongoing support and monitoring the client's progress. Follow-up visits provide opportunities for the nurse to reassess the client's condition, adjust the care plan as needed, and continue providing education and support. Nevertheless, this is a subsequent step after initial safety concerns are addressed.
Choice D reason:
The first and most critical action for a nurse caring for a client in a situational crisis, especially after the sudden loss of a child, is to determine if the client has thoughts of self-harm. A situational crisis can lead to overwhelming emotions, which may result in suicidal ideation or attempts. Ensuring the client's safety is the top priority, and immediate intervention is required if there is any indication of self-harm thoughts.
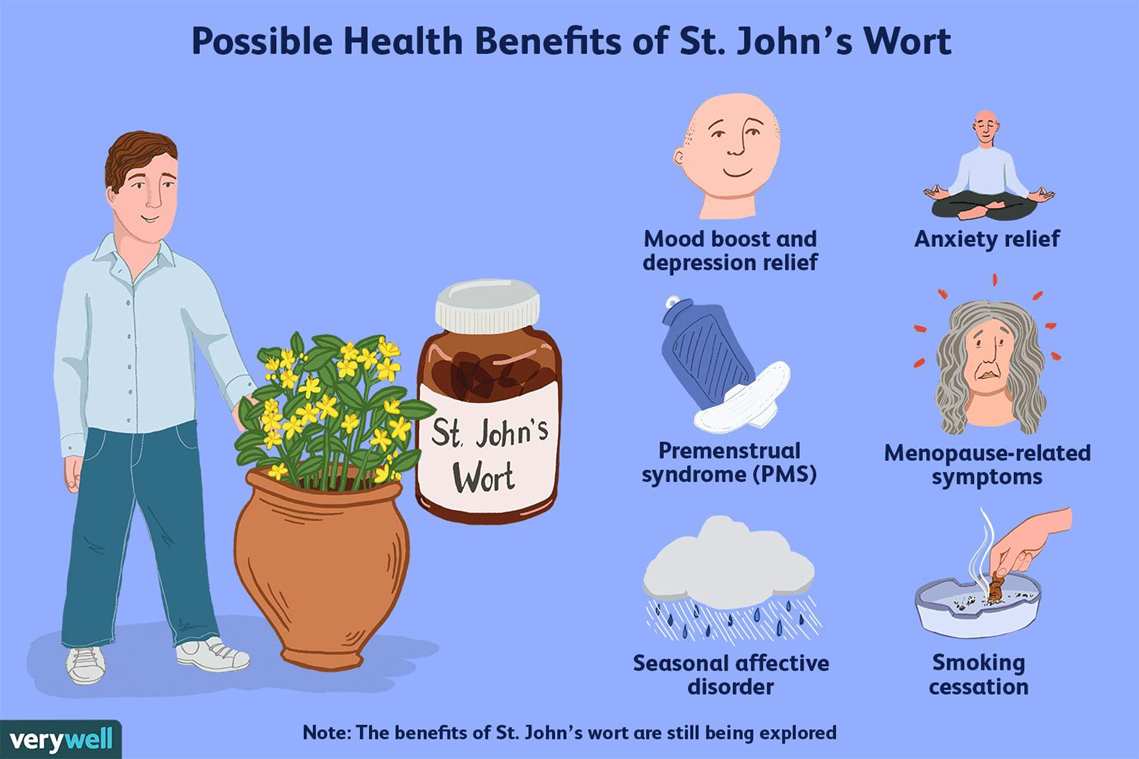
A nurse is teaching a client who is about to start taking fluoxetine. The nurse should instruct the client that which of the following supplements interacts adversely with fluoxetine?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
St. John's wort is known to interact adversely with fluoxetine. Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used to treat depression and other conditions. St. John's wort also has effects on serotonin, and when taken with fluoxetine, it can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include confusion, rapid heart rate, dilated pupils, loss of muscle coordination, heavy sweating, and muscle rigidity³. Therefore, it is crucial for patients on fluoxetine to avoid taking St. John's wort to prevent any serious complications.
Choice B reason:
Soy protein is not known to have a significant interaction with fluoxetine. Soy products are commonly consumed foods and are generally considered safe. However, patients should always consult with their healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it does not interfere with their medication regimen.
Choice C reason:
Echinacea is commonly used to support the immune system, especially for colds and other respiratory infections. There is no well-documented interaction between echinacea and fluoxetine, but as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before combining it with prescription medications.
Choice D reason:
Ginkgo biloba is often used for memory enhancement or to improve circulation. While there are some concerns about ginkgo's potential to affect bleeding due to its blood-thinning properties, there is no direct adverse interaction with fluoxetine. However, patients taking fluoxetine should be cautious with any supplements that can affect bleeding, especially if they are also taking other medications with similar effects.
A nurse is caring for a client who was involuntarily committed and is scheduled to receive electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). The client refuses the treatment and will not discuss why with the healthcare team. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Asking the client's family to encourage the client to receive ECT may be a supportive measure, but it should not be the first action taken. The client's autonomy and right to refuse treatment must be respected, even if they are involuntarily committed. Family members can be involved in the discussion, but the client's decision should be paramount.
Choice B reason:
Telling the client they cannot refuse treatment because they were involuntarily committed is incorrect. Involuntary commitment does not automatically override a client's right to refuse treatment. Clients have the right to be informed about their treatment and to refuse it unless specific legal criteria are met.
Choice C reason:
Documenting the client's refusal of the treatment in the medical record is the correct action. It is essential to record the client's decision and the discussion surrounding it. This documentation ensures that the client's rights are respected and provides a legal record of the interaction.
Choice D reason:
Informing the client that ECT does not require client consent is incorrect and unethical. Consent is a fundamental patient right, and all clients, including those involuntarily committed, have the right to be informed about their treatment options and to give or withhold consent unless they are legally deemed incompetent to make such decisions.
A nurse is caring for a client who is scheduled for electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). The client states, "I no longer want to have the treatment." Which of the following statements would be an appropriate response from the nurse?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Telling a client that they cannot refuse treatment because they were admitted involuntarily is incorrect. Even if a client is admitted involuntarily, they still have the right to refuse treatment unless they are deemed incompetent or a danger to themselves or others. It is essential to respect the client's autonomy and rights.
Choice B reason:
While it may be true that the client could feel better after ECT, this statement dismisses the client's current concerns and does not acknowledge their right to refuse treatment. It is important to address the client's feelings and provide support rather than making promises about the outcome.
Choice C reason:
This is the correct response because it respects the client's decision and autonomy. It also involves the provider, who can discuss the decision with the client, provide more information, or explore other options. It is a nurse's responsibility to communicate the client's decisions to the provider.
Choice D reason:
Administering medication to help the client relax without addressing their concerns about the treatment is not appropriate. It does not respect the client's right to refuse treatment and could be considered coercive.
For which of the following adverse effects should a nurse monitor a client taking citalopram?
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Urinary retention is not commonly associated with citalopram. Citalopram, an SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor), primarily affects serotonin levels in the brain and does not typically impact the urinary system to the extent of causing retention.
Choice B reason:
Decreased libido is a known adverse effect of citalopram. SSRIs, including citalopram, can affect sexual function, leading to decreased libido, difficulty achieving orgasm, or erectile dysfunction. This is due to the increased serotonin levels which can negatively impact the sexual response cycle.
Choice C reason:
While bruising is not a hallmark side effect of citalopram, it can occur, especially if there is an interaction with other medications that affect blood clotting. Citalopram can potentially increase the risk of bleeding, and easy bruising may be a sign of this. However, it is less common than other side effects like sexual dysfunction.
Choice D reason:
Jaundice is not a typical adverse effect of citalopram. Jaundice usually indicates a problem with the liver, and while liver function abnormalities have been reported with citalopram use, they are rare. Monitoring for jaundice is not part of the routine assessment for patients on citalopram unless there is a pre-existing liver condition or concurrent use of other hepatotoxic drugs.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 65 questions on the ATI Rn Mental Health 2023 Exam 3 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



