RN PREDICTOR ASSESSMENT EXIT
ATI RN PREDICTOR ASSESSMENT EXIT
Total Questions : 164
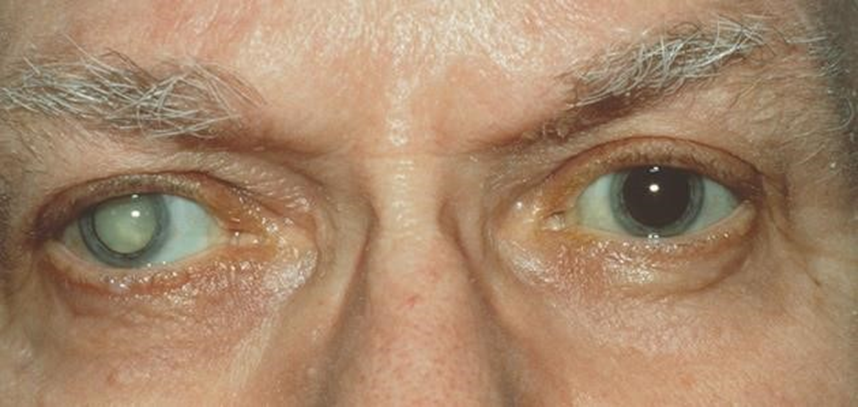
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse is assisting with the admission of an older adult client. Which of the following subjective findings suggests that the client may have cataracts?
Explanation
A. Sudden dimmed vision: Sudden dimmed vision may indicate other ocular issues, such as retinal detachment or macular degeneration, but it is not a specific indicator of cataracts.
Cataracts typically cause a gradual clouding of vision.
B. Cloudy vision: Cloudy or blurred vision is a classic symptom of cataracts. Cataracts cause the lens of the eye to become cloudy, leading to vision problems such as difficulty seeing in low light, blurry vision, or seeing halos around lights.
C. Intermittent flashes of light: Intermittent flashes of light are more commonly associated with conditions such as retinal detachment or migraine aura, rather than cataracts.
D. Pain in the eyes: Pain in the eyes is not typically associated with cataracts unless there are complications such as increased intraocular pressure or inflammation.
A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who is in active labor. Which of the following data is the priority for the nurse to collect following an amniotomy?
Explanation
A. Amniotic fluid color: While the color of amniotic fluid can provide important information about fetal well-being and possible complications, the priority immediately following an amniotomy is to assess the fetal heart rate to ensure fetal well-being and monitor for any signs of fetal distress.
B. The client's temperature: While maternal temperature should be monitored regularly during labor to detect signs of infection, it is not the priority immediately following an amniotomy. Fetal well-being takes precedence.
C. Frequency of contractions: Monitoring the frequency of contractions is important for assessing progress in labor and identifying any abnormalities, but it is not the priority immediately following an amniotomy. Fetal well-being should be assessed first.
D. Fetal heart rate: Following an amniotomy, the priority is to assess the fetal heart rate to ensure that the umbilical cord has not prolapsed and that the fetus is not experiencing distress due to changes in amniotic fluid volume or other factors related to the amniotomy. Monitoring fetal heart rate allows for early detection of any signs of fetal distress and prompt intervention if needed.
A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a newborn. Which of the following information should the nurse use to identify the newborn?
Explanation
A. Name and medical record number: This information is unique to each individual and is used to accurately identify patients in healthcare settings, including newborns.
B. Birth date and mother's name: While important for identification, this information alone may not be sufficient to accurately identify a newborn, especially in situations where there may be multiple newborns with similar birth dates or mothers with the same name.
C. Age and diagnosis: Age and diagnosis are important clinical information but are not typically used as primary identifiers for medication administration.
D. Footprints and identification number: While footprints and identification numbers may be used as supplemental identifiers, they are not as reliable or commonly used as name and medical record number for medication administration.
A nurse is collecting data from a client who has a gastrostomy tube and is experiencing diarrhea. Which of the following factors should the nurse identify as a potential cause of the diarrhea?
Explanation
- A: The formula infusion rate being too slow typically does not cause diarrhea; instead, it could lead to inadequate nutritional intake.
- B: Administering formula that is too cold can cause diarrhea because the cold temperature can stimulate gastrointestinal motility, leading to increased bowel movements.
- C: A partially obstructed feeding tube is more likely to cause reduced or stopped flow of the formula, potentially leading to inadequate nutrition, rather than diarrhea.
- D: Delayed gastric emptying would typically cause symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, not diarrhea. Diarrhea is more likely when substances pass too quickly through the digestive system.
A newly licensed nurse is having difficulty finishing client care tasks during their shift. Which of the following techniques should the nurse plan use to assist with time management?
Explanation
Rationale for A: Delegating complicated tasks to an RN might not always be appropriate, especially if the task falls within the scope of the newly licensed nurse. Time management involves prioritizing and organizing tasks effectively, not shifting responsibility unnecessarily.
Rationale for B: Documenting all client care at the end of the shift can lead to missed or inaccurate documentation. It is more efficient to document in real-time or shortly after completing tasks, ensuring accuracy and preventing a backlog of work.
Rationale for C: Performing quick tasks before time-consuming ones may lead to neglecting critical or urgent tasks. Time-consuming tasks might be of higher priority and should be addressed based on urgency rather than the time they take.
Rationale for D: Completing one task before moving on to the next allows the nurse to focus on each task fully, reducing the chance of errors and ensuring that all tasks are completed systematically. This approach improves efficiency and task management.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sustained a full-thickness burn and is in the emergent phase of the burn. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
A. Hypernatremia: Hypernatremia (elevated sodium levels) is not typically associated with the emergent phase of burn injuries.
B. Hypercalcemia: Hypercalcemia (elevated calcium levels) is not typically associated with the emergent phase of burn injuries.
C. Hypermagnesemia: Hypermagnesemia (elevated magnesium levels) is not typically associated with the emergent phase of burn injuries.
D. Hyperkalemia: Hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels) is a common electrolyte imbalance seen in the emergent phase of burn injuries due to the release of potassium from damaged cells.
It can lead to cardiac dysrhythmias and other complications if not promptly addressed.
A nurse is establishing a baseline postoperative assessment for a client who is recovering from a right femoropopliteal bypass graft. Which of the following findings in the assessment of the client's right leg should be of the most concern to the nurse?
Explanation
A. The client's foot feels cooler than in the previous assessment: While decreased temperature can indicate decreased perfusion, the absence of a palpable pedal pulse is a more concerning finding.
B. The client's pedal pulse in the right foot is not palpable: This finding suggests compromised blood flow distal to the site of the bypass graft, which could indicate graft occlusion or impaired circulation.
C. The client's capillary refill time is 5 seconds in the toes: While prolonged capillary refill time can indicate impaired circulation, the absence of a palpable pedal pulse is a more concerning finding.
D. The client reports a pain level of 8 on a scale from 3 to 10: Pain is subjective and can be managed with analgesics, but the absence of a palpable pedal pulse indicates a more serious issue related to perfusion.
A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a 12-month-old infant following cleft palate repair. Which of the following actions should the nurse include?
Explanation
A) Allowing the infant to have soft foods is not recommended immediately following surgery to protect the surgical site.
B) Maintaining elbow restraints prevents the infant from touching or injuring the repair site, which is crucial for proper healing.
C) Feeding the infant with a spoon could disrupt the surgical site and is not advised until cleared by a healthcare provider.
D) While oral hygiene is important, brushing the infant's teeth could harm the repair site; however, specific post-operative care instructions regarding oral hygiene should be provided by the healthcare provider, which may or may not include a temporary cessation of brushing.
A nurse is caring for an older adult client who states, "I can't pay for my care because my kid took all my money." Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
A. Instruct the client to report the theft to the police: While reporting theft to the police may be necessary, the immediate concern is the safety and well-being of the client, especially if financial exploitation or abuse is suspected.
B. Report the possible abuse to adult protective services: Suspected financial exploitation or abuse of an older adult should be reported to the appropriate authorities, such as adult protective services, for investigation and intervention.
C. Ask the client if there is another family member they can call for financial help: While involving other family members may be appropriate in some situations, suspected abuse or exploitation requires intervention from trained professionals.
D. Restrict visitation for the client's family until discharge: Restricting visitation should only be done if there is a clear risk to the client's safety, and it should not be the first action taken in response to suspected abuse.
A nurse is admitting a client who has active tuberculosis. Which of the following nursing interventions is appropriate?
Explanation
A. Place the client in a room that is ventilated to the outside: Clients with active tuberculosis should be placed in negative pressure rooms with air exhausted directly to the outside to prevent the spread of airborne pathogens.
B. Wear a gown when delivering the client's food tray: Gowns are not typically necessary for routine care of clients with tuberculosis unless there is potential for contact with respiratory secretions.
C. Prohibit visitors while the client's infection is active: Visitors should be educated about tuberculosis precautions and provided with appropriate personal protective equipment if necessary, but prohibiting visitors may not be necessary.
D. Administer a tuberculin skin test prior to discharge: Tuberculin skin testing is used for screening and diagnosis of tuberculosis infection, not for management of active tuberculosis.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 164 questions on the ATI RN PREDICTOR ASSESSMENT EXIT Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



